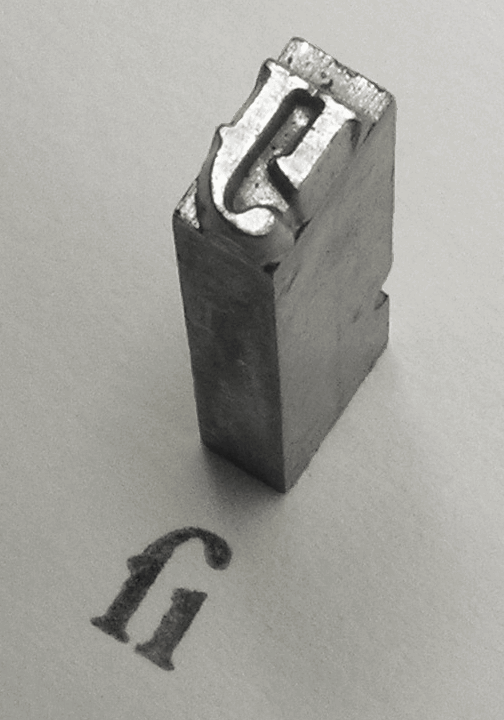|
Italics
In typography, italic type is a cursive font based on a stylised form of calligraphic handwriting. Owing to the influence from calligraphy, italics normally slant slightly to the right. Italics are a way to emphasise key points in a printed text, to identify many types of creative works, to cite foreign words or phrases, or, when quoting a speaker, a way to show which words they stressed. One manual of English usage described italics as "the print equivalent of underlining"; in other words, underscore in a manuscript directs a typesetter to use italic. The name comes from the fact that calligraphy-inspired typefaces were first designed in Italy, to replace documents traditionally written in a handwriting style called chancery hand. Aldus Manutius and Ludovico Arrighi (both between the 15th and 16th centuries) were the main type designers involved in this process at the time. Along with blackletter and Roman type, it served as one of the major typefaces in the history of Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oblique Type
Oblique type is a form of type that slants slightly to the right, used for the same purposes as italic type. Unlike italic type, however, it does not use different glyph shapes; it uses the same glyphs as roman type, except slanted. Oblique and italic type are technical terms to distinguish between the two ways of creating slanted font styles; oblique designs may be labelled italic by companies selling fonts or by computer programs. Oblique designs may also be called slanted or sloped roman styles. Oblique fonts, as supplied by a font designer, may be simply slanted, but this is often not the case: many have slight corrections made to them to give curves more consistent widths, so they retain the proportions of counter (typography), counters and the thick-and-thin quality of strokes from the regular design. Type designers have described oblique type as less organic and calligraphic than italics, which in some situations may be preferred. Contemporary type designer Jeremy Tankard st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Font
In metal typesetting, a font is a particular size, weight and style of a typeface. Each font is a matched set of type, with a piece (a "sort") for each glyph. A typeface consists of a range of such fonts that shared an overall design. In modern usage, with the advent of computer fonts, the term "font" has come to be used as a synonym for "typeface", although a typical typeface (or "font family") consists of a number of fonts. For instance, the typeface "Bauer Bodoni" (sample shown here) includes fonts "Roman" (or "Regular"), " Bold" and ''" Italic"''; each of these exists in a variety of sizes. The term "font" is correctly applied to any one of these alone but may be seen used loosely to refer to the whole typeface. When used in computers, each style is in a separate digital "font file". In both traditional typesetting and modern usage, the word "font" refers to the delivery mechanism of the typeface. In traditional typesetting, the font would be made from metal or wood type: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sans-serif
In typography and lettering, a sans-serif, sans serif, gothic, or simply sans letterform is one that does not have extending features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. Sans-serif typefaces tend to have less stroke width variation than serif typefaces. They are often used to convey simplicity and modernity or minimalism. Sans-serif typefaces have become the most prevalent for display of text on computer screens. On lower-resolution digital displays, fine details like serifs may disappear or appear too large. The term comes from the French word , meaning "without" and "serif" of uncertain origin, possibly from the Dutch word meaning "line" or pen-stroke. In printed media, they are more commonly used for display use and less for body text. Before the term "sans-serif" became common in English typography, a number of other terms had been used. One of these outmoded terms for sans-serif was gothic, which is still used in East Asian typography and sometimes seen in typeface na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Western Typography
Modern typographers view typography as a craft with a very long history tracing its origins back to the first punches and dies used to make seals and coinage currency in ancient times. The basic elements of typography are at least as old as civilization and the earliest writing systems—a series of key developments that were eventually drawn together into one systematic craft. While woodblock printing and movable type had precedents in East Asia, typography in the Western world developed after the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the mid-15th century. The initial spread of printing throughout Germany and Italy led to the enduring legacy and continued use of blackletter, roman, and italic types. Medieval design roots Typography, type-founding, and typeface design began as closely related crafts in mid-15th-century Europe with the introduction of movable type printing at the junction of the medieval era and the Renaissance. Handwritten letterfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underline
An underscore, ; also called an underline, low line, or low dash; is a line drawn under a segment of text. In proofreading, underscoring is a convention that says "set this text in italic type", traditionally used on manuscript or typescript as an instruction to the printer. Its use to add emphasis in modern documents is a deprecated practice. The underscore character, , originally appeared on the typewriter and was primarily used to emphasise words as in the proofreader's convention. To produce an underscored word, the word was typed, the typewriter carriage was moved back to the beginning of the word, and the word was overtyped with the underscore character. In modern usage, underscoring is achieved by markup or with combining characters. The original free-standing underscore character continues in use to create visual spacing within a sequence of characters, where a whitespace character is not permitted (e.g., in computer filenames, email addresses, and in Internet URLs) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swash (typography)
A swash is a typographical flourish, such as an exaggerated serif, terminal, tail, entry stroke, etc., on a glyph. The use of swash characters dates back to at least the 16th century, as they can be seen in Ludovico Vicentino degli Arrighi's ''La Operina,'' which is dated 1522. As with italic type in general, they were inspired by the conventions of period handwriting. Arrighi's designs influenced designers in Italy and particularly in France. Typefaces with swashes Most typefaces with swashes are serif fonts, among which (if present) they are often found solely in italics. Advanced digital fonts often supply two italic designs: one with swashes and a more restrained standard italic. Among old-style typefaces, some releases of Caslon, such as Adobe Caslon, and Garamond, including Adobe Garamond Pro and EB Garamond, have swash designs. Old-style typefaces which include swashes but do not follow a specific historical model include Minion by Robert Slimbach and Nexus by Martin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typeface
A typeface (or font family) is the design of lettering that can include variations in size, weight (e.g. bold), slope (e.g. italic), width (e.g. condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font. There are list of typefaces, thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly. The art and craft of designing typefaces is called ''type design''. Designers of typefaces are called ''type designers'' and are often employed by ''type foundry, type foundries''. In desktop publishing, type designers are sometimes also called ''font developers'' or ''font designers''. Every typeface is a collection of glyphs, each of which represents an individual letter, number, punctuation mark, or other symbol. The same glyph may be used for character (symbol), characters from different scripts, e.g. Roman uppercase A looks the same as Cyrillic uppercase А and Greek uppercase alpha. There are typefaces tailored for special applications, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldine Press
The Aldine Press was the printing office started by Aldus Manutius in 1494 in Venice, from which were issued the celebrated Aldine editions of the classics (Latin and Greek masterpieces, plus a few more modern works). The first book that was dated and printed under his name appeared in 1495. The Aldine Press is famous in the history of typography, among other things, for the introduction of italics. The press was the first to issue printed books in the small octavo size, similar to that of a modern paperback, and like that intended for portability and ease of reading. According to Curt F. Bühler, the press issued 132 books during twenty years of activity under Aldus Manutius. After Aldus’s death in 1515, the press was continued by his wife Maria and her father, Andrea Torresani (), until his son, Paulus Manutius (1512–1574) took over. His grandson Aldus Manutius the Younger then ran the firm until his death in 1597. Today, the antique books printed by the Aldine Press in Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typography
Typography is the art and technique of arranging type to make written language legible, readable and appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, point sizes, line lengths, line-spacing ( leading), and letter-spacing (tracking), as well as adjusting the space between pairs of letters (kerning). The term ''typography'' is also applied to the style, arrangement, and appearance of the letters, numbers, and symbols created by the process. Type design is a closely related craft, sometimes considered part of typography; most typographers do not design typefaces, and some type designers do not consider themselves typographers. Typography also may be used as an ornamental and decorative device, unrelated to the communication of information. Typography is the work of typesetters (also known as compositors), typographers, graphic designers, art directors, manga artists, comic book artists, and, now, anyone who arranges words, letters, numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berthold Ullman
Berthold Louis Ullman (August 18, 1882 in Chicago, Illinois – June 26, 1965 in Vatican City) was an American Classical scholar. Ullman was born in Chicago to Louis Ullman and Eleanora Fried. He was educated at the University of Chicago (A.B. 1903, Ph.D. 1908). He joined the faculty at Chicago and also taught at the University of Pittsburgh and Iowa State University. He taught at the University of Chicago from 1925 until 1944 before moving to the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, becoming Kenan professor of Latin and department chair. Ullman's library collection formed the core of the present classics department library at the University of North Carolina. Ullman was also president of the American Philological Association in 1935. In 1948, he was elected as a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He married Mary Louise Bates on September 1, 1909. Their son Edward Ullman, born in 1912, became a geographer. As a scholar Ullman focused on Latin language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niccolò De' Niccoli
Niccolò de' Niccoli (1364 – 22 January 1437) was an Italian Renaissance humanist. He was born and died in Florence, and was one of the chief figures in the company of learned men which gathered around the patronage of Cosimo de' Medici. Niccoli's chief services to classical literature consisted in his work as a copyist and collator of ancient manuscripts; he corrected the text, introduced divisions into chapters, and made tables of contents. His lack of critical faculty was compensated by his excellent taste; in Greek (of which he knew very little) he had the assistance of Ambrogio Traversari. Many of the most valuable manuscripts in the Laurentian library are by his hand, amongst them those of Lucretius and of twelve comedies of Plautus. The pursuit of ancient manuscripts was a dangerous and expensive task; agents working in the field at the time included Poggio Bracciolini. Thanks to the patronage of Cosimo de' Medici, Niccoli was able to build up his personal library of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Griffo
Francesco Griffo (1450–1518), also called Francesco da Bologna, was a fifteenth-century Italian punchcutter. He worked for Aldus Manutius, designing the printer's more important humanist typefaces, including the first italic type. He cut Roman, Greek, Hebrew and first italic type. Aldus gives Griffo credit in the introduction of the ''Virgil'' of 1501. However, as Manutius had achieved a monopoly on italic printing and Greek publishing with the permission of the Venetian government, he had a falling-out with Griffo. Griffo then went to work for Gershom Soncino, whose family were Hebrew printers. It was with Soncino that Griffo's second italic type was cut in 1503. In 1516 he returned to Bologna where he began print publishing. In 1518 Griffo was charged with the murder of his son-in-law, who had been beaten to death with an iron bar. This is his last appearance in the historical record. He is presumed to have been executed. Influence Griffo's typefaces have been very influential. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |