|
Isolated Congenital Asplenia
Isolated congenital asplenia is a rare disease in humans that can cause life-threatening bacterial infections in children due to primary immunodeficiency. The infections can include pneumococal sepsis and meningitis. ICAS is a ribosomopathy, due to autosomal dominant mutation of the ''RPSA'' gene on chromosome 3p21. Unlike heterotaxy syndrome, the absent spleen (asplenia) is not associated with other structural developmental defects. In some cases the spleen is present, but very small and nonfunctional (hyposplenism). Immunodeficiency The spleen is an organ within the lymphatic system and its primary function is to filter blood. However, the spleen also plays a key role in immune responses as it detects pathogens within the blood and secretes phagocytes to fight potential infection. Without these immune functions, individuals with isolated congenital asplenia are extremely susceptible to infection. ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' is a common bacteria that affects individuals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogenic Bacteria
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often Probiotic, beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract. The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decomposition, decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immune system, immunity or innate immunity, innate resistance against many microorganisms. Pathogenic bacteria are specially adapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterotaxy Syndrome
Situs ambiguus is a rare congenital defect in which the major visceral organs are distributed abnormally within the chest and abdomen. Clinically heterotaxy spectrum generally refers to any defect of Left-right asymmetry and arrangement of the visceral organs; however, classical heterotaxy requires multiple organs to be affected. This does not include the congenital defect situs inversus, which results when arrangement of all the organs in the abdomen and chest are mirrored, so the positions are opposite the normal placement. Situs inversus is the mirror image of situs solitus, which is normal asymmetric distribution of the abdominothoracic visceral organs. Situs ambiguus can also be subdivided into left-isomerism and right isomerism based on the defects observed in the spleen, lungs and atria of the heart. Individuals with situs inversus or situs solitus do not experience fatal dysfunction of their organ systems, as general anatomy and morphology of the abdominothoracic organ-vess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorders
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otitis Media
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. The other main type is otitis media with effusion (OME), typically not associated with symptoms, although occasionally a feeling of fullness is described; it is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear which may persist for weeks or months often after an episode of acute otitis media. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation that results in a perforated tympanic membrane with discharge from the ear for more than six weeks. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three types of otitis media may be associated with hearing loss. If children with hearing loss due to OME do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
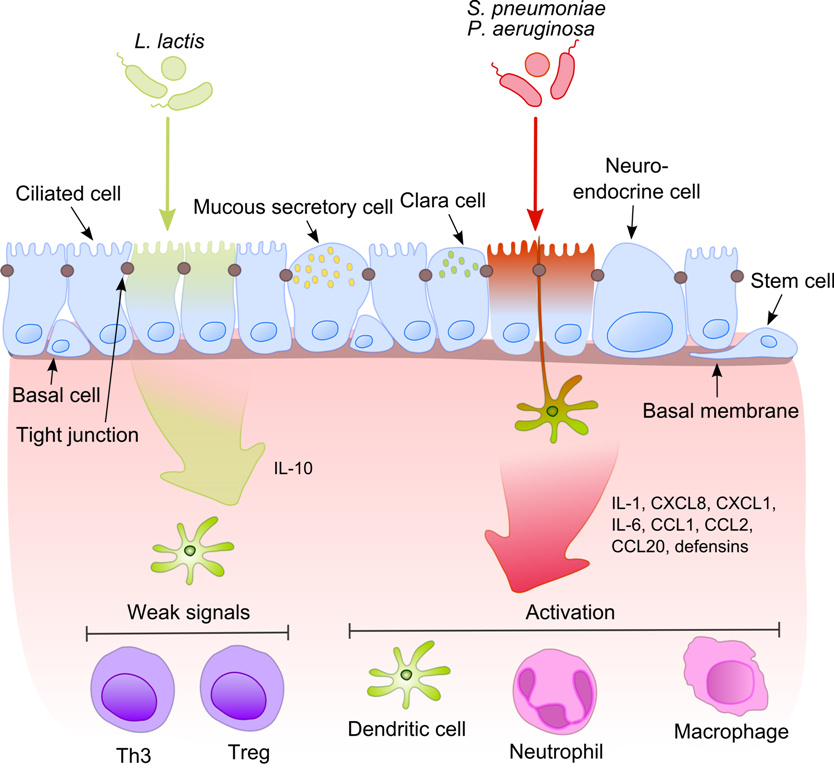
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic (under aerobic conditions) or beta-hemolytic (under anaerobic conditions), aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. They are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not form spores and are non motile. As a significant human pathogenic bacterium ''S. pneumoniae'' was recognized as a major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century, and is the subject of many humoral immunity studies. ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' resides asymptomatically in healthy carriers typically colonizing the respiratory tract, sinuses, and nasal cavity. However, in susceptible individuals with weaker immune systems, such as the elderly and young children, the bacterium may become pathogenic and spread to other locations to cause disease. It spreads by direct person-to-person contact via respiratory droplets and by auto inoculation in persons carrying the bacteria in their upper res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocyte
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek ', "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek ''kutos'', "hollow vessel". They are essential for fighting infections and for subsequent immunity. Phagocytes are important throughout the animal kingdom and are highly developed within vertebrates. One litre of human blood contains about six billion phagocytes. They were discovered in 1882 by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov while he was studying starfish larvae.Ilya Mechnikov retrieved on November 28, 2008. Fro ''Physiology or Medicine 1901–1921'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
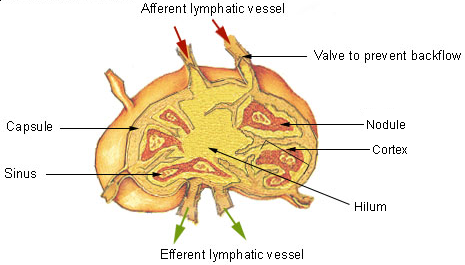
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .σπλήν Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek-English Lexicon'', on Perseus Digital Library The spleen plays very important roles in regard to s (erythrocytes) and the . It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood, which can be valuable in case of |
Asplenia
Asplenia refers to the absence of normal spleen function and is associated with some serious infection risks. Hyposplenism is used to describe reduced ('hypo-') splenic functioning, but not as severely affected as with asplenism. ''Functional'' asplenia occurs when splenic tissue is present but does not work well (e.g. sickle-cell disease, polysplenia) -such patients are managed as if asplenic-, while in ''anatomic'' asplenia, the spleen itself is absent. Causes Congenital * Congenital asplenia is rare. There are two distinct types of genetic disorders: heterotaxy syndromeOnline Mendelian Inheritance in Man. OMIM entry 208530: Right atrial isomerism; RAI. Johns Hopkins University/ref> and isolated congenital asplenia.Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Johns Hopkins UniversityOMIM entry 271400: Asplenia, isolated congenital; ICAS./ref> * polysplenia Acquired Acquired asplenia occurs for several reasons: * Following splenectomy due to splenic rupture from trauma or because of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 3
Chromosome 3 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 3 spans almost 200 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents about 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 3. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. List of genes The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 3. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. p-arm Partial list of the genes located on p-arm (short arm) of human chromosome 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Immunodeficiency
Primary immunodeficiencies are disorders in which part of the body's immune system is missing or does not function normally. To be considered a ''primary'' immunodeficiency (PID), the cause of the immune deficiency must not be secondary in nature (i.e., caused by other disease, drug treatment, or environmental exposure to toxins). Most primary immunodeficiencies are genetic disorders; the majority are diagnosed in children under the age of one, although milder forms may not be recognized until adulthood. While there are over 430 recognized PIDs as of 2019, most are very rare. About 1 in 500 people in the United States are born with a primary immunodeficiency. Immune deficiencies can result in persistent or recurring infections, auto-inflammatory disorders, tumors, and disorders of various organs. There are currently limited treatments available for these conditions; most are specific to a particular type of PID. Research is currently evaluating the use of stem cell transplants (H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |