|
Igor Volk
Igor Petrovich Volk (russian: Игорь Петрович Волк, ; 12 April 1937 – 3 January 2017) was a Soviet test pilot and cosmonaut in the Buran programme. Military and test pilot Volk became a pilot in the Soviet Air Forces in 1956. After graduation from the Fedotov Test Pilot School in 1965, he has joined the Gromov Flight Research Institute. He logged over 7000 flight hours in over 80 different aircraft types. Over the years, he flew on all types of Soviet fighters, bombers, and transport aircraft. He showed outstanding abilities in complex tests of various airplanes at critical angles of attack, stall, and spin. He was the first who tested aircraft behavior at high super-critical angles of attack (around 90°) and performed aerobatics such as the " cobra" maneuver. Space program Igor Volk was selected as a cosmonaut on 12 July 1977 and subsequently assigned to the Buran programme. As part of his preparations for a space shuttle flight, he also accomplishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zmiiv
Zmiiv or Zmiyiv ( uk, Зміїв), Zmiev, or Zmeev (), also known as Gotwald ( uk, Готвальд) from 1976 to 1990, is a city in Chuhuiv Raion, Kharkiv, Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Zmiiv urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The population in 2001 was 17,063, rising to by 2021. The town is located 42 km from Kharkiv. Until 2020, Zmiiv was the administrative centre of Zmiiv Raion, before it was merged into Chuhuiv Raion as part of that year's administrative reform. Toponymy The name ''Zmiiv'' or ''Zmiyiv'' ( uk, Зміїв) is almost certainly derived from the Ukrainian word for snakes, ''Zmiji'' ( uk, Змії). In addition, there are at least five potential origins for the source of the name Zmiiv or Zmiev: # There is an old legend that in the dense forests and impenetrable swamps surrounding the town, there lived a winged many-headed serpent, the Zmii Horynych, who was harnessed to a large plough by Nikita Kozhemyak, and the Zmiiv ramparts w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
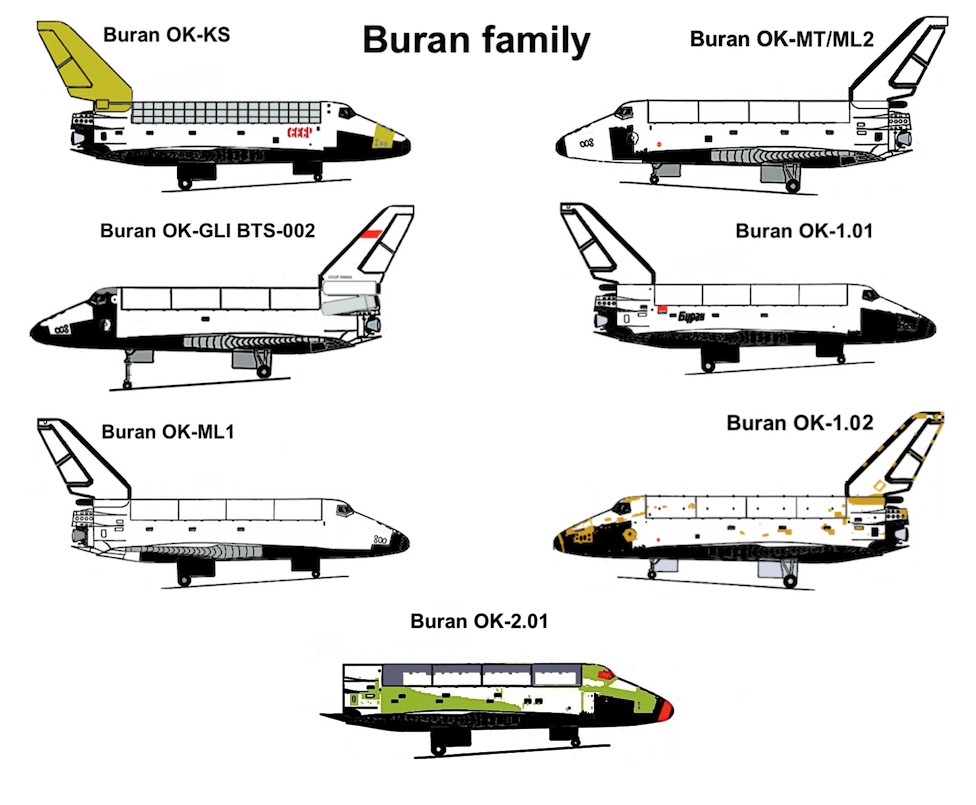
Buran Programme
The ''Buran'' program (russian: Буран, , "Snowstorm", "Blizzard"), also known as the "VKK Space Orbiter program" (russian: ВКК «Воздушно-Космический Корабль», lit=Air and Space Ship), was a Soviet and later Russian reusable spacecraft project that began in 1974 at the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute in Moscow and was formally suspended in 1993. In addition to being the designation for the whole Soviet/Russian reusable spacecraft project, ''Buran'' was also the name given to Orbiter K1, which completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988 and was the only Soviet reusable spacecraft to be launched into space. The ''Buran''-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket as a launch vehicle. Unlike the Space Shuttle, Buran had a capability of flying uncrewed missions, as well as performing fully automated landings. The Buran program was started by the Soviet Union as a response to the United States Space Shuttle program. The project was the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Car
A flying car or roadable aircraft is a type of vehicle which can function both as a road vehicle and as an aircraft. As used here, this includes vehicles which drive as motorcycles when on the road. The term "flying car" is also sometimes used to include hovercars and/or VTOL personal air vehicles. Many prototypes have been built since the early 20th century, using a variety of flight technologies. Most have been designed to take off and land conventionally using a runway. Although VTOL projects are increasing, none has yet been built in more than a handful of numbers. Their appearance is often predicted by futurologists, and many concept designs have been promoted. Their failure to become a practical reality has led to the catchphrase "Where's my flying car?", as a paradigm for the failure of predicted technologies to appear. Flying cars are also a popular theme in fantasy and science fiction stories. History Early 20th century In the late 1800s, American immigrant Gusta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concept Car
A concept car (also known as a concept vehicle, show vehicle or prototype) is a car made to showcase new styling and/or new technology. They are often exhibited at motor shows to gauge customer reaction to new and radical designs which may or may not be mass-produced. General Motors designer Harley Earl is generally credited with inventing the concept car, and did much to popularize it through its traveling Motorama shows of the 1950s. Concept cars never go into production directly. In modern times all would have to undergo many changes before the design is finalized for the sake of practicality, safety, regulatory compliance, and cost. A " production-intent" prototype, as opposed to a concept vehicle, serves this purpose. Design Concept cars are often radical in engine or design. Some use non-traditional, exotic, or expensive materials, ranging from paper to carbon fiber to refined alloys. Others have unique layouts, such as gullwing doors, 3 or 5 (or more) wheels, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fédération Aéronautique Internationale
The (; FAI; en, World Air Sports Federation) is the world governing body for air sports, and also stewards definitions regarding human spaceflight. It was founded on 14 October 1905, and is headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland. It maintains world records for aeronautical activities, including ballooning, aeromodeling, and unmanned aerial vehicles (drones), as well as flights into space. History The FAI was founded at a conference held in Paris 12–14 October 1905, which was organized following a resolution passed by the Olympic Congress held in Brussels on 10 June 1905 calling for the creation of an Association "to regulate the sport of flying, ... the various aviation meetings and advance the science and sport of Aeronautics." The conference was attended by representatives from 8 countries: Belgium (Aero Club Royal de Belgique, founded 1901), France ( Aéro-Club de France, 1898), Germany ( Deutscher Aero Club e.V.), Great Britain ( Royal Aero Club, 1901), Italy (Aero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Aero Club Of Russia
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900-1924 * National Supermarkets, a defunct American grocery store chain * National String Instrument Corporation, a guitar company formed to manufacture the first resonator g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceflight (magazine)
''Spaceflight'' is the monthly magazine of the British Interplanetary Society (BIS), reporting on space exploration topics. It was first published in 1956. In 2008, the magazine – edited by Clive Simpson – was the winner of the Sir Arthur Clarke Award in the category of Best Space Reporting. External links BIS PublicationsBritish Interplanetary Society 1956 establishments in the United Kingdom Monthly magazines published in the United Kingdom Science and technology magazines published in the United Kingdom Magazines established in 1956 magazine A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combinatio ... Astronomy magazines {{UK-sci-mag-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Interplanetary Society
The British Interplanetary Society (BIS), founded in Liverpool in 1933 by Philip E. Cleator, is the oldest existing space advocacy organisation in the world. Its aim is exclusively to support and promote astronautics and space exploration. Structure It is a non-profit organisation with headquarters in London and is financed by members' contributions. It is situated on South Lambeth Road ( A203) near Vauxhall station. History The BIS was only preceded in astronautics by the American Interplanetary Society (founded 1930), the German VfR (founded 1927), and Soviet Society for Studies of Interplanetary Travel (founded 1924), but unlike those it never became absorbed into a national industry. Thus it is now the world's oldest existing space advocacy body. When originally formed in October 1933, the BIS aimed not only to promote and raise the public profile of astronautics, but also to undertake practical experimentation into rocketry along similar lines to the organisations abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buran (spacecraft)
''Buran'' (russian: Буран, , meaning "Snowstorm" or "Blizzard"; GRAU index serial number: 11F35 1K, construction number: 1.01) was the first spaceplane to be produced as part of the Soviet/Russian Buran program. Besides describing the first operational Soviet/Russian shuttle orbiter, "Buran" was also the designation for the entire Soviet/Russian spaceplane project and its orbiters, which were known as "Buran-class orbiters". Buran completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988, and was destroyed in the 2002 collapse of its storage hangar. The Buran-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket, a class of super heavy-lift launch vehicle. It is named after the Asian wind. Construction The construction of the Buran spacecraft began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale orbiter was rolled out. Over 1000 companies all over the Soviet Union were involved in construction and development. The Buran spacecraft was made to be launched on the Soviet Union's super-heavy li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut 7
Salyut 7 (russian: Салют-7; en, Salute 7) (a.k.a. DOS-6, short for Durable Orbital Station) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including 12 crewed and 15 uncrewed launches in total. Supporting spacecraft included the Soyuz T, Progress, and TKS spacecraft. It was part of the Soviet Salyut programme, and launched on 19 April 1982 on a Proton rocket from Site 200/40 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Soviet Union. Salyut 7 was part of the transition from monolithic to modular space stations, acting as a testbed for docking of additional modules and expanded station operations. It was the eighth space station of any kind launched. Salyut 7 was the last of both the second generation of DOS-series space stations and of the monolithic Salyut Program overall, to be replaced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OK-GLI
The OK-GLI (russian: Орбитальный корабль для горизонтальных лётных испытаний, ОК-ГЛИ, translit=Orbital'nyy korabl' dlya gorizontal'nykh lotnykh ispytaniy, lit=Orbital ship for horizontal flight tests), also known as Buran Analog BTS-02 (russian: БТС-02, Большой транспортный самолёт второй, translit=bolshoi transportny samolyot vtoroi, lit=big transport aircraft, the second), was a test vehicle ("Buran aerodynamic analogue") in the Buran programme. It was constructed in 1984, and was used for 25 test flights between 1985 and 1988 before being retired. It is now an exhibit at the Technik Museum Speyer in Germany. Construction The development of the Buran began in the late 1970s as a response to the U.S. Space Shuttle program. The construction of the orbiters began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale Buran was rolled out. The first suborbital test flight of a scale-model took place as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes to date have been rocket-powered but then landed as unpowered gliders. Four types of spaceplanes have successfully launched to orbit, reentered Earth's atmosphere, and landed: the U.S. Space Shuttle, Russian Buran, U.S. X-37, and the Chinese CSSHQ. Another, Dream Chaser, is under development in the U.S. As of 2019 all past, current, and planned orbital vehicles launch vertically on a separate rocket. Orbital spaceflight takes place at high velocities, with orbital kinetic energies typically at least 50 times greater than suborbital trajectories. Consequently, heavy heat shielding is requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)