|
Islamic Influence On Medieval Europe
During the High Middle Ages, the Islamic world was at its cultural peak, supplying information and ideas to Europe, via Al-Andalus, Sicily and the Crusader kingdoms in the Levant. These included Latin translations of the Greek Classics and of Arabic texts in astronomy, mathematics, science, and medicine. Translation of Arabic philosophical texts into Latin "led to the transformation of almost all philosophical disciplines in the medieval Latin world", with a particularly strong influence of Muslim philosophers being felt in natural philosophy, psychology and metaphysics. Other contributions included technological and scientific innovations via the Silk Road, including Chinese inventions such as paper and gunpowder. The Islamic world also influenced other aspects of medieval European culture, partly by original innovations made during the Islamic Golden Age, including various fields such as the arts, agriculture, alchemy, music, pottery, etc. Many Arabic loanwords in We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
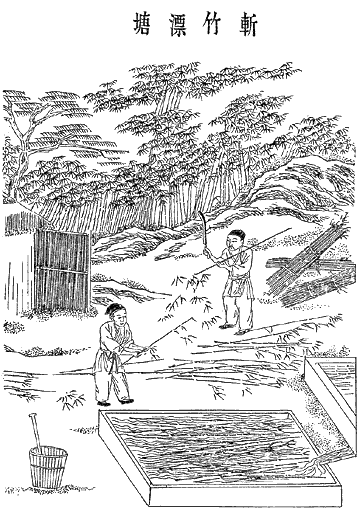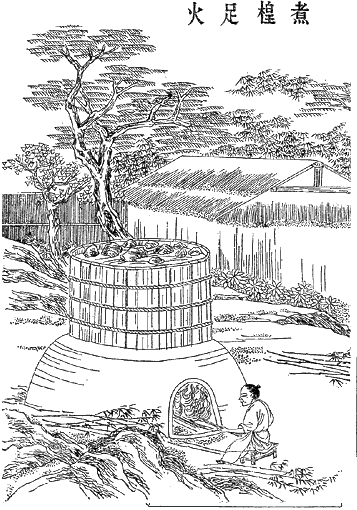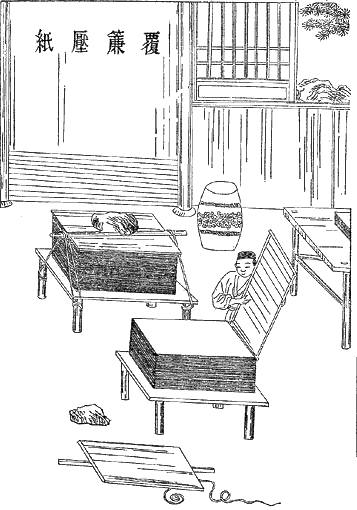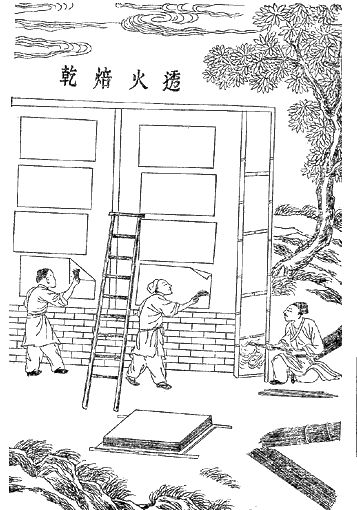
History Of Paper
Paper is a thin nonwoven material traditionally made from a combination of milled plant and textile fibres. The first paper-like plant-based writing sheet was papyrus in Egypt (4th Century BC), but the first true paper, the first true papermaking process was documented in China during the Eastern Han period (25–220 AD), traditionally attributed to the court official Cai Lun. This plant-puree conglomerate produced by pulp mills and paper mills was used for writing, drawing, and money. During the 8th century, Chinese paper making spread to the Islamic world, replacing papyrus. By the 11th century, papermaking was brought to Europe, where it replaced animal-skin-based parchment and wood panels. By the 13th century, papermaking was refined with paper mills using waterwheels in Spain. Later improvements to the papermaking process came in 19th century Europe with the invention of wood-based papers. Although there were precursors such as papyrus in the Mediterranean world and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldebaran
Aldebaran (Arabic: “The Follower”, "الدبران") is the brightest star in the zodiac constellation of Taurus. It has the Bayer designation α Tauri, which is Latinized to Alpha Tauri and abbreviated Alpha Tau or α Tau. Aldebaran varies in brightness from an apparent visual magnitude 0.75 down to 0.95, making it (typically) the fourteenth-brightest star in the night sky. It is located at a distance of approximately 65 light-years from the Sun. The star lies along the line of sight to the nearby Hyades cluster. Aldebaran is a giant star that is cooler than the Sun with a surface temperature of , but its radius is about 44 times the Sun's, so it is over 400 times as luminous. It spins slowly and takes 520 days to complete a rotation. Aldebaran is believed to host a planet several times the mass of Jupiter, named . The planetary exploration probe Pioneer 10 is heading in the general direction of the star and should make its closest approach in about two million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Arabic Star Names
This is a list of Arabic star names. In Western astronomy, most of the accepted star names are Arabic, a few are Greek and some are of unknown origin. Typically only bright stars have names. History of Arabic star names Very old star names originated among people who lived in the Arabian Peninsula more than a thousand years ago, after the rise of Islam. However, some Arabic language star names sprang up later in history, as translations of ancient Greek language descriptions. The astronomer Claudius Ptolemy in his ''Almagest'' (2nd century) tabulated the celestial position and brightness (visual magnitude) of 1,025 stars. Ptolemy's book was translated into Arabic in the 8th and 9th centuries and became famous in Europe as a 12th-century Latin translation. Many of the Arabic-language star descriptions in the ''Almagest'' came to be widely used as names for stars. Ptolemy used a strategy of "figure reference" to identify stars according to their position within a familiar constell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influence Of Arabic On Other Languages
Arabic has had a great influence on other languages, especially in vocabulary. The influence of Arabic has been most profound in those countries visited by Islam or Islamic power. Arabic loanwords have made into many languages as diverse as Amharic, Albanian, Armenian, Azerbaijani, Balochi, Bengali, Berber, Bosnian, Bulgarian, Catalan, Chaldean, Chechen, Croatian, Dagestani, English, French, Georgian, German, Greek, Gujarati, Hausa, Hebrew, Hindi, Indonesian, Italian, Kazakh, Kurdish, Kutchi, Kyrgyz, Macedonian, Malaysian, Odia, Pashto, Persian, Portuguese, Punjabi, Romanian, Serbian, Sicilian, Spanish, Sindhi, Somali, Swahili, Tagalog, Tigrinya, Turkish, Turkmen, Urdu, Uyghur, Uzbek, Visayan and Wolof as well as other languages in countries where these languages are spoken. Other languages such as Maltese and Nubi derive from Arabic, rather than merely borrowing vocabulary. Spanish has one of the largest Arabic-influenced vocabularies of any European la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Pottery
Medieval Islamic pottery occupied a geographical position between Chinese ceramics, the unchallenged leaders of Eurasian production, and the pottery of the Byzantine Empire and Europe. For most of the period it can fairly be said to have been between the two in terms of aesthetic achievement and influence as well, borrowing from China and exporting to and influencing Byzantium and Europe. The use of drinking and eating vessels in gold and silver, the ideal in ancient Rome and Persia as well as medieval Christian societies, is prohibited by the Hadiths, with the result that pottery and glass were used for tableware by Muslim elites, as pottery (but less often glass) also was in China but was much rarer in Europe and Byzantium. In the same way, Islamic restrictions greatly discouraged figurative wall-painting, encouraging the architectural use of schemes of decorative and often geometrically-patterned titles, which are the most distinctive and original specialty of Islamic cerami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Music
Arabic music or Arab music ( ar, الموسيقى العربية, al-mūsīqā al-ʿArabīyyah) is the music of the Arab world with all its diverse music styles and genres. Arabic countries have many rich and varied styles of music and also many linguistic dialects, with each country and region having their own traditional music. Arabic music has a long history of interaction with many other regional musical styles and genres. It represents the music of all the peoples that make up the Arab world today, all the 22 states. History Pre-Islamic period (Arabian Peninsula) Pre-Islamic Arabia was the cradle of many intellectual achievements, including music, musical theory and the development of musical instruments. In Yemen, the main center of pre-Islamic Arab sciences, literature and arts, musicians benefited from the patronage of the Kings of Sabaʾ who encouraged the development of music. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemy And Chemistry In Medieval Islam
Alchemy in the medieval Islamic world refers to both traditional alchemy and early practical chemistry (the early chemical investigation of nature in general) by Muslim scholars in the medieval Islamic world. The word ''alchemy'' was derived from the Arabic word كيمياء or ''kīmiyāʾ''p. 854, "Arabic alchemy", Georges C. Anawati, pp. 853-885 in '' Encyclopedia of the history of Arabic science'', eds. Roshdi Rashed and Régis Morelon, London: Routledge, 1996, vol. 3, . and may ultimately derive from the ancient Egyptian word ''kemi'', meaning black. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the focus of alchemical development moved to the Caliphate and the Islamic civilization. Much more is known about Islamic alchemy as it was better documented; most of the earlier writings that have come down through the years were preserved as Arabic translations. Definition and relationship with medieval western sciences In considering Islamic sciences as a distinct, loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Agricultural Revolution
The Arab Agricultural Revolution was the transformation in agriculture from the 8th to the 13th century in the Islamic region of the Old World. The agronomic literature of the time, with major books by Ibn Bassal and Abū l-Khayr al-Ishbīlī, demonstrates the extensive diffusion of useful plants to Medieval Spain (al-Andalus), and the growth in Islamic scientific knowledge of agriculture and horticulture. Medieval Arab historians and geographers described al-Andalus as a fertile and prosperous region with abundant water, full of fruit from trees such as the olive and pomegranate. Archaeological evidence demonstrates improvements in animal husbandry and in irrigation such as with the ''sakia'' water wheel. These changes made agriculture far more productive, supporting population growth, urbanisation, and increased stratification of society. The revolution was first described by the historian Antonio Garcia Maceira in 1876. The name was coined by the historian Andrew Watson in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
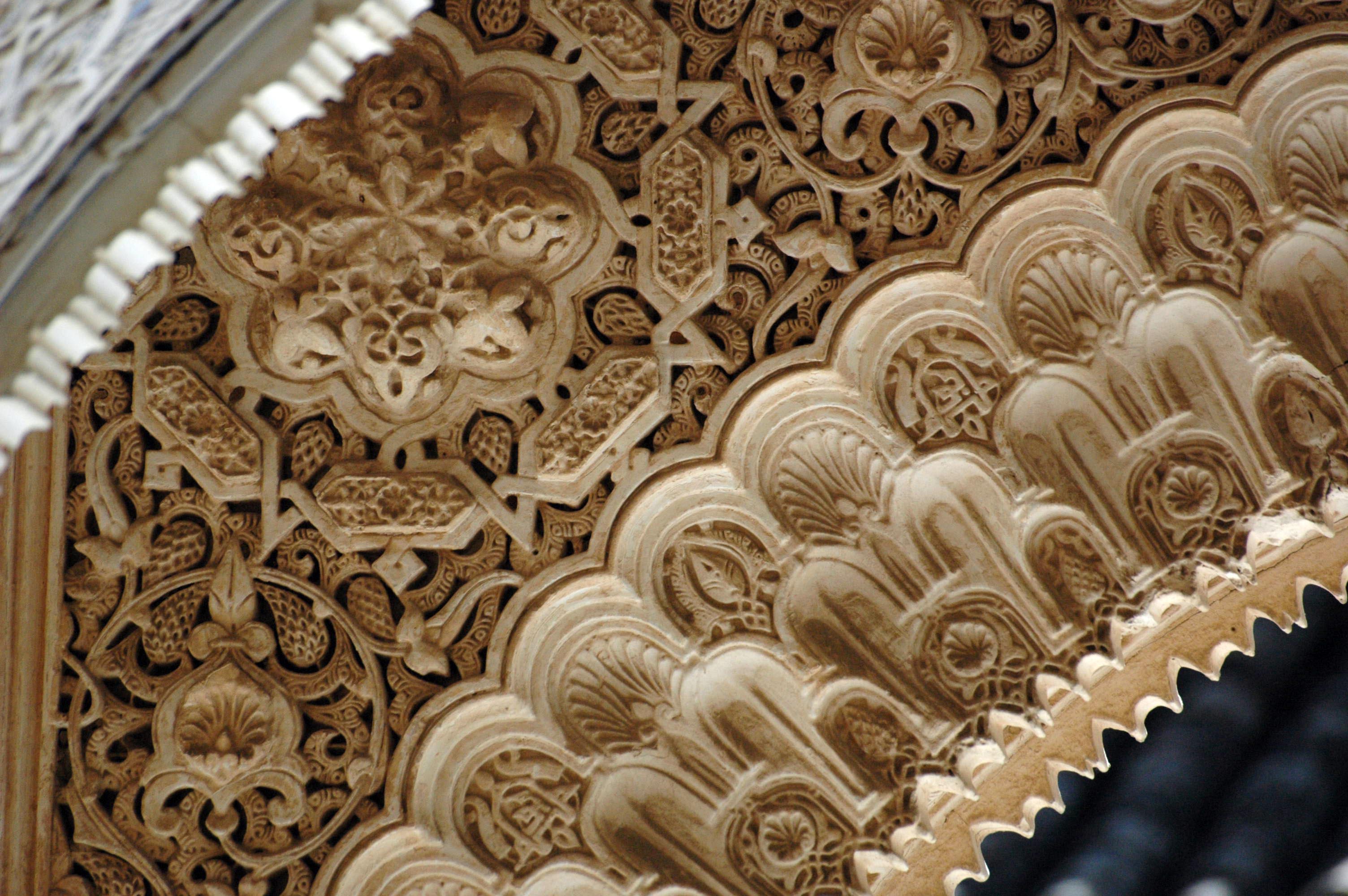
Islamic Art
Islamic art is a part of Islamic culture and encompasses the visual arts produced since the 7th century CE by people who lived within territories inhabited or ruled by Muslim populations. Referring to characteristic traditions across a wide range of lands, periods, and genres, Islamic art is a concept used first by Western art historians since the late 19th century. Public Islamic art is traditionally non- representational, except for the widespread use of plant forms, usually in varieties of the spiralling arabesque. These are often combined with Islamic calligraphy, geometric patterns in styles that are typically found in a wide variety of media, from small objects in ceramic or metalwork to large decorative schemes in tiling on the outside and inside of large buildings, including mosques. Other forms of Islamic art include Islamic miniature painting, artefacts like Islamic glass or pottery, and textile arts, such as carpets and embroidery. The early developments of Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



