|
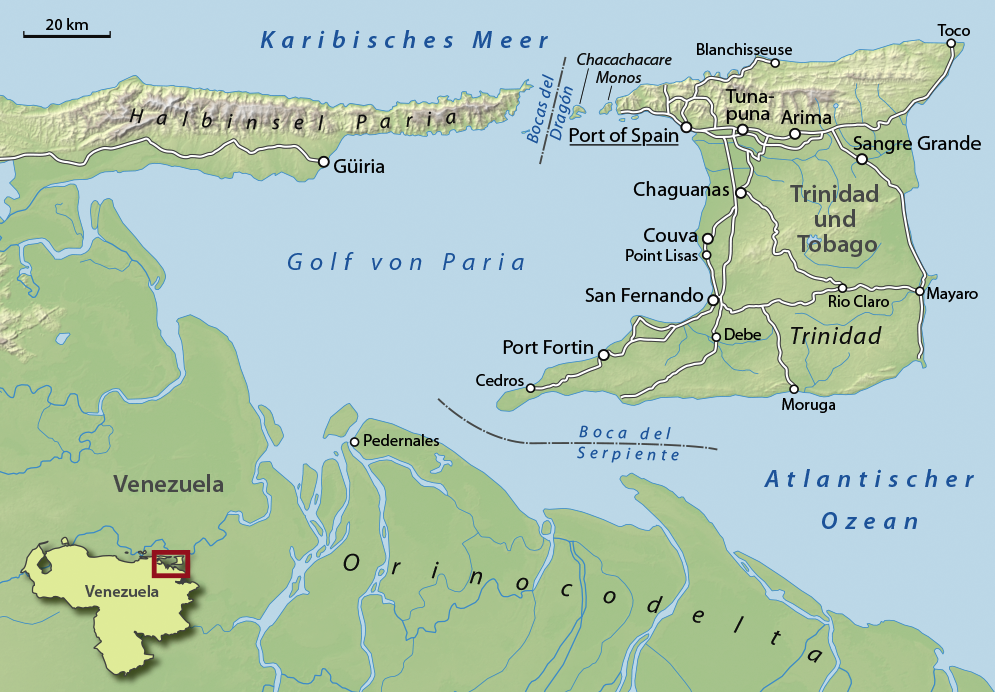
Isla De Patos
Patos Island ( es, Isla de Patos, Duck Island) is a small uninhabited island in the northwestern Gulf of Paria. The island is a part of the ''Dependencias Federales'' (Federal Dependencies) of Venezuela. Geography Patos Island is located about northeast of Caracas in the ''Golfo de Paria'' (Gulf of Paria). The coordinates are . It lies in the ''Boca Grande'' strait of the Bocas del Dragón (Dragon's Mouth), approximately off the Paria Peninsula of mainland Venezuela and about west-south-west of Chacachacare, which is part of Trinidad and Tobago. The uninhabited island has an area of only Excursión a la Isla de Patos (1964) – PDVSA-Intevep, 1997 with a length of and wide with the highest point reaching about . History Patos Island was part of the former British colony of |
Federal Dependencies Of Venezuela
The Federal Dependencies of Venezuela ( es, link=no, Dependencias Federales de Venezuela) encompass most of Venezuela's offshore islands in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Venezuela, excluding those islands that form the State of Nueva Esparta and some Caribbean coastal islands that are integrated with nearby states. These islands, with a total area of 342 square kilometres, are sparsely populated – according to the preliminary results of the 2011 Census only 2,155 people live there permanently, with another hundred from Margarita Island who live there seasonally to engage in fishing. Local government is officially under the authority of Central government in Caracas, although ''de facto'' power is often held by the heads of the sparse and somewhat isolated communities that decorate the territories. History The origins of the population of the Federal Dependencies can be found in the Archipelago of Los Roques dating back to approximately 1200 BC, when it is believed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patos2
Patos is a municipality of the state of Paraíba in the Northeast Region of Brazil. It is classified by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics as a sub-regional center A. It is located in the Espinharas River valley, surrounded by the Borborema Plateau to east and south, and by the pediplain Sertanejo to the west. It originated from the village of Patos, spun off from the Parish of Nossa Senhora do Bom Sucesso de Pombal on October 6, 1788. The city is 306 km from the city of João Pessoa, the center of its immediate and intermediate geographic regions. It stands out as an educational, commercial, banking, religious and health center, both in the back country of Paraíba, and in areas of Pernambuco and Rio Grande do Norte. It is the third most important municipality in the state considering the economic, political and social aspects (behind João Pessoa and Campina Grande). According to IBGE estimates for 2021, it is the fourth most populous municipali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Paria
The Gulf of Paria ( ; es, Golfo de Paria) is a shallow (180 m at its deepest) semi-enclosed inland sea located between the island of Trinidad (Republic of Trinidad and Tobago) and the east coast of Venezuela. It separates the two countries by as little as 15 km at its narrowest and 120 km at its widest points. The tides within the Gulf are semi-diurnal in nature with a range of approximately 1m. The Gulf of Paria is considered to be one of the best natural harbors on the Atlantic coast of the Americas. The jurisdiction of the Gulf of Paria is split between Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela with Trinidad and Tobago having control over approximately (37.7%) and Venezuela the remainder (62.3%). It was originally named the Gulf of the Whale ( es, Golfo de la Ballena) by Christopher Columbus, but the 19th-century whaling industry eliminated whales from the area and populations have never recovered. Cartographic sources of the late 18th century repeatedly refer to it a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caracas
Caracas (, ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas, abbreviated as CCS, is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the northern part of the country, within the Caracas Valley of the Venezuelan coastal mountain range (Cordillera de la Costa). The valley is close to the Caribbean Sea, separated from the coast by a steep 2,200-meter-high (7,200 ft) mountain range, Cerro El Ávila; to the south there are more hills and mountains. The Metropolitan Region of Caracas has an estimated population of almost 5 million inhabitants. The center of the city is still ''Catedral'', located near Bolívar Square, though some consider the center to be Plaza Venezuela, located in the Los Caobos area. Businesses in the city include service companies, banks, and malls. Caracas has a largely service-based economy, apart from some industrial activity in its metropolitan ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channel that lies between two land masses. Some straits are not navigable, for example because they are either too narrow or too shallow, or because of an unnavigable reef or archipelago. Straits are also known to be loci for sediment accumulation. Usually, sand-size deposits occur on both the two opposite strait exits, forming subaqueous fans or deltas. Terminology The terms ''channel'', ''pass'', or ''passage'' can be synonymous and used interchangeably with ''strait'', although each is sometimes differentiated with varying senses. In Scotland, ''firth'' or ''Kyle'' are also sometimes used as synonyms for strait. Many straits are economically important. Straits can be important shipping routes and wars have been fought for control of them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bocas Del Dragón
The Bocas del Dragón (Dragon's Mouths) is the name of the series of straits separating the Gulf of Paria from the Caribbean Sea. There are four Bocas, from west to east: * The Boca Grande or Grand Boca separates Chacachacare from the Paria Peninsula and Patos Island of Venezuela. The international border between Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela runs through this strait. * The Boca de Navios or Third Boca which separates Chacachacare from Huevos. * The Boca de Huevos or Second Boca which separates Huevos from Monos. * The Boca de Monos or First Boca which separates Monos from the Chaguaramas Peninsula of Trinidad Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos .... The passage was named by Christopher Columbus on his third voyage. References Gulf of Paria Bodies of water o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paria Peninsula
The Paria Peninsula () is a large peninsula on the Caribbean Sea, in the state of Sucre in northern Venezuela. Geography Separating the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Paria, the peninsula is part of the mountain range, in the Venezuelan Coastal Range portion of the northern Andes. Its tip is within sight of the naked eye from the island of Trinidad. ;National Park Península de Paria National Park The Península de Paria National Park ( es, link=no, Parque nacional ''Península de Paria''), or Peninsula of Paria National Park, Is a national park on Paria Peninsula in Venezuela. Geography The park is located between the Gulf of Paria and t ... protects a section of the peninsula. Paria Region As a political subdivision, the Paria Region of the Paria Peninsula is the aggregation of six municipalities within Sucre State: *Bermúdez Municipality – (capital: Carúpano), *Arismendi Municipality – (capital: Río Caribe), *Benítez Municipality – (capital: El Pilar), *L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chacachacare
Chacachacare is an island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, located at 10° 41' north latitude and 61° 45' west longitude. The island is in area. It is one of the Bocas Islands, which lie in the ''Bocas del Dragón'' (''Dragons' Mouth'') between Trinidad and Venezuela. Chacachacare is the westernmost of the Bocas Islands which belong to Trinidad and Tobago. Patos Island, which lies further west, was part of Trinidad and Tobago until 1942, when it was ceded to Venezuela in exchange for Soldado Rock. History The island was spotted by Christopher Columbus on his third New World voyage on 12 August 1498, and his little fleet spent the night anchored in Monkey Harbour. He named the island 'Port of Cats' because he heard roars of what he thought were wildcats, mistaking the call of howler monkeys for wildcats. It has also been called "El Caracol" (the Snail) because of its shape. At various times in its history Chacachacare has served as a cotton plantation, a whaling station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad And Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of Grenada and off the coast of northeastern Venezuela. It shares maritime boundaries with Barbados to the northeast, Grenada to the northwest and Venezuela to the south and west. Trinidad and Tobago is generally considered to be part of the West Indies. The island country's capital is Port of Spain, while its largest and most populous city is San Fernando. The island of Trinidad was inhabited for centuries by Indigenous peoples before becoming a colony in the Spanish Empire, following the arrival of Christopher Columbus, in 1498. Spanish governor José María Chacón surrendered the island to a British fleet under the command of Sir Ralph Abercromby in 1797. Trinidad and Tobago were ceded to Britain in 1802 under the Treaty of Amiens as se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soldado Rock
Soldado Rock or ''Soldier's Rock'', formerly known as ''Soldado Island'', is a small island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located in the Gulf of Paria 10 km off Icacos Point in TrinidadIUCN 1982, p.348 and north of the Venezuelan mainland. The island was originally a possession of the Venezuelan government, but became part of the territory of Trinidad and Tobago in 1942. The island is a wildlife sanctuary since being declared in 1934. Characteristics Soldado Rock is made up of limestone fossils from the Paleocene age and includes Eocene rock formations. The highest elevation point is 35 meters (115 ft) and its area is .IUCN 1982, p.349 Reefs surround the island to the east for 1.2 km (0.75 miles), and to the south-south east and south-east.Green 1885, p.84 There are no trees on the island but different types of vegetation including plumbago and portulaca. There are other small rock formations near the island, including ''Pelican Rock'' and ''Black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Dependencies Of Venezuela
The Federal Dependencies of Venezuela ( es, link=no, Dependencias Federales de Venezuela) encompass most of Venezuela's offshore islands in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Venezuela, excluding those islands that form the State of Nueva Esparta and some Caribbean coastal islands that are integrated with nearby states. These islands, with a total area of 342 square kilometres, are sparsely populated – according to the preliminary results of the 2011 Census only 2,155 people live there permanently, with another hundred from Margarita Island who live there seasonally to engage in fishing. Local government is officially under the authority of Central government in Caracas, although ''de facto'' power is often held by the heads of the sparse and somewhat isolated communities that decorate the territories. History The origins of the population of the Federal Dependencies can be found in the Archipelago of Los Roques dating back to approximately 1200 BC, when it is believed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |