|
Isla De Pascua (province)
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, called ''moai'', which were created by the early Rapa Nui people. In 1995, UNESCO named Easter Island a World Heritage Site, with much of the island protected within Rapa Nui National Park. Experts disagree on when the island's Polynesian inhabitants first reached the island. While many in the research community cited evidence that they arrived around the year 800, there is compelling evidence presented in a 2007 study that places their arrival closer to 1200. The inhabitants created a thriving and industrious culture, as evidenced by the island's numerous enormous stone ''moai'' and other artifacts. However, land clearing for cultivation and the introduction of the Polynesian rat led to gradual deforest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Chile
A province is the second largest administrative division in Chile with 56 in total. The largest administrative division in Chile is that of a region with 16 in total. Each provincial presidential delegation (''delegación presidencial provincial'') is headed by a provincial presidential delegate (''delegado presidencial provincial'') appointed by the President. The governor exercises their powers in accordance with instructions from the regional presidential delegate (''delegado presidencial regional''). The provincial delegate is advised by the Provincial Economic and Social Council (''Consejo Económico y Social Provincial'' or CESPRO). No provincial presidential delegations exist in those provinces where the regional capital is located; its functions were merged with those of the regional presidential delegate. The country's provinces are further divided into 346 communes which are administered by an alcalde and municipal council. Until 1976, a province was the main admini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laura Alarcón Rapu
Laura Tarita Alarcón Rapu is a Rapa Nui Chilean politician, current governor of Easter Island since 16 March 2018. She earned a degree in anthropology and until 2018 was member of the Valparaíso Region Council for the province of Easter for two tenures. On 5 March 2018, being a defensor of Rapa Nui traditions, culture, heritage and language, at the age of 41 newly elected president of Chile Sebastián Piñera named her the new governor of the Island, succeeding Melania Hotu Melania Carolina Hotu Hey (born 8 February 1959) is a Rapa Nui Chilean politician. She has served as the provincial governor of Easter Island (known locally as ''Rapa Nui'' or as ''Isla de Pascua'' in Spanish), in Chilean Polynesia, in the first an .... She worked in the "Te Hokinga Mai" project, consisting of the return of local heritage that was abroad. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
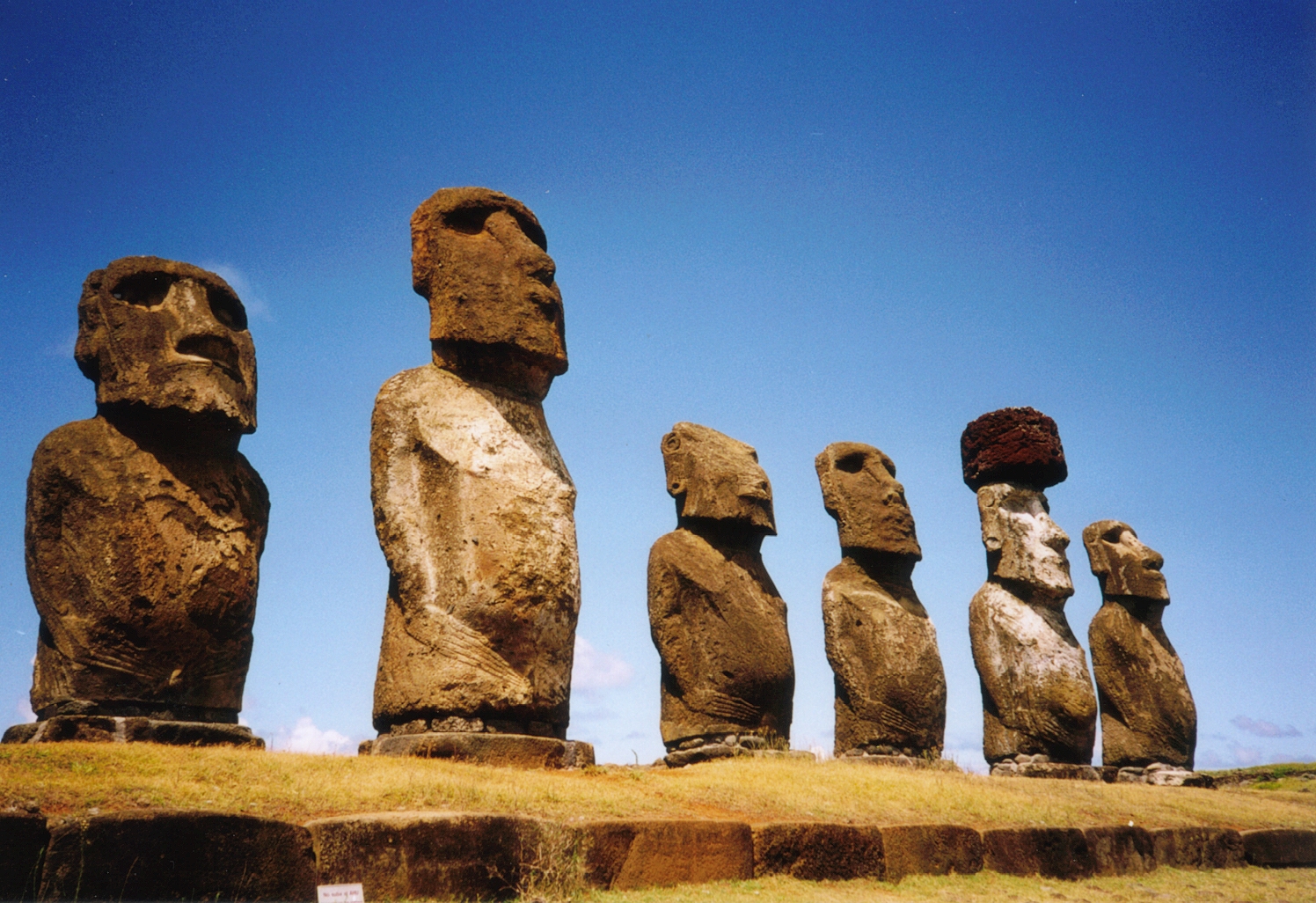
Moai
Moai or moʻai ( ; es, moái; rap, moʻai, , statue) are monolithic human figures carved by the Rapa Nui people on Easter Island, Rapa Nui in eastern Polynesia between the years 1250 and 1500. Nearly half are still at Rano Raraku, the main moai quarry, but hundreds were transported from there and set on stone platforms called Ahu (Easter Island), ahu around the island's perimeter. Almost all moai have overly large heads, which comprise three-eighths the size of the whole statue - which has no legs. The moai are chiefly the living faces (''aringa ora'') of deified ancestors (''aringa ora ata tepuna''). The statues still gazed inland across their clan lands History of Easter Island#European contacts, when Europeans first visited the island in 1722, but all of them had fallen by the latter part of the 19th century. The moai were toppled in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, possibly as a result of European contact or endemic warfare, internecine tribal wars. The production a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapa Nui National Park
Rapa Nui National Park ( es, Parque nacional Rapa Nui) is a national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site located on Easter Island, Chile. Rapa Nui is the Polynesian name of Easter Island; its Spanish name is Isla de Pascua. The island is located in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeastern extremity of the Polynesian Triangle. The island was taken over by Chile in 1888. Its fame and World Heritage status arise from the 887 extant stone statues known by the name "moai", whose creation is attributed to the early Rapa Nui people who inhabited the island starting between 300 and 1200 AD. Much of the island has been declared as Rapa Nui National Park which, on 22 March 1996, UNESCO designated a World Heritage Site under cultural criteria (i), (iii), & (v). Rapa Nui National Park is now under the administrative control of the Ma´u Henua Polynesian Indigenous Community, which is the first autonomous institute on the island. The indigenous Rapa Nui people have regained authori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) is a combat support agency within the United States Department of Defense whose primary mission is collecting, analyzing, and distributing geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) in support of national security. Initially known as the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA) from 1996 to 2003, it is a member of the United States Intelligence Community. NGA headquarters, also known as NGA Campus East or NCE, is located at Fort Belvoir North Area in Springfield, Virginia. The agency also operates major facilities in the St. Louis, Missouri area (referred to as NGA Campus West or NCW), as well as support and liaison offices worldwide. The NGA headquarters, at , is the third-largest government building in the Washington metropolitan area after The Pentagon and the Ronald Reagan Building. In addition to using GEOINT for U.S. military and intelligence efforts, NGA provides assistance during natural and man-made disasters, aids in security ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapa Nui Language
Rapa Nui or Rapanui (, Rapa Nui: , Spanish: ), also known as Pascuan () or ''Pascuense'', is an Eastern Polynesian language of the Austronesian language family. It is spoken on the island of Rapa Nui, also known as ''Easter Island''. The island is home to a population of just under 6,000 and is a special territory of Chile. According to census data, there are 9,399 people (on both the island and the Chilean mainland) who identify as ethnically Rapa Nui. Census data does not exist on the primary known and spoken languages among these people. In 2008, the number of fluent speakers was reported as low as 800. Rapa Nui is a minority language and many of its adult speakers also speak Spanish. Most Rapa Nui children now grow up speaking Spanish and those who do learn Rapa Nui begin learning it later in life. History The Rapa Nui language is isolated within Eastern Polynesian, which also includes the Marquesic and Tahitic languages. Within Eastern Polynesian, it is closest to Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 4217
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individual currencies and their minor units. This data is published in three tables: * Table A.1 – ''Current currency & funds code list'' * Table A.2 – ''Current funds codes'' * Table A.3 – ''List of codes for historic denominations of currencies & funds'' The first edition of ISO 4217 was published in 1978. The tables, history and ongoing discussion are maintained by SIX Group on behalf of ISO and the Swiss Association for Standardization. The ISO 4217 code list is used in banking and business globally. In many countries, the ISO 4217 alpha codes for the more common currencies are so well known publicly that exchange rates published in newspapers or posted in banks use only these to delineate the currencies, instead of translated c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Country Calling Codes
Country calling codes or country dial-in codes are telephone number prefixes for reaching telephone subscribers in the networks of the member countries or regions of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The codes are defined by the ITU-T in standards E.123 and E.164. The prefixes enable international direct dialing (IDD) and are also referred to as ''international subscriber dialing'' (ISD) codes. Country codes are a component of the international telephone numbering plan and are necessary only when dialing a telephone number to establish a call to another country. Country codes are dialed before the national telephone number. By convention, international telephone numbers are represented by prefixing the country code with a plus sign (+), which also indicates to the subscriber that the local international call prefix must first be dialed. For example, the international call prefix in all countries of the North American Numbering Plan is 011, while it is 00 in most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time In Chile
Time in Chile is divided into three time zones. Most of Continental Chile uses the time offset UTC−04:00 in winter time and UTC−03:00 in summer time, while the Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica region uses the time offset UTC-03:00 the whole year. Additionally, Easter Island uses the time offset UTC−06:00 in winter time and UTC−05:00 in summer time. Until 2015, Continental Chile used the time offset UTC−04:00 and Easter Island used UTC−06:00 for standard time, with daylight saving time roughly between October and March every year. In January 2015, the Chilean government announced that the entire country would keep the time offset used during daylight saving time permanently. However, the annual time change was reinstated in 2016 after feedback from the public about an increase in truancy during the winter months, complaints about older computers and other electronic devices not using the right time zone, and fruit growers reporting a 15% loss in productivity. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Statistics Institute (Chile)
The National Statistics Institute of Chile ( es, link=no, Instituto Nacional de Estadística de Chile, INE) is a state-run organization of the Government of Chile, created in the second half of the 19th century and tasked with performing a general census of population and housing, then collecting, producing and publishing official demographic statistics of people in Chile, in addition to other specific tasks entrusted to it by law. Background Its antecedents lie in the initiatives of president Manuel Bulnes and his minister, Manuel Rengifo, to draw up the second population census and obtain statistical data of the country. By Decree No. 18 March 27, 1843, the Office of Statistics was created, Ministry of the Interior to provide knowledge of the departments and provinces. It put the INE in charge of producing the national population census every 10 years, as required by the Census Act of July 12, 1843. Law No. 187 of September 17, 1847 established the office as a permanent body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |