|
Ivan Bohun
Ivan Bohun ( ua, Іван Богун) (died 1664) was a Ukrainian Cossack colonel. Close associate and friend of Bohdan Khmelnytsky, he opposed both the pacts with Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (Treaty of Hadiach of 1658) and with Tsardom of Russia (Pereiaslav Agreement of 1654). Biography Bohun was born in Ukrainian-Ruthenian nobility family. He took part in the Khmelnytsky Uprising against Polish rule in Ukraine. In June 1651 he was elected colonel of troops of Bracław and took part in the Battle of Berestechko against Polish troops led by King John II Casimir Vasa, which the Cossacks lost. Surviving the defeat he regathered his forces and in June 1652 took part in the battle of Batih. In this instance the Cossacks were successful; the Polish commander Marcin Kalinowski was killed and the future hetman Stefan Czarniecki barely escaped with his life. The Polish defeat was complete and allowed the Cossack forces to start a successful offensive and effectively gain control over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratslav
Bratslav ( uk, Брацлав; pl, Bracław; yi, בראָצלעוו, ''Brotslev'', today also pronounced Breslev or '' Breslov'' as the name of a Hasidic group, which originated from this town) is an urban-type settlement in Ukraine, located in Tulchyn Raion of Vinnytsia Oblast, by the Southern Bug river. It is a medieval European city and a regional center of the Eastern Podolia region (see Bratslav Voivodeship) founded by government of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, which dramatically lost its importance during the 19th-20th centuries. Population: History The first written mention of Bratslav dates back to 1362. City status was granted Magdeburg Rights in 1564. Bratslav belonged to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania until the Lublin Union of 1569, when it became a voivodeship center in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland as part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In the early 16th century, the Starosta of Bratslav and Vinnytsia (Winnica) was Hetman Kostiantyn Ostrozky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Batoh
The Battle of Batoh, also Battle of Batih, was a battle in 1652 in which Polish-Lithuanian forces under hetman Marcin Kalinowski were defeated by a united army of Crimean Tatars and Zaporozhian Cossacks in what is now Ukraine. A day after the battle the Cossacks bought the Polish captives from the Tatars. In the following two days all the prisoners were slain. The Battle of Batoh destroyed many of the best Polish-Lithuanian units. Although Poland managed to rebuild her army soon after the battle, the loss of the most experienced troops resulted in its temporary weakness in Ukraine. Defeat of the Poles contributed to the wars to come with Russia, which in turn resulted in the " Deluge" of the country by Swedish armies. Background After the Treaty of Bila Tserkva was not ratified by the Polish Sejm the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth deployed Crown forces under the command of Field Hetman Marcin Kalinowski in the Bracław Voivodeship According to the historian Hrusc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henryk Sienkiewicz
Henryk Adam Aleksander Pius Sienkiewicz ( , ; 5 May 1846 – 15 November 1916), also known by the pseudonym Litwos (), was a Polish writer, novelist, journalist and Nobel Prize laureate. He is best remembered for his historical novels, especially for his internationally known best-seller ''Quo Vadis'' (1896). Born into an impoverished Polish noble family in Russian-ruled Congress Poland, in the late 1860s he began publishing journalistic and literary pieces. In the late 1870s he traveled to the United States, sending back travel essays that won him popularity with Polish readers. In the 1880s he began serializing novels that further increased his popularity. He soon became one of the most popular Polish writers of the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, and numerous translations gained him international renown, culminating in his receipt of the 1905 Nobel Prize in Literature for his "outstanding merits as an epic writer." Many of his novels remain in print. In Poland he is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Hlukhiv
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. The art of conducting and resisting sieges is called siege warfare, siegecraft, or poliorcetics. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block the provision of supplies and the reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (also known as sapping), or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konotop
Konotop ( uk, Конотоп ) is a city in Sumy Oblast in northeastern Ukraine. Konotop serves as the administrative center of Konotop Raion. Konotop is located about 129 km from Sumy, the oblast administrative center. It is host to Konotop air base, now held by Ukraine. The population is History During the beginning of the 17th century, Cossacks were first based in that area. The settlement was first mentioned in 1634 in various documents as Novoselytsia. In 1642 a Polish fortress was built in that place named after the river Konotopka. Probably the river disappeared, and another one was created, Yezuch. The fortification became a key point in the struggle against the Moscow state. Another hypothesis is that the name of the city could originate from the name of the ancient Warmian knyaz (князь) Christopher of Kononowitz of the noble Polish-Belarusian-Lithuanian family Kononowicz-Piłsudski that still exists and uses the Polish coat of arms of Radwan. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Vyhovsky
Ivan Vyhovsky ( uk, Іван Виговський; pl, Iwan Wyhowski / Jan Wyhowski; date of birth unknown, died 1664), a Ukrainian military and political figure and statesman, served as hetman of the Zaporizhian Host and of the Cossack Hetmanate for three years (1657–1659) during the Russo-Polish War (1654–1667). He succeeded the famous hetman and rebel leader Bohdan Khmelnytsky (see Hetmans of Ukrainian Cossacks). His time as hetman was characterized by his generally pro-Polish policies, which led to his defeat by pro-Russian elements among the Cossacks. Vyhovsky belonged to the Orthodox noble family of the Vyhovsky coat of arms Abdank. Origin and family Vyhovsky was born in his family estate of Vyhiv, near Ovruch in the Kyiv Voivodeship of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a son of Ostap Vyhovsky, a vicegerent of Kyiv fortress under voivode Adam Kisiel and an Orthodox nobleman from the Kyiv region. There is also a possibility that the birth occurred at anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Konotop (1659)
The Battle of Konotop or Battle of Sosnivka was fought between a coalition led by the Hetman of Ukrainian Cossacks Ivan Vyhovsky and cavalry units of the Russian Tsardom under the command of Semyon Pozharsky and Semyon Lvov, supported by Cossacks of Ivan Bezpaly,Davies B. L. Warfare, state and society on the Black Sea steppe, 1500–1700. – Routledge, UK: Taylor & Francis, 2007. – P. 128–131. – on 29 June 1659, near the town of Konotop, Ukraine, during the Russo-Polish War (1654–1667). Vyhovsky's coalition defeated the Russians and their allies and forced the main Russian army to interrupt the siege of Konotop. However, the result of the battle only intensified political tensions in Ukraine and led to Vyhovsky's removal from power several months later. Prelude The Battle of Konotop took place during the period of Ukrainian history that is generally referred to as the Ruin. This was the time after the death of Hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky, during which many power strug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Zboriv
The Treaty of Zboriv was signed on August 18, 1649, after the Battle of Zboriv when the Crown forces of about 25,000, led by King John II Casimir of Poland, clashed against a combined force of Cossacks and Crimean Tatars, led by Hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky and Khan İslâm III Giray of Crimea respectively, which numbered about 80,000. Signing parties * Ukrainian side representatives: Bohdan Khmelnytskyi, Ivan Vyhovsky * Polish side representatives: Adam Kysil, Jerzy Ossoliński, Janusz Radziwiłł, Władysław Dominik Zasławski Scope According to the concluded agreement, the number of Registered Cossacks increased to 40,000; the Polish army and Jews were banned from the territory of the Kiev Voivodeship, Bratslav Voivodeship, and Chernihiv Voivodeship; governmental offices in the Cossack Hetmanate could be held only by Cossack leaders, the Orthodox Church was granted privileges and the Crimean Khanate was to be paid a large sum of money. The treaty was ratified by the Diet, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
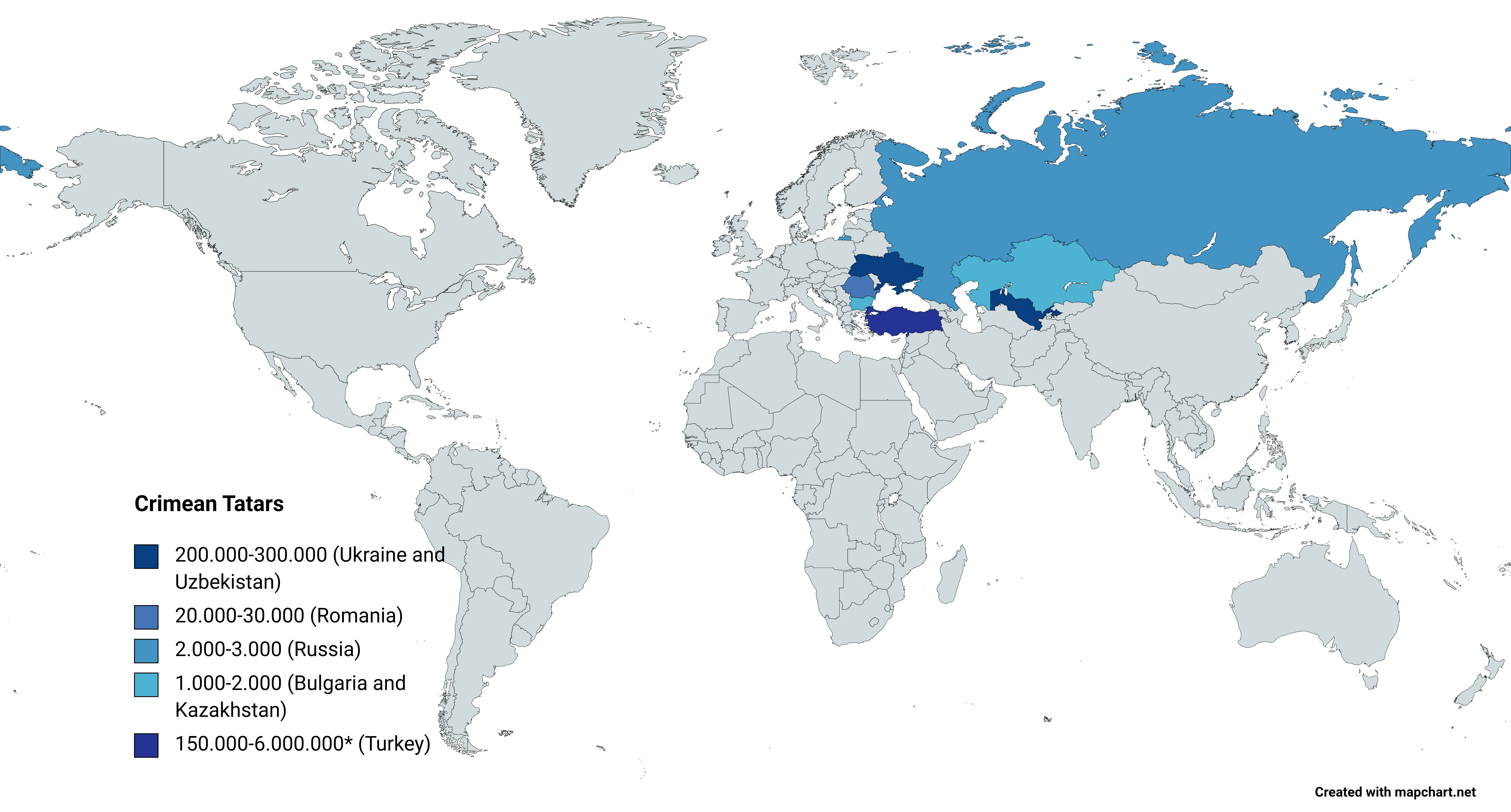
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uman
Uman ( uk, Умань, ; pl, Humań; yi, אומאַן) is a city located in Cherkasy Oblast in central Ukraine, to the east of Vinnytsia. Located in the historical region of the eastern Podolia, the city rests on the banks of the Umanka River at around . Uman serves as the administrative center of Uman Raion (district). It hosts the administration of Uman urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: Among Ukrainians, Uman is known for its depiction of the Haidamak rebellions in Taras Shevchenko's longest of poems, ''Haidamaky'' ("The Haidamaks", 1843). The city is also a pilgrimage site for Breslov Hasidic Jews and a major center of gardening research containing the dendrological park Sofiyivka and the University of Gardening. Uman (Humań) was a privately owned city of Poland and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. History Uman was first mentioned in historical documents in 1616, when it was under Polish rule. It was part of the Bracław Voivodeship of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Polish War (1654–1667)
The Russo-Polish War of 1654–1667, also called the Thirteen Years' War and the First Northern War, was a major conflict between the Tsardom of Russia and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Between 1655 and 1660, the Swedish invasion was also fought in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and so the period became known in Poland as "The Deluge" or Swedish Deluge. The Commonwealth initially suffered defeats, but it regained its ground and won several decisive battles. However, its plundered economy was not able to fund the long conflict. Facing internal crisis and civil war, the Commonwealth was forced to sign a truce. The war ended with significant Russian territorial gains and marked the beginning of the rise of Russia as a great power in Eastern Europe. Background The conflict was triggered by the Khmelnytsky Rebellion of Zaporozhian Cossacks against the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Cossack leader, Bohdan Khmelnytsky, derived his main foreign support from Ale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |