|
Islam In West Sumatra
Islam is the most adhered religion in West Sumatra, a province of Indonesia, embraced by 97.42% of the whole population. The Muslim population increases to 99.6% if it excludes the Mentawai Islands, where the majority of the non-Muslim (Protestantism in Indonesia, Protestant) West Sumatrans reside. Denomination among Islam in West Sumatra is predominantly Sunni Islam, and there is a small Shia Islamic pocket within the coastal city of Pariaman. Minangkabau people, indigenous to West Sumatra and comprise 88% of the West Sumatran population today, have historically played an important role within the Muslim community in Indonesia. Up until today the region is considered one of the strongholds of Islam in Indonesia. History Introduction of Islam Introduction of Islam in the West Sumatran region, especially the Minangkabau Highlands, the home of Minangkabau people, is assumed to take two routes. One from the east Minangkabau between the 7th -8th century, and another from the west coas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Festival Budaya Minangkabau 2016
A festival is an event ordinarily celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, Melā, mela, or Muslim holidays, eid. A festival constitutes typical cases of glocalization, as well as the high culture-low culture interrelationship. Next to religion and folklore, a significant origin is agriculture, agricultural. Food is such a vital resource that many festivals are associated with harvest time. Religious commemoration and thanksgiving for good harvests are blended in events that take place in autumn, such as Halloween in the northern hemisphere and Easter in the southern. Festivals often serve to fulfill specific communal purposes, especially in regard to commemoration or thanking to the gods, goddesses or saints: they are called patronal festivals. They may also provide entertainment, which was particularly important to local communities before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aceh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a special autonomous status, Aceh is a religiously conservative territory and the only Indonesian province practicing the Sharia law officially. There are ten indigenous ethnic groups in this region, the largest being the Acehnese people, accounting for approximately 80% to 90% of the region's population. Aceh is where the spread of Islam in Indonesia began, and was a key factor of the spread of Islam in Southeast Asia. Islam reached Aceh (Kingdoms of Fansur and Lamuri) around 1250 AD. In the early 17th century the Sultanate of Aceh was the most wealthy, powerful and cultivated state in the Malacca Straits region. Aceh has a history of political independence and resistance to control by outsiders, including the former Dutch colonists and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matriarchal
Matriarchy is a social system in which women hold the primary power positions in roles of authority. In a broader sense it can also extend to moral authority, social privilege and control of property. While those definitions apply in general English, definitions specific to anthropology and feminism differ in some respects. Matriarchies may also be confused with matrilineal, matrilocal, and matrifocal societies. While there are those who may consider any non-patriarchal system to be matriarchal, most academics exclude those systems from matriarchies as strictly defined. Definitions, connotations, and etymology According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED''), matriarchy is a "form of social organization in which the mother or oldest female is the head of the family, and descent and relationship are reckoned through the female line; government or rule by a woman or women."''Oxford English Dictionary'' (online), entry ''matriarchy'', as accessed November 3, 2013. A pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wasat (Islamic Term)
In Islam, ''wasat'' (moderation) is one of the most basic terms and deliberately used topics. In the sense of shariah, it is a central characteristic of Islamic creed and has been used from the very beginning of Islam. It refers to a justly balanced way of life, avoiding extremes and experiencing things in moderation. Etymology ''Wasat'', also called ''wasatiyyah'' () is the Arabic word for ''best'', ''middle'', ''centered'', ''balanced'', ''middle way'' or ''moderation'' in the Islamic context, meanwhile ''Qasd''قصد and ''Iqtisad''اقتصاد are other terms for moderation in Islam, which mean "right way," "middle way," and "honest, truthful way." The term is also used in the Qur'an and Hadith to mean moderation. For example: Surah Nahl (16) in verse 9, Surah Ma'idah (5) in verse 66, Surah Tawba (9) in verse 42, Surah Luqman (31) in verse 19 and 32, and Surah Fatir (35) in verse 32. The person who follows wasat/qasd is called ''wasati/wasiti'/Muqsidin'. In addition, the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
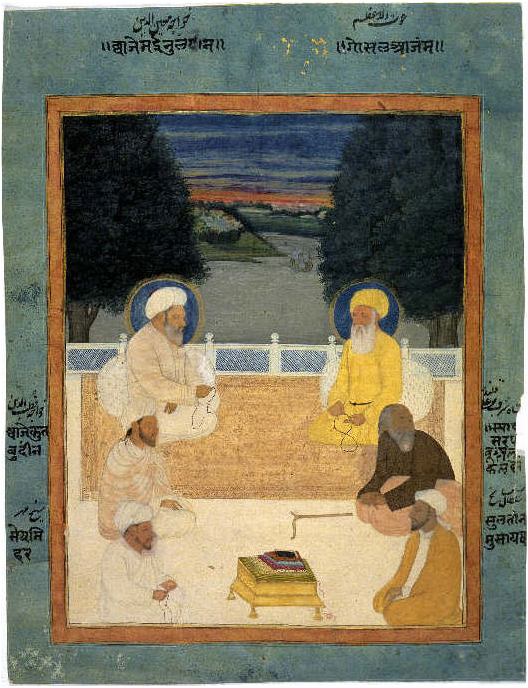
Tuanku Nan Tuo
Tuanku Nan Tuo (1723–1830) or Tuan Ku Nan Tua was one of the leading Minangkabau ulamas. He was known as a '' wasatiyyah'' (moderate) cleric, who took syncretic approaches in the religious outlook, and was a Sufi and aspired for reformation and purification of Islam in the Agam region of West Sumatra at the same time. He also played a crucial role in the birth of Minangkabau Islamic reformers known as '' padri''. Tuo however, disagreed with the more radically puritanical views espoused by padris including Tuanku Nan Renceh and Tuanku Imam Bonjol. Early life Tuanku Nan Tuo was born in Koto Tuo, IV Angkek, Agam, in 1723. During his youth, he was a passionate teenager about studying the Islamic sciences. He studied Islam from Tuanku Mansiangan Nan Tuo in Paninjau, Tanah Datar. He also acquired ''ilmu mantiq'' (logic) and ''ilmu ma'ani'' (kalam) from Tuanku Nan Kaciak in Koto Gadang, studied the discipline of ''sharaf'' and ''nahwu'' (sciences of Arabic comprehension) from Tuanku in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharia
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the Hadith. In Arabic, the term ''sharīʿah'' refers to God's immutable divine law and is contrasted with ''fiqh'', which refers to its human scholarly interpretations. In the historical course, fiqh sects have emerged that reflect the preferences of certain societies and state administrations on behalf of people who are interested in the theoretical (method) and practical application (Ahkam / fatwa) studies of laws and rules, but sharia has never been a valid legal system on its own. It has been used together with " customary (Urf) law" since Omar or the Umayyads. It may also be wrong to think that the Sharia, as a religious argument or belief, is entirely within or related to Allah's commands and prohibitions. Several non-graded crimes are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasawwuf
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ritualism, asceticism and esotericism. It has been variously defined as "Islamic mysticism",Martin Lings, ''What is Sufism?'' (Lahore: Suhail Academy, 2005; first imp. 1983, second imp. 1999), p.15 "the mystical expression of Islamic faith", "the inward dimension of Islam", "the phenomenon of mysticism within Islam", the "main manifestation and the most important and central crystallization" of mystical practice in Islam, and "the interiorization and intensification of Islamic faith and practice". Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and historically typically belonged to "orders" known as (pl. ) – congregations formed around a grand who would be the last in a chain of successive teachers linking back to Muhamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ismail Al-Khalidi Al-Minangkabawi
Ismail al-Khalidi al-Minangkabawi was an Islamic scholar who belonged to the Khalidiyya branch of the Naqshbandi tariqa in the 18th to 19th century. He hailed from today's Tanah Datar Regency, West Sumatra. pp.436-439. pp.53. He is regarded as the pioneer of the tariqa in Minangkabau region, as well as the whole Indonesian archipelago. He was also known as a scholar of Islamic jurisprudence, kalam theology and ''tasawwuf'' (the science of Islamic mysticism). Biography Early life Ismail was born in a religious family and environment. He received the religious education since childhood. After studying the Qur'an in several suraus in his village, he learned the basics of Islamic science through kitab kuning written in Arabic-Malay script. Fields of Islamic science he studied include the jurisprudence, ''tawhid'' (science of monotheism), tafsir, hadith, and the sciences of the Arabic language. Mecca years He went to Mecca to perform the pilgrimage as well as to deepen the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naqshbandi
The Naqshbandi ( fa, نقشبندی)), Neqshebendi ( ku, نهقشهبهندی), and Nakşibendi (in Turkish) is a major Sunni order of Sufism. Its name is derived from Baha-ud-Din Naqshband Bukhari. Naqshbandi masters trace their lineage to the Islamic prophet Muhammad through Abu Bakr, the first Caliph of Sunni Islam and Ali, the fourth Caliph of Sunni Islam. It is because of this dual lineage through Ali and Abu Bakr through the 6th Imam Jafar al Sadiq that the order is also known as the "convergence of the two oceans" or "Sufi Order of Jafar al Sadiq". History The Naqshbandi order owes many insights to Yusuf Hamdani and Abdul Khaliq Gajadwani in the 12th century, the latter of whom is regarded as the organizer of the practices and is responsible for placing stress upon the purely silent ''invocation''. It was later associated with Baha-ud-Din Naqshband Bukhari in the 14th century, hence the name of the order. The name can be interpreted as "engraver (of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufi Orders
A tariqa (or ''tariqah''; ar, طريقة ') is a school or order of Sufism, or specifically a concept for the mystical teaching and spiritual practices of such an order with the aim of seeking ''haqiqa'', which translates as "ultimate truth". A tariqa has a ''murshid'' (guide) who plays the role of leader or spiritual director. The members or followers of a tariqa are known as ''muridin'' (singular ''murid''), meaning "desirous", viz. "desiring the knowledge of God and loving God" (also called a ''fakir''). Tariqa is also believed to be the same as Tzadik of Judaism meaning the "rightly guided one". The metaphor of "way, path" is to be understood in connection of the term ''sharia'' which also has the meaning of "path", more specifically "well-trodden path; path to the waterhole". The "path" metaphor of ''tariqa'' is that of a further path, taken by the mystic, which continues from the "well-trodden path" or exoteric of ''sharia'' towards the esoteric ''haqiqa''. A fourth "sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minangkabau Royal Seal
Minangkabau may refer to: * Minangkabau culture, culture of the Minangkabau people * Minangkabau Culture Documentation and Information Center * Minangkabau Express, an airport rail link service serving Minangkabau International Airport (''see below'') * Minangkabau F.C., a football club based in Padang, West Sumatra * Minangkabau Highlands, West Sumatra * Minangkabau International Airport, West Sumatra ** Minangkabau International Airport railway station, an airport railway station * Minangkabau (legend), a folklore story * Minangkabau people, an ethnic group indigenous to the Minangkabau Highlands of West Sumatra ** Overseas Minangkabau, demographic group of Minangkabau people of Minangkabau Highlands origin in West Sumatra, Indonesia who have settled in other parts of the world * Minangkabau language * Minangkabau War or Padri War The Padri War (also called the Minangkabau War) was fought from 1803 until 1837 in West Sumatra, Indonesia between the Padri and the Adat. The Padri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surau
A surau is an Islamic assembly building in some regions of Sumatra and the Malay Peninsula used for worship and religious instruction. Generally smaller physical structures, its ritual functions are similar to a mosque, allow men and women, and are used more for religious instruction and festive prayers. They depend more on grassroots support and funding. They can be compared to the Arab zawiya. In Minangkabau society, they continued pre-Islamic traditions of a men's house, and are built on high posts. In contemporary usage, "surau" is often used to refer to either a small mosque, or a designated room in a public building (such as a shopping mall, a university, or a rest stop along a highway) for men or women to do salah. Indonesia Surau among the Minankabau of Sumatra date to pre-Islamic times. Men lived together in them. The first Islamic Surau in Minangkabau is believed to have been built in the late 17th century in the coastal town of Ulakan. Smaller surau are known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |