|
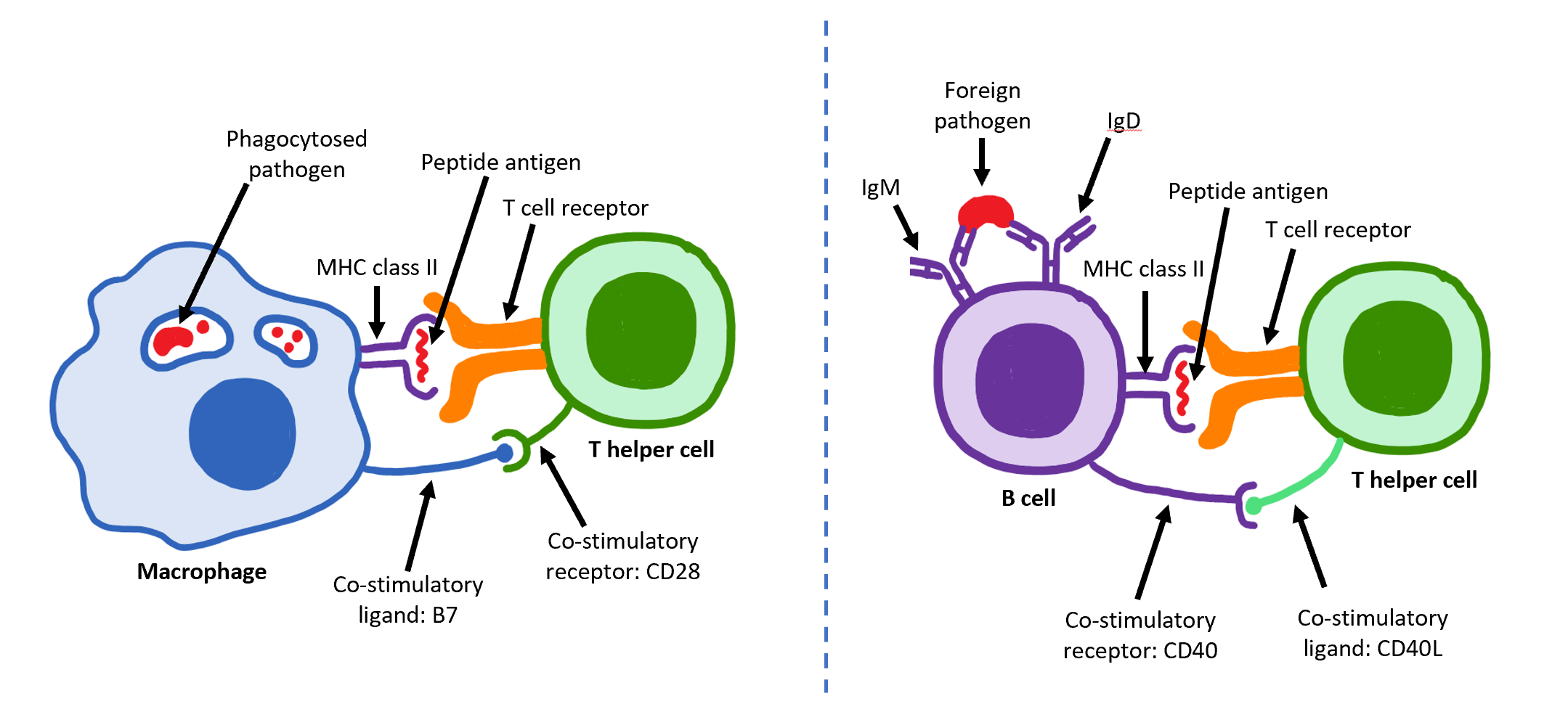
IL12RB2
Interleukin 12 receptor, beta 2 subunit is a subunit of the interleukin 12 receptor. IL12RB2 is its human gene. ''IL12RB2'' orthologs have been identified in all mammals for which complete genome data are available. The protein encoded by this gene is a type I transmembrane protein identified as a subunit of the interleukin 12 receptor complex. The co-expression of this and IL12Rβ1 proteins was shown to lead to the formation of high-affinity IL12 binding sites and reconstitution of IL12 dependent signaling. While the IL12Rβ1 subunit is constitutively expressed, the expression of the IL12RB2 gene is up-regulated by interferon gamma. In Th1 cells, IL-12 signaling through the IL12 receptor leads to the phosphorylation of STAT4 and continued Th1 differentiation. The IL12Rβ2 subunit plays an important role in Th1 cell differentiation, since its absence leads to an abortive Th1 differentiation that has dysfunctional production of Th1 effector molecules. The up-regulation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 12 Receptor
Interleukin 12 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor, binding interleukin 12. It consists of beta 1 and beta 2 subunits. References External links * Type I cytokine receptors {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthologs
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Protein
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span (or bitopic) or multi-span (polytopic). Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do not pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 12 Receptor, Beta 1 Subunit
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins and signal molecules) that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins. The function of the immune system primarily depends on interleukins, and rare deficiencies of a number of them have been described, all featuring autoimmune diseases or immune deficiency. The majority of interleukins are synthesized by CD4 helper T-lymphocyte, as well as through monocytes, macrophages, and endothelial cells. They promote the development and differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and hematopoietic cells. Interleukin receptors on astrocytes in the hippocampus are also known to be involved in the development of spatial memories in mice. History and name The name "interleukin" was chosen in 1979, to replace the various different names used by different research groups to designate interleukin 1 (lymphocyte act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 12
Interleukin 12 (IL-12) is an interleukin that is naturally produced by dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and human B- lymphoblastoid cells ( NC-37) in response to antigenic stimulation. IL-12 belongs to the family of interleukin-12. IL-12 family is unique in comprising the only heterodimeric cytokines, which includes IL-12, IL-23, IL-27 and IL-35. Despite sharing many structural features and molecular partners, they mediate surprisingly diverse functional effects. Gene and structure IL12 is a heterodimeric cytokine encoded by two separate genes, IL-12A (p35) and IL-12B (p40). The active heterodimer (referred to as 'p70'), and a homodimer of p40 are formed following protein synthesis. IL12A is composed of a bundle of four alpha helices. IL12B has three beta sheet domains. Functions IL-12 is involved in the differentiation of naive T cells into Th1 cells. It is known as a T cell-stimulating factor, which can stimulate the growth and function of T cells. It stimulate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon-gamma
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. Wheelock as a product of human leukocytes stimulated with phytohemagglutinin, and by others as a product of antigen-stimulated lymphocytes. It was also shown to be produced in human lymphocytes. or tuberculin-sensitized mouse peritoneal lymphocytes challenged with Mantoux test (PPD); the resulting supernatants were shown to inhibit growth of vesicular stomatitis virus. Those reports also contained the basic observation underlying the now widely employed IFN-γ release assay used to test for tuberculosis. In humans, the IFN-γ protein is encoded by the ''IFNG'' gene. Through cell signaling, IFN-γ plays a role in regulating the immune response of its target cell. A key signaling pathway that is activated by type II IFN is the JAK-STAT sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell antibody class switching, breaking cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological insult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT4
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4) is a transcription factor belonging to the STAT protein family, composed of STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STAT5A, STAT5B, STAT6. STAT proteins are key activators of gene transcription which bind to DNA in response to cytokine gradient. STAT proteins are a common part of Janus kinase (JAK)- signalling pathways, activated by cytokines.STAT4 is required for the development of Th1 cells from naive CD4+ T cells and IFN-γ production in response to IL-12. There are two known STAT4 transcripts, STAT4α and STAT4β, differing in the levels of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ )production downstream. Structure Human as well murine STAT4 genes lie next to STAT1 gene locus suggesting that the genes arose by gene duplication. STAT proteins have six functional domains: 1. N-terminal interaction domain – crucial for dimerization of inactive STATs and nuclear translocation; 2.helical coiled coil domain – association with regulatory factors; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |