|
Iterative Viterbi Decoding
Iterative Viterbi decoding is an algorithm that spots the subsequence ''S'' of an observation ''O'' = having the highest average probability (i.e., probability scaled by the length of ''S'') of being generated by a given hidden Markov model ''M'' with ''m'' states. The algorithm uses a modified Viterbi algorithm as an internal step. The scaled probability measure was first proposed by John S. Bridle. An early algorithm to solve this problem, sliding window, was proposed by Jay G. Wilpon et al., 1989, with constant cost ''T'' = ''mn''2/2. A faster algorithm consists of an iteration of calls to the Viterbi algorithm, reestimating a filler score until convergence. The algorithm A basic (non-optimized) version, finding the sequence ''s'' with the smallest normalized distance from some subsequence of ''t'' is: // input is placed in observation s[1..n], template t[1..m], // and distance matrix d[1..n,1..m] // remaining elements in matrices are solely for internal computations (int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
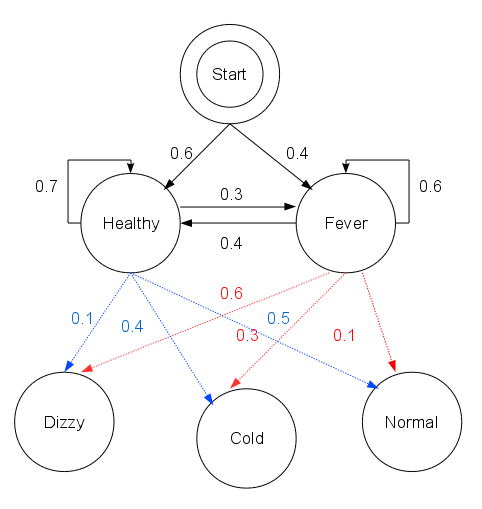
Hidden Markov Model
A hidden Markov model (HMM) is a Markov model in which the observations are dependent on a latent (or ''hidden'') Markov process (referred to as X). An HMM requires that there be an observable process Y whose outcomes depend on the outcomes of X in a known way. Since X cannot be observed directly, the goal is to learn about state of X by observing Y. By definition of being a Markov model, an HMM has an additional requirement that the outcome of Y at time t = t_0 must be "influenced" exclusively by the outcome of X at t = t_0 and that the outcomes of X and Y at t < t_0 must be conditionally independent of at given at time . Estimation of the parameters in an HMM can be performed using maximum likelihood estimation. For linear chain HMMs, the Baum–Welch algorithm can be used to estimate parameters. Hidden Markov models are known for their applications to thermodynamics, statistical mechanics, physics, chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Viterbi Algorithm
The Viterbi algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm for obtaining the maximum a posteriori probability estimate of the most likely sequence of hidden states—called the Viterbi path—that results in a sequence of observed events. This is done especially in the context of Markov information sources and hidden Markov models (HMM). The algorithm has found universal application in decoding the convolutional codes used in both CDMA and GSM digital cellular, dial-up modems, satellite, deep-space communications, and 802.11 wireless LANs. It is now also commonly used in speech recognition, speech synthesis, diarization, keyword spotting, computational linguistics, and bioinformatics. For example, in speech-to-text (speech recognition), the acoustic signal is treated as the observed sequence of events, and a string of text is considered to be the "hidden cause" of the acoustic signal. The Viterbi algorithm finds the most likely string of text given the acoustic signal. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
John S
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John (disambigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sliding Window
A sliding window protocol is a feature of packet-based data transmission Protocol (computing), protocols. Sliding window protocols are used where reliable in-order delivery of packets is required, such as in the data link layer (OSI model#Layer 2: Data link layer, OSI layer 2) as well as in the Transmission Control Protocol (i.e., TCP windowing). They are also used to improve efficiency when the channel may include high Network delay, latency. Packet-based systems are based on the idea of sending a batch of data, the ''packet'', along with additional data that allows the receiver to ensure it was received correctly, perhaps a checksum. The paradigm is similar to a window sliding sideways to allow entry of fresh packets and reject the ones that have already been acknowledged. When the receiver verifies the data, it sends an Acknowledgement (data networks), acknowledgment signal, or ACK, back to the sender to indicate it can send the next packet. In a simple automatic repeat requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jay G
Jays are a paraphyletic grouping of passerine birds within the family (biology), family Corvidae. Although the term "jay" folk taxonomy, carries no taxonomic weight, most or all of the birds referred to as jays share a few similarities: they are small to medium-sized, usually have colorful feathers and are quite noisy. These superificial characteristics set them apart from most other corvids such as crows, ravens, jackdaws, Rook (bird), rooks and magpies, which are larger and have darker plumage. Many so-called "jays" are genetically closer to these other corvids than other jays, however. Systematics and species Jays are not a monophyletic group. Anatomical and molecular evidence indicates they can be divided into a New World and an Old World lineage (the latter including the ground jays and the piapiac), while the grey jays of the genus ''Perisoreus'' form a group of their own.http://www.nrm.se/download/18.4e32c81078a8d9249800021299/Corvidae%5B1%5D.pdf PDF fulltext The black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Distance Matrix
In mathematics, computer science and especially graph theory, a distance matrix is a square matrix (two-dimensional array) containing the distances, taken pairwise, between the elements of a set. Depending upon the application involved, the ''distance'' being used to define this matrix may or may not be a metric (mathematics), metric. If there are elements, this matrix will have size . In graph-theoretic applications, the elements are more often referred to as points, nodes or vertices. Non-metric distance matrix In general, a distance matrix is a weighted adjacency matrix of some graph. In a Network (mathematics), network, a directed graph with weights assigned to the arcs, the distance between two nodes of the network can be defined as the minimum of the sums of the weights on the shortest paths joining the two nodes (where the number of steps in the path is bounded). This distance function, while well defined, is not a metric. There need be no restrictions on the weights oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Error Detection And Correction
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunications, error detection and correction (EDAC) or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communication channels. Many communication channels are subject to channel noise, and thus errors may be introduced during transmission from the source to a receiver. Error detection techniques allow detecting such errors, while error correction enables reconstruction of the original data in many cases. Definitions ''Error detection'' is the detection of errors caused by noise or other impairments during transmission from the transmitter to the receiver. ''Error correction'' is the detection of errors and reconstruction of the original, error-free data. History In classical antiquity, copyists of the Hebrew Bible were paid for their work according to the number of stichs (lines of verse). As the prose books of the Bible were hardly ever w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |