|
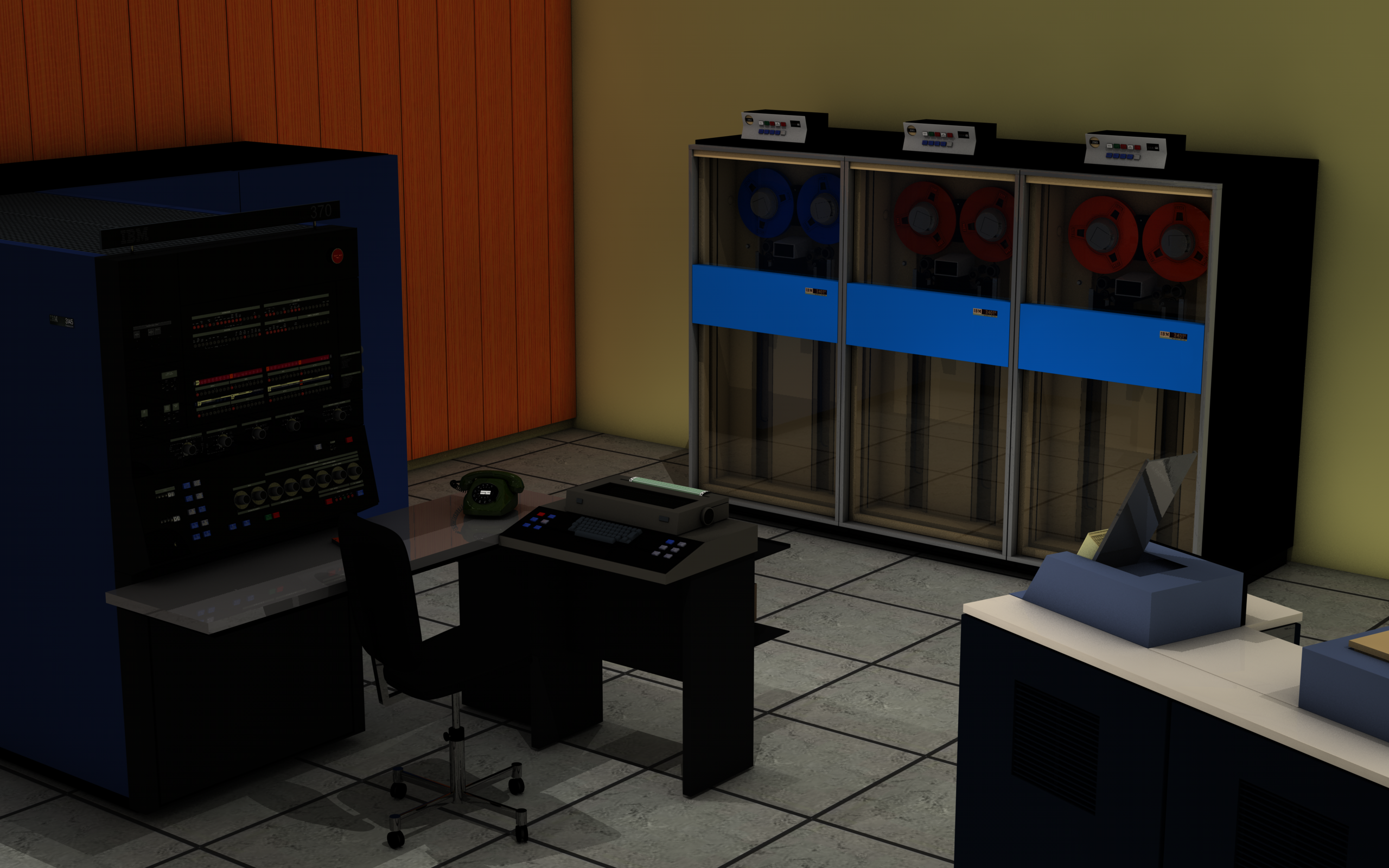
IBM 3505
The IBM 3505 is a reader for 80-column punched cards. It can read cards punched in EBCDIC or column binary at up to 1200 cards per minute (CPM). The IBM 3525 is a multi-function punched card device, capable of reading, punching, and printing on punched cards. The 3505 contains an integrated control unit that attaches to a System/370 byte multiplexer, selector, or block multiplexer channel. An optional feature of the 3505 allows the control unit to also control a 3525, although the two are separately-addressed devices. The 3505/3525 units attach to a System/370 Model 135 and up, or to a System/360 Model 195. The 3505 and 3525 were developed at the IBM General Systems Division in Rochester, Minnesota Rochester is a city in the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Olmsted County. Located on rolling bluffs on the Zumbro River's south fork in Southeast Minnesota, the city is the home and birthplace of the renowned Mayo Clinic. Acco ... in 1971. 3505 The 3505 is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 2540
The IBM 2540 is a punched-card computer peripheral manufactured by IBM Corporation for use of System/360 and later computer systems. The 2540 was designed by IBM's Data Processing Division in Rochester, Minnesota, and was introduced in 1965. The 2540 can read punched-cards at 1000 cards per minute (CPM) and punch at 300 CPM. The 2540 is based on the design of the older, slightly slower, 1402. Description The 2540 attaches to a System/360 multiplexer or selector channel through an IBM 2821 Control Unit. A standard 2540 processes standard IBM 80 column punched cards. The card reader (2540R) and card punch (2540P) devices are separately addressable and function independently. The 2540 normally reads and punches EBCDIC data, called data-mode 1. Card reader On the right side of the device is the reader, consisting of an input hopper holding approximately 3100 cards, and three output stackers (right to left – R1, R2, and RP3) each holding approximately 1350 cards. Cards can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Card Reader
A computer punched card reader or just computer card reader is a computer input device used to read computer programs in either source or executable form and data from punched cards. A computer card punch is a computer output device that punches holes in cards. Sometimes computer punch card readers were combined with computer card punches and, later, other devices to form multifunction machines. It is a input device and also an output device. Most early computers, such as the ENIAC, and the IBM NORC, provided for punched card input/output. Card readers and punches, either connected to computers or in off-line card to/from magnetic tape configurations, were ubiquitous through the mid-1970s. Punched cards had been in use since the 1890s; their technology was mature and reliable. Card readers and punches developed for punched card machines were readily adaptable for computer use. Businesses were familiar with storing data on punched cards and keypunch machines were widely employe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to directly control automated machinery. Punched cards were widely used through much of the 20th century in the data processing industry, where specialized and increasingly complex unit record equipment, unit record machines, organized into semiautomatic data processing systems, used punched cards for data input, output, and storage. The IBM 12-row/80-column punched card format came to dominate the industry. Many early digital computers used punched cards as the primary medium for input of both computer programs and Data (computing), data. While punched cards are now obsolete as a storage medium, as of 2012, some voting machines still used punched cards to record votes. They also had a significant cultural impact. History The idea of contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EBCDIC
Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC; ) is an eight-bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems. It descended from the code used with punched cards and the corresponding six-bit binary-coded decimal code used with most of IBM's computer peripherals of the late 1950s and early 1960s. It is supported by various non-IBM platforms, such as Fujitsu-Siemens' BS2000/OSD, OS-IV, MSP, and MSP-EX, the SDS Sigma series, Unisys VS/9, Unisys MCP and ICL VME. History EBCDIC was devised in 1963 and 1964 by IBM and was announced with the release of the IBM System/360 line of mainframe computers. It is an eight-bit character encoding, developed separately from the seven-bit ASCII encoding scheme. It was created to extend the existing Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) Interchange Code, or BCDIC, which itself was devised as an efficient means of encoding the two ''zone'' and ''number'' punches on punched cards into six bits. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Card Input/output
A computer punched card reader or just computer card reader is a computer input device used to read computer programs in either source or executable form and data from punched cards. A computer card punch is a computer output device that punches holes in cards. Sometimes computer punch card readers were combined with computer card punches and, later, other devices to form multifunction machines. It is a input device and also an output device. Most early computers, such as the ENIAC, and the IBM NORC, provided for punched card input/output. Card readers and punches, either connected to computers or in off-line card to/from magnetic tape configurations, were ubiquitous through the mid-1970s. Punched cards had been in use since the 1890s; their technology was mature and reliable. Card readers and punches developed for punched card machines were readily adaptable for computer use. Businesses were familiar with storing data on punched cards and keypunch machines were widely employe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/370
The IBM System/370 (S/370) is a model range of IBM mainframe computers announced on June 30, 1970, as the successors to the System/360 family. The series mostly maintains backward compatibility with the S/360, allowing an easy migration path for customers; this, plus improved performance, were the dominant themes of the product announcement. In September 1990, the System/370 line was replaced with the System/390. Evolution The original System/370 line was announced on June 30, 1970, with first customer shipment of the Models 155 and 165 planned for February 1971 and April 1971 respectively. The 155 first shipped in January 1971. System/370 underwent several architectural improvements during its roughly 20-year lifetime. The following features mentioned in Principles of Operation are either optional on S/360 but standard on S/370, introduced with S/370 or added to S/370 after announcement. *Branch and Save *Channel Indirect Data Addressing *Channel-Set Switching *Clear I/O *Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel I/O
In computing, channel I/O is a high-performance input/output (I/O) architecture that is implemented in various forms on a number of computer architectures, especially on mainframe computers. In the past, channels were generally implemented with custom devices, variously named channel, I/O processor, I/O controller, I/O synchronizer, or ''DMA controller''. Overview Many I/O tasks can be complex and require logic to be applied to the data to convert formats and other similar duties. In these situations, the simplest solution is to ask the CPU to handle the logic, but because I/O devices are relatively slow, a CPU could waste time (in computer perspective) waiting for the data from the device. This situation is called 'I/O bound'. Channel architecture avoids this problem by processing some or all of the I/O task without the aid of the CPU by offloading the work to dedicated logic. Channels are logically self-contained, with sufficient logic and working storage to handle I/O tasks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/370 Model 135
The IBM System/370 Model 135 was announced March 8, 1971, the only 370 introduced that year. The 135 was IBM's fifth System 370, and it was withdrawn October 16, 1979. Special features Although microcode was not a uniquely new feature at the time of the 135's introduction, having been used in most System/360 models and in most System/370 models introduced so far, the ability to upgrade a system's microcode without changing hardware, by storing the microcode in read-write memory rather than read-only memory, was not common at that time. The read-write memory containing the firmware was loaded from a "reading device located in the Model 135 console"; this allowed updates and adding features to the Model 135's microcode. The "reading device" was a built-in (read-only) floppy disk drive. The 145, introduced the prior year, also had this feature. Optional features The Model 135 was the last of the 370s to be introduced without Virtual memory. Four of the five could be upgraded. Unlik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/360 Model 195
The IBM System/360 Model 195 is a discontinued IBM computer introduced on August 20, 1969. The Model 195 was a reimplementation of the IBM System/360 Model 91 design using monolithic integrated circuits. It offers "an internal processing speed about twice as fast as the Model 85, the next most powerful System/360". The Model 195 was discontinued on February 9, 1977, the same date as the System/370 Model 195. About 20 Model 195 systems were produced. Technical specifications The basic CPU cycle time is 54 nanoseconds (ns). The system has a high degree of parallelism and can process up to seven operations at a time. The system can be configured with 1, 2, or 4 MB of magnetic core memory (models 195J, 195K, and 195L) with a cycle time of 756 ns. A 32 KB cache, called a ''buffer memory'' in the IBM announcement, is standard. Memory blocks are brought into cache in units of 64 bytes. The normal operating system for the Model 195 is OS/360 Multiprogramming with a Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rochester, Minnesota
Rochester is a city in the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Olmsted County. Located on rolling bluffs on the Zumbro River's south fork in Southeast Minnesota, the city is the home and birthplace of the renowned Mayo Clinic. According to the 2020 census, the city had a population of 121,395, making it Minnesota's third-largest city. The Rochester metropolitan area, which also includes the nearby rural agricultural areas, has a population of 226,329. History Rochester was established by white settlers from the eastern United States on land belonging to the Wahpeton tribe who were a part of the alliance called Oceti Ŝakowiŋ — The Seven Council Fires.Minnesota Historical Society, "The Seven Council Fires," URL: https://www.mnhs.org/sevencouncilfires, last accessed November 17, 2021 Within the Seven Council Fires, the Wahpeton people were a part of the Santee or Eastern Dakota tribe. The area developed as a stagecoach stop between Saint Paul, Minnesota, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 3505
The IBM 3505 is a reader for 80-column punched cards. It can read cards punched in EBCDIC or column binary at up to 1200 cards per minute (CPM). The IBM 3525 is a multi-function punched card device, capable of reading, punching, and printing on punched cards. The 3505 contains an integrated control unit that attaches to a System/370 byte multiplexer, selector, or block multiplexer channel. An optional feature of the 3505 allows the control unit to also control a 3525, although the two are separately-addressed devices. The 3505/3525 units attach to a System/370 Model 135 and up, or to a System/360 Model 195. The 3505 and 3525 were developed at the IBM General Systems Division in Rochester, Minnesota Rochester is a city in the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Olmsted County. Located on rolling bluffs on the Zumbro River's south fork in Southeast Minnesota, the city is the home and birthplace of the renowned Mayo Clinic. Acco ... in 1971. 3505 The 3505 is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
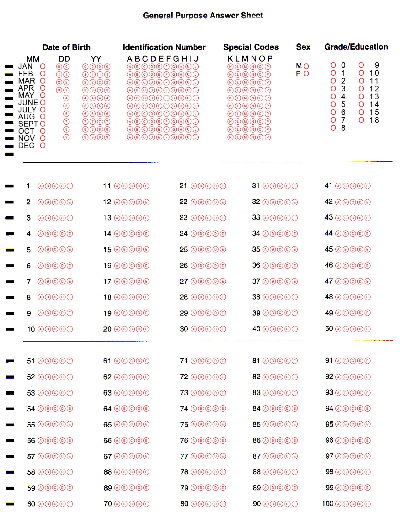
Optical Mark Recognition
Optical mark recognition (also called optical mark reading and OMR) is the process of reading information that people mark on surveys, tests and other paper documents. OMR is used to read questionnaires, multiple choice examination papers in the form of shaded areas. OMR background Many OMR devices have a scanner that shines a light onto a form. The device then looks at the contrasting reflectivity of the light at certain positions on the form. It will detect the black marks because they reflect less light than the blank areas on the form. Some OMR devices use forms that are printed on transoptic paper. The device can then measure the amount of light that passes through the paper. It will pick up any black marks on either side of the paper because they reduce the amount of light passing through. In contrast to the dedicated OMR device, desktop OMR software allows a user to create their own forms in a word processor or computer and print them on a laser laser printer. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)