|
Ideonella Sakaiensis
''Ideonella sakaiensis'' is a bacterium from the genus'' Ideonella'' and family Comamonadaceae capable of breaking down and consuming the plastic polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using it as both a carbon and energy source. The bacterium was originally isolated from a sediment sample taken outside of a plastic bottle recycling facility in Sakai City, Japan. * Discovery ''Ideonella sakaiensis'' was first identified in 2016 by a team of researchers led by Kohei Oda of Kyoto Institute of Technology and Kenji Miyamoto of Keio University after collecting a sample of PET-contaminated sediment at a plastic bottle recycling facility in Sakai, Japan. The bacteria was first isolated from a consortium of microorganisms in the sediment sample, which included protozoa and yeast-like cells. The entire microbial community was shown to mineralize 75% of the degraded PET into carbon dioxide once it had been initially degraded and assimilated by ''Ideonella sakaiensis''. Characterization Phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideonella Azotifigens
''Ideonella azotifigens'' is a nitrogen-fixing, Gram-negative, oxidase- and weak catalase-positive aerobic, motile bacterium from the genus'' Ideonella'' and family Comamonadaceae, which was isolated from grass rhizosphere soil in Ithaca Ithaca most commonly refers to: *Homer's Ithaca, an island featured in Homer's ''Odyssey'' *Ithaca (island), an island in Greece, possibly Homer's Ithaca *Ithaca, New York, a city, and home of Cornell University and Ithaca College Ithaca, Ithaka ... in the United States. References External linksType strain of ''Ideonella azotifigens'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Comamonadaceae Bacteria described in 2009 {{betaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire (as opposed to organisms that ferment) to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism and may have originated abiogenically. Even though it is branded as a 'cycle', it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized. The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from the citric acid (a tricarboxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase
In enzymology, a protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction : 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate + O2 \rightleftharpoons 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate (protocatechuic acid) and O2, whereas its product is 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on single donors with O2 as oxidant and incorporation of two atoms of oxygen into the substrate (oxygenases). The systematic name of this enzyme class is protocatechuate:oxygen 3,4-oxidoreductase (decyclizing). Other names in common use include protocatechuate oxygenase, protocatechuic acid oxidase, protocatechuic 3,4-dioxygenase, and protocatechuic 3,4-oxygenase. This enzyme participates in benzoate degradation via hydroxylation and 2,4-dichlorobenzoate degradation. It employs one cofactor, iron. This enzyme has been found effective at improving organic fluorophore-stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catechol
Catechol ( or ), also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is a toxic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is the ''ortho'' isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances. Catechol occurs as feathery white crystals that are very rapidly soluble in water. Isolation and synthesis Catechol was first isolated in 1839 by Edgar Hugo Emil Reinsch (1809–1884) by distilling it from the solid tannic preparation catechin, which is the residuum of catechu, the boiled or concentrated juice of ''Mimosa catechu'' (''Acacia catechu''). Upon heating catechin above its decomposition point, a substance that Reinsch first named ''Brenz-Katechusäure'' (burned catechu acid) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,2-dihydroxy-3,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dicarboxylate Dehydrogenase
Onekama ( ) is a village in Manistee County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 411 at the 2010 census. The village is located on the shores of Portage Lake and is surrounded by Onekama Township. The town's name is derived from "Ona-ga-maa," an Anishinaabe word which means "singing water." Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of , all land. The M-22 highway runs through downtown Onekama. History The predecessor of the village of Onekama was the settlement of Portage at Portage Point, first established in 1845, at the western end of Portage, at the outlet of Portage Creek. In 1871, when landowners around the land-locked lake became exasperated with the practices of the Portage Sawmill, they took the solution into their own hands and dug a channel through the narrow isthmus, opening a waterway that lowered the lake by 12 to 14 feet and brought it to the same level as Lake Michigan. When this action dried out Portage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
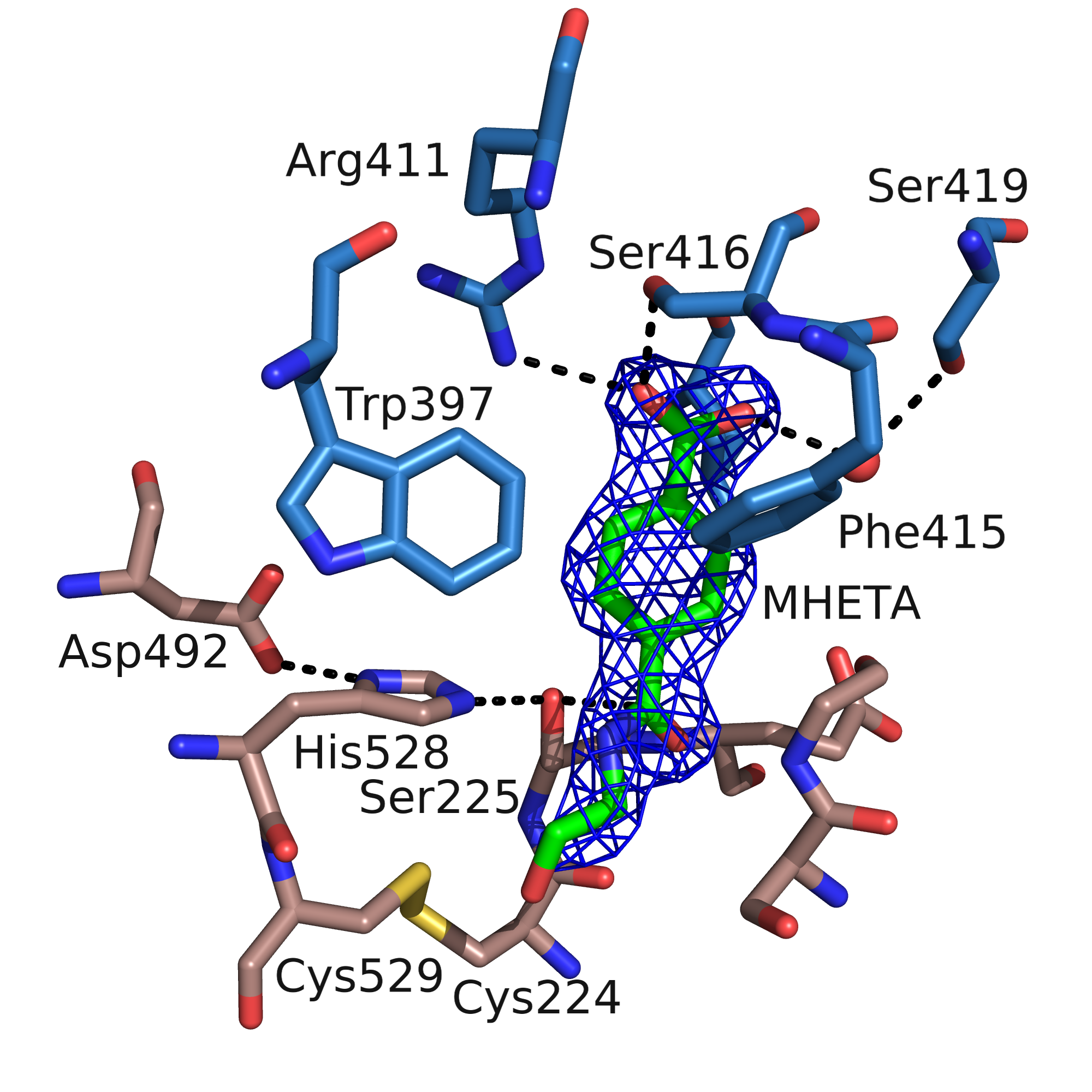
MHETase
The Enzyme MHETase is a hydrolase, which was discovered in 2016. It cleaves Mono-(2-hydroxyethyl)terephthalic acid, the PET degradation product by PETase, to ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. This pair of enzymes, PETase and MHETase, enable the bacterium ''Ideonella sakaiensis'' to live on the plastic PET as sole carbon source. Chemical reaction The first enzyme of the PET degradation pathway, PETase, cleaves this plastic into the intermediates MHET ( Mono-(2-hydroxyethyl)terephthalic acid) and minor amounts BHET ( Bis-(2-hydroxyethyl)terephthalic acid). MHETase hydrolyses the ester bond of MHET forming terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. Besides its natural substrate MHET the chromogenic substrate MpNPT, Mono-p-nitrophenyl-terephthalate, is also hydrolyzed well. This can be used to measure the enzymatic activity and determine the kinetic parameters. Ferulate and gallate esters, substrates of the closest relatives in the tannase family, are not converted. p-Nitropheny ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Glycol
Ethylene glycol (IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odorless, colorless, flammable, viscous liquid. Ethylene glycol has a sweet taste, but it is toxic in high concentrations. Production Industrial routes Ethylene glycol is produced from ethylene (ethene), via the intermediate ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide reacts with water to produce ethylene glycol according to the chemical equation: This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases, or can occur at neutral pH under elevated temperatures. The highest yields of ethylene glycol occur at acidic or neutral pH with a large excess of water. Under these conditions, ethylene glycol yields of 90% can be achieved. The major byproducts are the oligomers diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, and tetraethylene glycol. The separation of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terephthalic Acid
Terephthalic acid is an organic compound with formula C6H4(CO2H)2. This white solid is a commodity chemical, used principally as a precursor to the polyester PET, used to make clothing and plastic bottles. Several million tonnes are produced annually. The common name is derived from the turpentine-producing tree ''Pistacia terebinthus'' and phthalic acid. History Terephthalic acid was first isolated (from turpentine) by the French chemist Amédée Cailliot (1805–1884) in 1846. Terephthalic acid became industrially important after World War II. Terephthalic acid was produced by oxidation of ''p''-xylene with dilute nitric acid. Air oxidation of ''p''-xylene gives ''p''-toluic acid, which resists further air-oxidation. Conversion of ''p''-toluic acid to methyl p-toluate (CH3C6H4CO2CH3) opens the way for further oxidation to monomethyl terephthalate, which is further esterified to dimethyl terephthalate. In 1955, Mid-Century Corporation and ICI announced the bromide-promoted oxida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", '' di-'' + '' -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins. A protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors have the ability to form both homo- and heterodimers with several typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Hydroxyethyl Terephthalic Acid
2-Hydroxyethyl terephthalic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC2H4O2CC6H4CO2H. It is the monoester of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. The compound is a precursor to poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET), a polymer that is produced on a large scale industrially. 2-Hydroxyethyl terephthalic acid is a colorless solid that is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. Near neutral pH, 2-hydroxyethyl terephthalic acid converts to 2-hydroxyethyl terephthalate, HOC2H4O2CC6H4CO2−. Occurrence and reactions 2-Hydroxyethyl terephthalic acid is an intermediate in both the formation and hydrolysis of PET. It is produced on a massive scale as the first intermediate in certain routes to PET. Specifically, it is produced in the course of the thermal condensation of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol: :HOC2H4OH + HO2CC6H4CO2H → HOC2H4O2CC6H4CO2H + H2O Further dehydration of 2-hydroxyethyl terephthalic acid gives PET. It is also produced by the partial hydrolys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |