|
Iris-class Cruiser
The ''Iris'' class consisted of two ships, and , built for the Royal Navy in the 1870s. They were the first British all-steel warships. Design and description The ''Iris''-class ships were designed as dispatch vessels by William White under the direction of Nathaniel Barnaby, Director of Naval Construction, and were later redesignated as second-class protected cruisers. The only visible difference between the sister ships was that had a clipper bow and was longer than with her straight stem. ''Iris'' was long overall while ''Mercury'' was long. The sisters had a beam of , and a draught of . They displaced at normal load and were the first British warships with an all-steel hull.Gardiner, p. 90 Their crew consisted of 275 officers and ratings.Lyon & Winfield, p. 270 The ships were not armoured but extensive internal subdivision gave them some protection against flooding, as did the double bottom under the propulsion machinery compartments. The ''Iris'' class was pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pembroke Dockyard
Pembroke Dockyard, originally called Pater Yard, is a former Royal Navy Dockyard in Pembroke Dock, Pembrokeshire, Wales. History It was founded in 1814, although not formally authorized until the Prince Regent signed the necessary Order in Council on 31 October 1815, and was known as ''Pater Yard'' until 1817. The Mayor of Pembroke had requested the change "in deference to the town of Pembroke some distant". The site selected for the dockyard was greenfield land and the closest accommodations were in Pembroke. Office space was provided by the old frigate after she was beached. The Royal Marine garrison was housed in the hulked 74-gun ship, , after she was run aground in 1832. Many of the workmen commuted by boat from nearby communities until Pembroke Dock town was built up. In 1860 the dockyard's policing was transferred to the new No. 4 Division of the Metropolitan Police, which remained in that role until the 1920s. After the end of the First World War, the dockyard was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (ship)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Deck
The main deck of a ship is the uppermost complete deck extending from bow to stern. A steel ship's hull may be considered a structural beam with the main deck forming the upper flange of a box girder and the keel forming the lower strength member. The main deck may act as a tension member when the ship is supported by a single wave amidships, or as a compression member Compression members are structural elements that are pushed together or carry a load; more technically, they are subjected only to axial compressive forces. That is, the loads are applied on the longitudinal axis through the centroid of the mem ... when the ship is supported between waves forward and aft. References {{reflist Nautical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
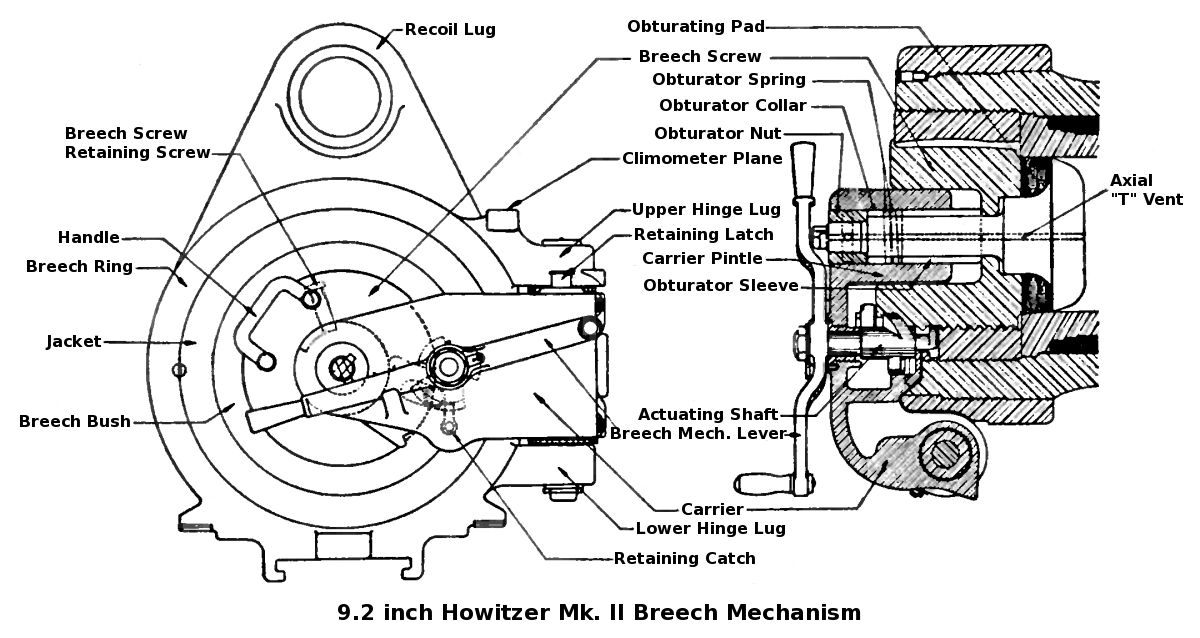
British Ordnance Terms
This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' ordnance (i.e.: weapons) and also ammunition. The terms may have slightly different meanings in the military of other countries. BD Between decks: applies to a naval gun mounting in which part of the rotating mass is below the deck, and part of it is above the deck. This allows for a lower profile of turret, meaning that turrets need not be superfiring (i.e. they can be mounted on the same deck and not obstruct each other at high angles of elevation.) BL The term BL, in its general sense, stood for breech loading, and contrasted with muzzle loading. The shell was loaded via the breech (i.e. the gunner's end of the barrel, which opened) followed by the propellant charge, and the breech mechanism was closed to seal the chamber. Breech loading, in its formal British ordnance sense, served to identify the gun as the type of Rifled breech-loader, rifled breechloading gun for which the powder charge was loaded in a silk or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzzle-loading Rifle
A muzzle-loading rifle is a muzzle-loaded small arm or artillery piece that has a rifled barrel rather than a smoothbore. The term " rifled muzzle loader" typically is used to describe a type of artillery piece, although it is technically accurate for small arms as well. A shoulder arm is typically just called a "rifle", as almost all small arms were rifled by the time breechloading became prevalent. Muzzle and breechloading artillery served together for several decades, making a clear distinction more important. In the case of artillery, the abbreviation " RML" is often prefixed to the guns designation; a Rifled breech loader would be "RBL", or often just "BL", since smoothbore breechloading artillery is almost nonexistent (except in tank guns). A muzzle loading weapon is loaded through the muzzle, or front of the barrel (or "tube" in artillery terms). This is the opposite of a breech-loading weapon or rifled breechloader (RBL), which is loaded from the breech-end of the barrel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barque
A barque, barc, or bark is a type of sailing vessel with three or more masts having the fore- and mainmasts rigged square and only the mizzen (the aftmost mast) rigged fore and aft. Sometimes, the mizzen is only partly fore-and-aft rigged, bearing a square-rigged sail above. Etymology The word "barque" entered English via the French term, which in turn came from the Latin ''barca'' by way of Occitan, Catalan, Spanish, or Italian. The Latin ''barca'' may stem from Celtic ''barc'' (per Thurneysen) or Greek ''baris'' (per Diez), a term for an Egyptian boat. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'', however, considers the latter improbable. The word ''barc'' appears to have come from Celtic languages. The form adopted by English, perhaps from Irish, was "bark", while that adopted by Latin as ''barca'' very early, which gave rise to the French ''barge'' and ''barque''. In Latin, Spanish, and Italian, the term ''barca'' refers to a small boat, not a full-sized ship. French influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Trials
A sea trial is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a "shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and it can last from a few hours to many days. Sea trials are conducted to measure a vessel's performance and general seaworthiness. Testing of a vessel's speed, maneuverability, equipment and safety features are usually conducted. Usually in attendance are technical representatives from the builder (and from builders of major systems), governing and certification officials, and representatives of the owners. Successful sea trials subsequently lead to a vessel's certification for commissioning and acceptance by its owner. Although sea trials are commonly thought to be conducted only on new-built vessels (referred by shipbuilders as 'builders trials'), they are regularly conducted on commissioned vessels as well. In new vessels, they are used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotch Marine Boiler
A "Scotch" marine boiler (or simply Scotch boiler) is a design of steam boiler best known for its use on ships. The general layout is that of a squat horizontal cylinder. One or more large cylindrical furnaces are in the lower part of the boiler shell. Above this are many small-diameter fire-tubes. Gases and smoke from the furnace pass to the back of the boiler, then return through the small tubes and up and out of the chimney. The ends of these multiple tubes are capped by a smokebox, outside the boiler shell. The Scotch boiler is a fire-tube boiler, in that hot flue gases pass through tubes set within a tank of water. As such, it is a descendant of the earlier Lancashire boiler, and like the Lancashire it uses multiple separate furnaces to give greater heating area for a given furnace capacity. It differs from the Lancashire in two respects: many small-diameter tubes (typically diameter each) are used to increase the ratio of heating area to cross-section. Secondly, the over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller Shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term ''driveshaft'' first appeared during the mid-19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke (engine)
In the context of an internal combustion engine, the term stroke has the following related meanings: * A phase of the engine's cycle (e.g. compression stroke, exhaust stroke), during which the piston travels from top to bottom or vice versa. * The type of power cycle used by a piston engine (e.g. two-stroke engine, four-stroke engine). * "Stroke length", the distance travelled by the piston during each cycle. The stroke length––along with bore diameter––determines the engine's displacement. Phases in the power cycle Commonly used engine phases or strokes (i.e. those used in a four-stroke engine) are described below. Other types of engines can have very different phases. Induction-intake stroke The induction stroke is the first phase in a four-stroke (e.g. Otto cycle or Diesel cycle) engine. It involves the downward movement of the piston, creating a partial vacuum that draws a air-fuel mixture (or air alone, in the case of a direct injection engine) into the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bore (engine)
In a piston engine, the bore (or cylinder bore) is the diameter of each cylinder. Engine displacement is calculated based on bore, stroke length and the number of cylinders: displacement = The stroke ratio, determined by dividing the bore by the stroke, traditionally indicated whether an engine was designed for power at high engine speeds ( rpm) or torque at lower engine speeds. The term "bore" can also be applied to the bore of a locomotive cylinder or steam engine pistons. Steam locomotive The term bore also applies to the cylinder of a steam locomotive or steam engine. See also * Bore pitch * Compression ratio * Engine displacement Engine displacement is the measure of the cylinder volume swept by all of the pistons of a piston engine, excluding the combustion chambers. It is commonly used as an expression of an engine's size, and by extension as a loose indicator of the ... References {{Steam engine configurations Engine technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maudslay, Sons And Field
Maudslay, Sons and Field was an engineering company based in Lambeth, London. History The company was founded by Henry Maudslay as Henry Maudslay and Company in 1798 and was later reorganised into Maudslay, Sons and Field in 1833 after his sons Thomas and Joseph, as well as Joshua Field joined the company. It specialised in building marine steam engines. The company produced a special steam-powered mill for the 1852 re-cutting of the Koh-i-Noor. See also * Great Wheel The Great Wheel, also known as the Gigantic Wheel, or Graydon Wheel, was built for the Empire of India Exhibition at Earls Court, London, in the United Kingdom. Construction began in March 1894 at the works of Maudslay, Sons and Field in Greenw ... References External links Chronology of the company Defunct shipbuilding companies of England Defunct companies based in London Engineering companies of England 1798 establishments in England Manufacturing companies established in 1798 Manufacturing com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_underway%2C_circa_in_1971.png)


.jpg)

