MHETase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
ESTHER Datenbank
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
MHETase is a hydrolase
Hydrolase is a class of enzyme that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are este ...
, which was discovered in 2016. It cleaves Mono-(2-hydroxyethyl)terephthalic acid, the PET degradation product by PETase
PETases are an esterase class of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic to monomeric mono-2-hydroxyethyl terephthalate (MHET). The idealized chemical reaction is (where n is the number of monomers in the ...
, to ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol (IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odo ...
and terephthalic acid
Terephthalic acid is an organic compound with formula C6H4(CO2H)2. This white solid is a commodity chemical, used principally as a precursor to the polyester PET, used to make clothing and plastic bottles. Several million tonnes are produced annua ...
. This pair of enzymes, PETase and MHETase, enable the bacterium ''Ideonella sakaiensis
''Ideonella sakaiensis'' is a bacterium from the genus'' Ideonella'' and family Comamonadaceae capable of breaking down and consuming the plastic polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using it as both a carbon and energy source. The bacterium was or ...
'' to live on the plastic PET as sole carbon source.
Chemical reaction
The first enzyme of the PET degradation pathway,PETase
PETases are an esterase class of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic to monomeric mono-2-hydroxyethyl terephthalate (MHET). The idealized chemical reaction is (where n is the number of monomers in the ...
, cleaves this plastic into the intermediates MHET ( Mono-(2-hydroxyethyl)terephthalic acid) and minor amounts BHET ( Bis-(2-hydroxyethyl)terephthalic acid). MHETase hydrolyses the ester bond of MHET forming terephthalic acid
Terephthalic acid is an organic compound with formula C6H4(CO2H)2. This white solid is a commodity chemical, used principally as a precursor to the polyester PET, used to make clothing and plastic bottles. Several million tonnes are produced annua ...
and ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol (IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odo ...
.
Besides its natural substrate MHET the chromogenic substrate MpNPT, Mono-p-nitrophenyl-terephthalate, is also hydrolyzed well. This can be used to measure the enzymatic activity and determine the kinetic parameters. Ferulate and gallate esters, substrates of the closest relatives in the tannase family, are not converted. p-Nitrophenyl ester of aliphatic monocarboxylic acids like the widely used esterase substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate are not hydrolyzed either.
The native enzyme is incapable of working on BHET, mono(2-hydroxyethyl)-isophthalate (MHEI), or mono(2-hydroxyethyl)-furanoate (MHEF). MHEI is a likely industrial PET degradation product due to the use of isophthalate comonomer. MHEF is a product of PEF degradation by PETase. Protein engineering
Protein engineering is the process of developing useful or valuable proteins. It is a young discipline, with much research taking place into the understanding of protein folding and recognition for protein design principles. It has been used to imp ...
research aims to overcome these barriers.
Structure
The structure of MHETase was solved in 2019. It shows the common fold of thealpha/beta hydrolase superfamily
The alpha/beta hydrolase superfamily is a superfamily of hydrolytic enzymes of widely differing phylogenetic origin and catalytic function that share a common fold. The core of each enzyme is an alpha/beta-sheet (rather than a barrel), containing ...
. According to the classification in the ESTHER database, MHETase belongs to the family of tannase
The enzyme tannase (EC 3.1.1.20) catalyzes the following reaction:
:digallate + H2O = 2 gallate
It is a key enzyme in the degradation of gallotannins and ellagicitannins, two types of hydrolysable tannins. Specifically, tannase catalyzes the hy ...
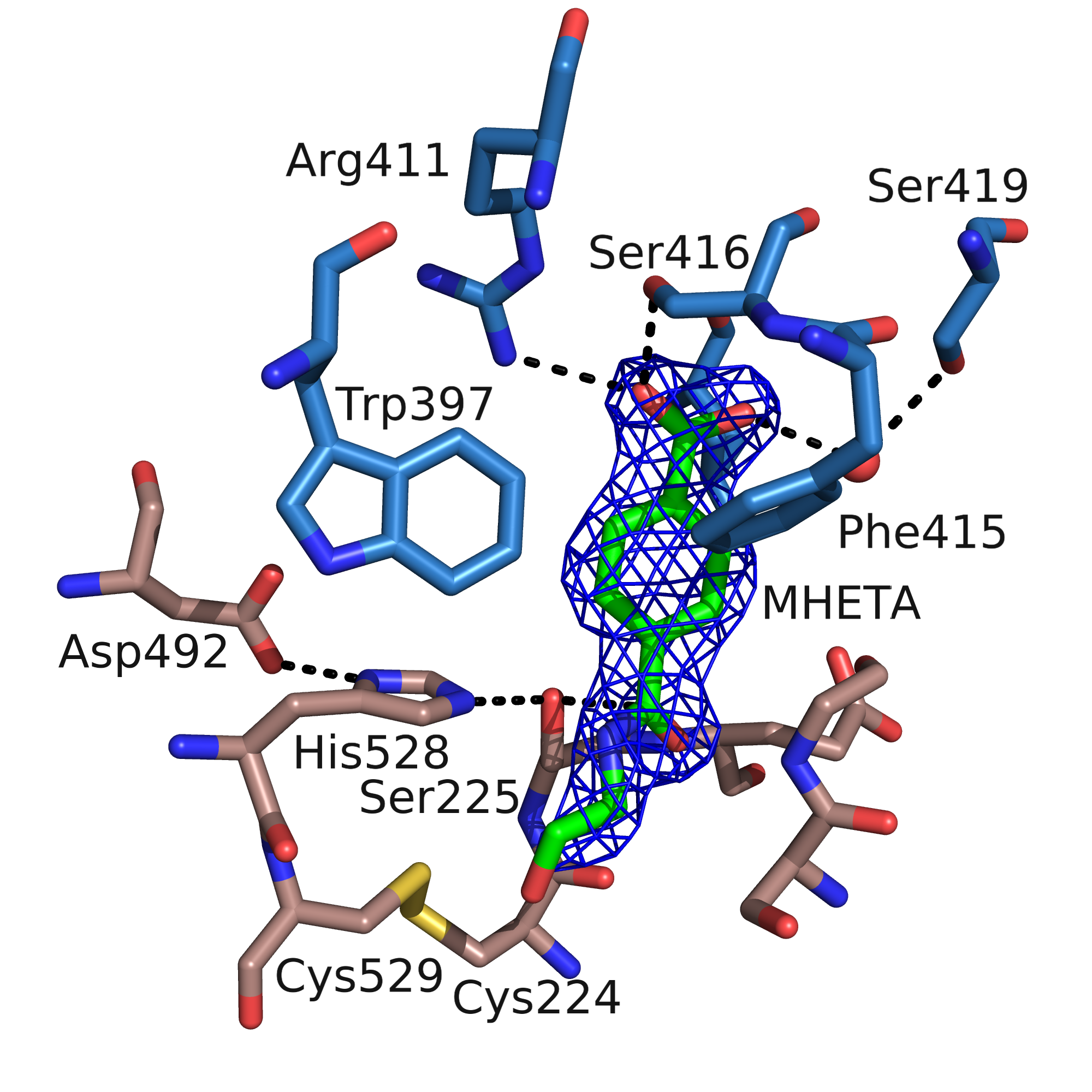
s within block X. This family mainly contains tannases und feruloyl esterases. The enzyme consists of two domains: the hydrolase domain harbors the catalytic residues Ser225, His528 and Asp492; the lid domain contributes most of the residues of the substrate binding site.

External links
ESTHER Datenbank
References
{{reflist Hydrolases