|
Issoca Assanga
''Issoca'' is a genus of land planarians from Brazil. Description Species of the genus ''Issoca'' are characterized by the presence of a spoon-shaped head having a cephalic retractor muscle, which allows those animals to pull their anterior end upwards and backwards. Associated to the muscle are cephalic glands, forming a so-called cephalic musculo-glandular organ in a way similar to the one found in the genera '' Choeradoplana'' and ''Luteostriata''. The copulatory apparatus usually lacks a permanent penis papilla, i. e., the penis is formed during copulation by folds in the male cavity which are pushed outwards.Froehlich, C. G. (1955). ''Sobre Morfologia e Taxonomia das Geoplanidae.'' Boletim da Faculdade de Filosofia, Ciências e Letras da Universidade de São Paulo, Série Zoologia. 19: 195-279.Carbayo, F. (2010). ''A new genus for seven Brazilian land planarian species, split off from'' Notogynaphalia ''(Platyhelminthes, Tricladida).'' Belgian Journal of Zoology. 140: 91- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudio Gilberto Froehlich
Claudio Gilberto Froehlich (born 10 June 1927) is a Brazilian zoologist.Neglected ScienceClaudio Gilberto Froehlich Retrieved 19 February 2017. Life Froehlich was born in 1927 in São Paulo, Brazil. In 1951 he started his doctoral studies at the Universidade de São Paulo together with Eudóxia Maria de Oliveira Pinto, who later would become his wife. They both had Ernst Marcus as their advisor. Marcus suggested that they should work on the taxonomy of land planarians since it was a poorly studied but highly diverse group in the region. Later, in 1960, he received his post-doctoral degree from Lund University. After his first academic years studying land planarians, Froehlich started to work with freshwater invertebrates, especially stoneflies.Entomologistas do BrasilClaudio Gilberto Froehlich. Retrieved 19 February 2017. Homages The beetle genus ''Claudiella ''Claudiella ingens'' is a species of beetle in the family Torridincolidae, the only species in the genus ''Claudi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issoca Rezendei
''Issoca'' is a genus of land planarians from Brazil. Description Species of the genus ''Issoca'' are characterized by the presence of a spoon-shaped head having a cephalic retractor muscle, which allows those animals to pull their anterior end upwards and backwards. Associated to the muscle are cephalic glands, forming a so-called cephalic musculo-glandular organ in a way similar to the one found in the genera '' Choeradoplana'' and ''Luteostriata''. The copulatory apparatus usually lacks a permanent penis papilla, i. e., the penis is formed during copulation by folds in the male cavity which are pushed outwards.Froehlich, C. G. (1955). ''Sobre Morfologia e Taxonomia das Geoplanidae.'' Boletim da Faculdade de Filosofia, Ciências e Letras da Universidade de São Paulo, Série Zoologia. 19: 195-279.Carbayo, F. (2010). ''A new genus for seven Brazilian land planarian species, split off from'' Notogynaphalia ''(Platyhelminthes, Tricladida).'' Belgian Journal of Zoology. 140: 91- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Planarian
Geoplanidae is a family of flatworms known commonly as land planarians or land flatworms. These flatworms are mainly predators of other invertebrates, which they hunt, attack and capture using physical force and the adhesive and digestive properties of their mucus. They lack water-retaining mechanisms and are therefore very sensitive to humidity variations of their environment. Because of their strict ecological requirements, some species have been proposed as indicators of the conservation state of their habitats. They are generally animals with low vagility (dispersal ability) and with very specific habitat requirements, so they can be also used to accurately determine the distribution of biogeographic realms. Today the fauna of these animals is being studied to select conservation priorities in the Atlantic rainforest in Brazil. At the other extreme, one species in this family, ''Platydemus manokwari'' has become an invasive species in both disturbed and wild habitats in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choeradoplana
''Choeradoplana'' is a genus of land planarians found in South America. Description Species of the genus ''Choeradoplana'' are characterized by the presence of a cephalic retractor muscle associated with cephalic glands, forming a cephalic musculo-glandular organ in a way similar to the one found in the genera ''Luteostriata'' and '' Issoca''. The head of ''Choeradoplana'' is highly rolled backwards and the ventral area thus visible has two "cushions" formed by the musculo-glandular organ.Ogren, R. E. and Kawakatsu, M. (1990). ''Index to the species of the family Geoplanidae (Turbellaria, Tricladida, Terricola) Part I: Geoplaninae.'' Bulletin of Fujis Women's College. 29: 79-166. This peculiar head shape makes it easy to identify a species as belonging to this genus. Etymology The name ''Choeradoplana'' comes from Greek word ''χοιράς'' ( scrofula) and the Latin word ''plana'' (flat) due to the two cushions on the ventral side of the head that resemble the neck swellings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luteostriata
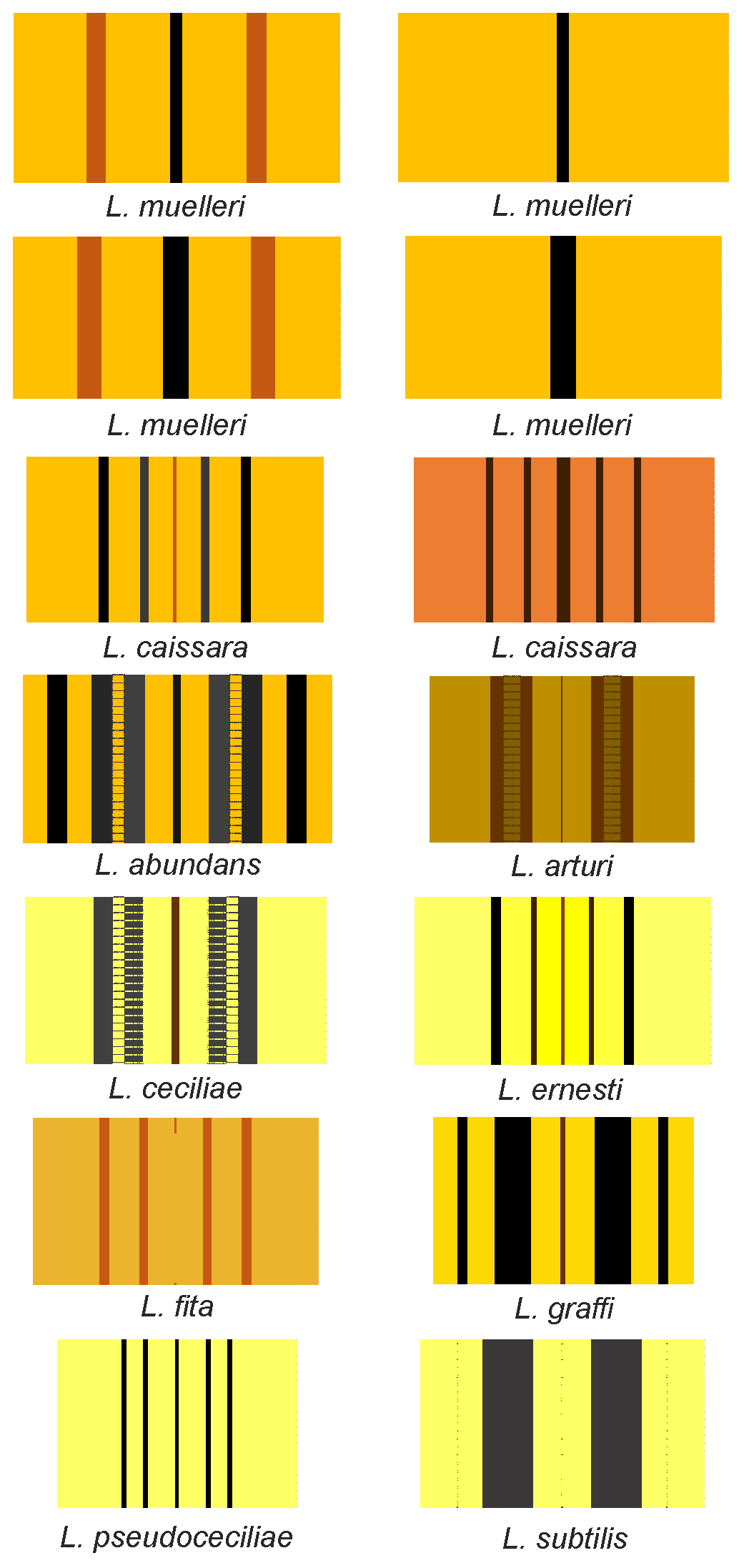
''Luteostriata'' is a genus of land planarians from Brazil characterized by a yellow body with dark longitudinal stripes. Description The genus ''Luteostriata'' is characterized by the presence of a cephalic retractor muscle, which allows those animals to pull their anterior end upwards and backwards. Associated to the muscle are cephalic glands, forming a so-called cephalic musculo-glandular organ in a way similar to the one found in the genera ''Choeradoplana'' and '' Issoca''. The copulatory apparatus has an reversible penis, i.e., there is no permanent penis papilla and the penis is formed during copulation by folds in the male cavity which are pushed outwards. Externally, species in this genus usually have a yellow to light brown dorsal color with a series of longitudinal dark stripes, hence the name ''Luteostriata'', from Latin ''luteus'' (saffron yellow) + ''striatus'' (striped). The anterior end is also usually marked by an orange tinge that posteriorly gradually fades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive System Of Planarians
The reproductive system of planarians is broadly similar among different families, although the associated structures can vary in complexity. All planarians are hermaphrodites, so their reproductive system has a male and a female part. Both parts communicate with the surface of the body via a single opening called gonopore, which is located on the ventral side of the posterior half of the body. Male part of the reproductive system The male part of the reproductive system in planarians has a set of several testicles, distributed throughout the body in two or more rows. They are usually concentrated in the anterior two thirds of the body, although they can reach close to the posterior end. The testicles are connected to a pair of sperm ducts which run posteriorly towards the gonopore. In some groups, the sperm ducts met in their distal part, forming the ejaculatory duct, which then opens in a cavity called “male atrium”. In others, like land planarians, both open in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupi Language
Old Tupi, Ancient Tupi or Classical Tupi (also spelled as Tupí) is an extinct Tupian language which was spoken by the aboriginal Tupi people of Brazil, mostly those who inhabited coastal regions in South and Southeast Brazil. It belongs to the Tupi–Guarani language family, and has a written history spanning the 16th, 17th, and early 18th centuries. In the early colonial period, Tupi was used as a ''lingua franca'' throughout Brazil by Europeans and aboriginal Americans, and had literary usage, but it was later suppressed almost to extinction. Today, only one modern descendant is living, the Nheengatu language. The names Old Tupi or classical Tupi are used for the language in English and by modern scholars (it is referred to as in Portuguese), but native speakers called it variously "the good language", "common language", "human language", in Old Tupi, or, in Portuguese, "general language", "Amazonian general language", "Brazilian language". History Old Tupi was firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issoca Assanga
''Issoca'' is a genus of land planarians from Brazil. Description Species of the genus ''Issoca'' are characterized by the presence of a spoon-shaped head having a cephalic retractor muscle, which allows those animals to pull their anterior end upwards and backwards. Associated to the muscle are cephalic glands, forming a so-called cephalic musculo-glandular organ in a way similar to the one found in the genera '' Choeradoplana'' and ''Luteostriata''. The copulatory apparatus usually lacks a permanent penis papilla, i. e., the penis is formed during copulation by folds in the male cavity which are pushed outwards.Froehlich, C. G. (1955). ''Sobre Morfologia e Taxonomia das Geoplanidae.'' Boletim da Faculdade de Filosofia, Ciências e Letras da Universidade de São Paulo, Série Zoologia. 19: 195-279.Carbayo, F. (2010). ''A new genus for seven Brazilian land planarian species, split off from'' Notogynaphalia ''(Platyhelminthes, Tricladida).'' Belgian Journal of Zoology. 140: 91- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issoca Jandaia
''Issoca'' is a genus of land planarians from Brazil. Description Species of the genus ''Issoca'' are characterized by the presence of a spoon-shaped head having a cephalic retractor muscle, which allows those animals to pull their anterior end upwards and backwards. Associated to the muscle are cephalic glands, forming a so-called cephalic musculo-glandular organ in a way similar to the one found in the genera '' Choeradoplana'' and ''Luteostriata''. The copulatory apparatus usually lacks a permanent penis papilla, i. e., the penis is formed during copulation by folds in the male cavity which are pushed outwards.Froehlich, C. G. (1955). ''Sobre Morfologia e Taxonomia das Geoplanidae.'' Boletim da Faculdade de Filosofia, Ciências e Letras da Universidade de São Paulo, Série Zoologia. 19: 195-279.Carbayo, F. (2010). ''A new genus for seven Brazilian land planarian species, split off from'' Notogynaphalia ''(Platyhelminthes, Tricladida).'' Belgian Journal of Zoology. 140: 91- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issoca Piranga
''Issoca'' is a genus of land planarians from Brazil. Description Species of the genus ''Issoca'' are characterized by the presence of a spoon-shaped head having a cephalic retractor muscle, which allows those animals to pull their anterior end upwards and backwards. Associated to the muscle are cephalic glands, forming a so-called cephalic musculo-glandular organ in a way similar to the one found in the genera '' Choeradoplana'' and ''Luteostriata''. The copulatory apparatus usually lacks a permanent penis papilla, i. e., the penis is formed during copulation by folds in the male cavity which are pushed outwards.Froehlich, C. G. (1955). ''Sobre Morfologia e Taxonomia das Geoplanidae.'' Boletim da Faculdade de Filosofia, Ciências e Letras da Universidade de São Paulo, Série Zoologia. 19: 195-279.Carbayo, F. (2010). ''A new genus for seven Brazilian land planarian species, split off from'' Notogynaphalia ''(Platyhelminthes, Tricladida).'' Belgian Journal of Zoology. 140: 91- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issoca Potyra
''Issoca'' is a genus of land planarians from Brazil. Description Species of the genus ''Issoca'' are characterized by the presence of a spoon-shaped head having a cephalic retractor muscle, which allows those animals to pull their anterior end upwards and backwards. Associated to the muscle are cephalic glands, forming a so-called cephalic musculo-glandular organ in a way similar to the one found in the genera '' Choeradoplana'' and ''Luteostriata''. The copulatory apparatus usually lacks a permanent penis papilla, i. e., the penis is formed during copulation by folds in the male cavity which are pushed outwards.Froehlich, C. G. (1955). ''Sobre Morfologia e Taxonomia das Geoplanidae.'' Boletim da Faculdade de Filosofia, Ciências e Letras da Universidade de São Paulo, Série Zoologia. 19: 195-279.Carbayo, F. (2010). ''A new genus for seven Brazilian land planarian species, split off from'' Notogynaphalia ''(Platyhelminthes, Tricladida).'' Belgian Journal of Zoology. 140: 91- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |