|
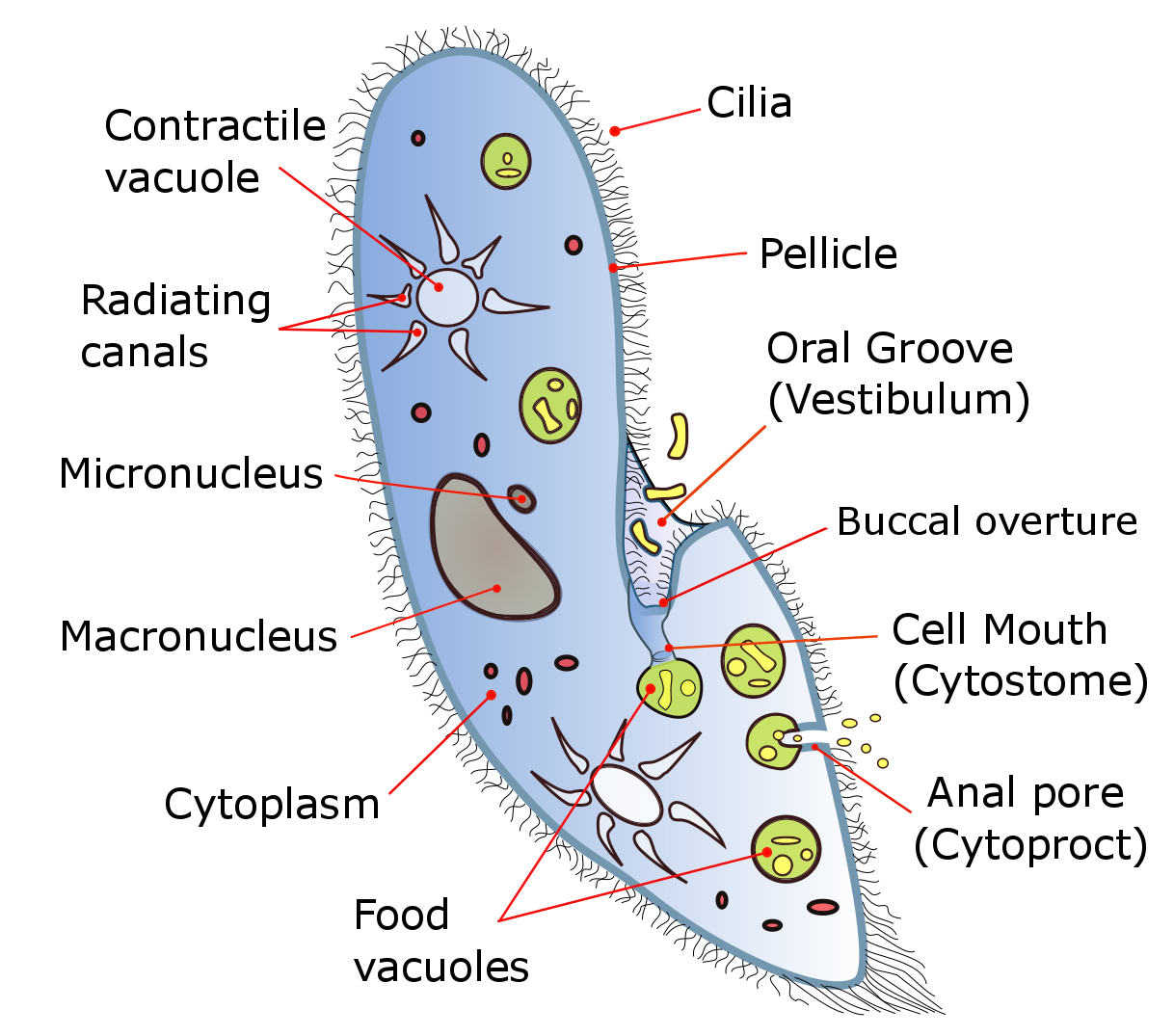
Isotricha
''Isotricha'' is a genus of protozoa (single-celled organisms) which are commensals of the rumen of ruminant animals. They are approximately long. Species include: * '' Isotricha intestinalis'' Stein 1858 * '' Isotricha prostoma'' Stein Stein is a German, Yiddish and Norwegian word meaning "stone" and "pip" or "kernel". It stems from the same Germanic root as the English word stone. It may refer to: Places In Austria * Stein, a neighbourhood of Krems an der Donau, Lower Austr ... 1858 References Biological interactions Ciliate genera Litostomatea Symbiosis {{ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotricha Intestinalis
''Isotricha intestinalis'' is a species of holotrich protozoa in the class Litostomatea. Description ''Isotricha intestinalis'' can be 200 micrometers long, and is distinguishable by its mouth position. They are the largest protozoans present in the rumen of sheep. This species has microbody-like organelle In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...s, and a highly granular appearance. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q3382340 Litostomatea Species described in 1859 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotricha Prostoma
''Isotricha'' is a genus of protozoa (single-celled organisms) which are commensals of the rumen of ruminant animals. They are approximately long. Species include: * ''Isotricha intestinalis'' Stein 1858 * '' Isotricha prostoma'' Stein Stein is a German, Yiddish and Norwegian word meaning "stone" and "pip" or "kernel". It stems from the same Germanic root as the English word stone. It may refer to: Places In Austria * Stein, a neighbourhood of Krems an der Donau, Lower Austr ... 1858 References Biological interactions Ciliate genera Litostomatea Symbiosis {{ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Von Stein
Samuel Friedrich Nathaniel Ritter von Stein (November 3, 1818 – January 9, 1885) was a German entomologist. He was Professor at the Royal Saxon Academy of Forestry in Tharandt from 1850–55; and Professor, and later Rector, at the Charles University in Prague, from 1855–76. His scientific work focused on invertebrates, and mainly on ''Diptera''. Early life, education, and family Stein was born in Niemegk, near Potsdam, Brandenburg. He completed his studies in 1841, conducting doctoral work at the University of Berlin. On May 29, 1844, in Berlin, he married Emma Johanne Couard Ottilie (born December 30, 1823, in Berlin; died 2 September 1903, in Asch). The couple had nine children. The next to last, daughter Adelheid von Stein (born May 25, 1859), married Joseph Neuwirth. Career Stein's scientific work focused on invertebrates, and mainly on ''Diptera'', as well as single-celled animals. His work on ''infusoria'' became the basis for all subsequent research in this area. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit from each other; amensalism, where one is harmed while the other is unaffected; parasitism, where one is harmed and the other benefits, and parasitoidism, which is similar to parasitism but the parasitoid has a free-living state and instead of just harming its host, it eventually ends up killing it. The commensal (the species that benefits from the association) may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is substantially unaffected. The commensal relation is often between a larger host and a smaller commensal; the host organism is unmodified, whereas the commensal species may show great structural adaptation consistent with its habits, as in the remoras that ride attached to sharks and other fishes. Remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment allows it to serve as the primary site for microbial fermentation of ingested feed. The smaller part of the reticulorumen is the reticulum, which is fully continuous with the rumen, but differs from it with regard to the texture of its lining. Brief anatomy The rumen is composed of several muscular sacs, the cranial sac, ventral sac, ventral blindsac, and reticulum. The lining of the rumen wall is covered in small fingerlike projections called papillae, which are flattened, approximately 5mm in length and 3mm wide in cattle. The reticulum is lined with ridges that form a hexagonal honeycomb pattern. The ridges are approximately 0.1–0.2mm wide and are raised 5mm above the reticulum wall. The hexagons in the reticulum are approximately 2� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Interactions
In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species (interspecific interactions). These effects may be short-term, like pollination and predation, or long-term; both often strongly influence the evolution of the species involved. A long-term interaction is called a symbiosis. Symbioses range from mutualism, beneficial to both partners, to competition, harmful to both partners. Interactions can be indirect, through intermediaries such as shared resources or common enemies. This type of relationship can be shown by net effect based on individual effects on both organisms arising out of relationship. Several recent studies have suggested non-trophic species interactions such as habitat modification and mutualisms can be important determinants of food web structures. However, it remains unclear whether these findings g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliate Genera
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some obligate and opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species range in size from as little as 10 µm in some colpodeans to as much as 4 mm in length in some gel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litostomatea
The Litostomatea are a class of ciliates. The group consists of three subclasses: Haptoria, Trichostomatia and Rhynchostomatia. Haptoria includes mostly carnivorous forms such as ''Didinium'', a species of which preys primarily on the ciliate ''Paramecium''. Trichostomatia (trichostomes) are mostly endosymbionts in the digestive tracts of vertebrates. These include the species ''Balantidium coli'', which is the only ciliate parasitic in humans. The group Rhynchostomatia includes two free-living orders previously included among the Haptoria, but now known to be genetically distinct from them, the Dileptida and the Tracheliida. Morphology In litostomes, the body cilia arise from structures in the cell cortex called monokinetids, which are made up of a single cilium and its associated structures, such as basal bodies and microtubular fibres. These have an ultrastructural arrangement characteristic to the group. The cell "mouth" (cytostome) is apical or subapical. In trichostomes it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)