|
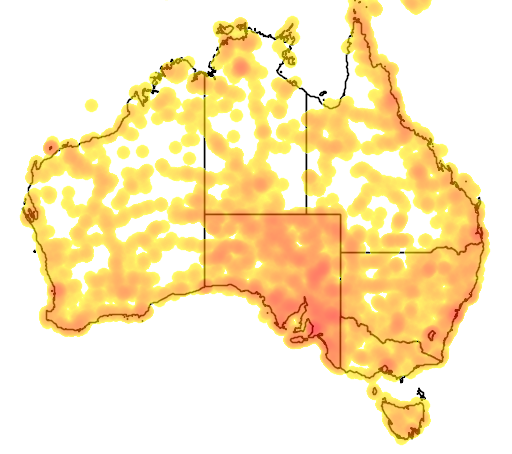
Iridomyrmex Rufoniger
''Iridomyrmex rufoniger'' is a species of ant in the genus ''Iridomyrmex''. It was described by Lowne in 1865. The species is endemic to Australia and introduced to several other countries. Taxonomy The species was first described by Lowne in 1865, and the species has three synonyms. This includes ''Iridomyrmex rufoniger domesticus'' (Forel, 1907), ''Acantholepis mamillatus'' (Lowne, 1865), and ''Iridomyrmex rufoniger septentrionalis'' (Forel, 1902). The species is classified in the genus ''Iridiomyrmex'', which is in the subfamily Dolichoderinae. Identification The species is a part of the ''Iridomyrmex purpureus'' group, and is among the most familiar ant the Australian public is affiliated with. A typical worker is a medium-sized ant in comparison to its relatives within its genus, and will have a broad head, with a blue or yellowish-green iridescence on the workers gaster. These ants in Sydney are different in variation and can be distinguished by their dark coloured appearan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridomyrmex
''Iridomyrmex'' is a genus of ants called rainbow ants (referring to their blue-green iridescent sheen) first described by Austrian entomologist Gustav Mayr in 1862. He placed the genus in the subfamily Dolichoderinae of the family Formicidae. It has 79 described species and five fossil species. Most of these ants are native to Australia; others are found in Asia and Oceania, and they have been introduced to Brazil, New Zealand, and the United Arab Emirates. Fossil species are known from China, France, and the United States. These ants are known to be an ecologically dominant and important group of ants, but they are sometimes regarded as pests because they disturb soil and enter human houses. Farmers in rural Australia place animal carcasses on meat ant ('' I. purpureus'') mounds as a method of disposing of them; meat ants consume the carcass and reduce it to bones in a matter of weeks. Meat ants also engage in ritualised fighting, which helps prevent casualties and solve te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualists, which in turn provide herbivore protection. Common nectar-consuming pollinators include mosquitoes, hoverflies, wasps, bees, butterflies and moths, hummingbirds, honeyeaters and bats. Nectar plays a crucial role in the foraging economics and evolution of nectar-eating species; for example, nectar foraging behavior is largely responsible for the divergent evolution of the African honey bee, ''A. m. scutellata'' and the western honey bee. Nectar is an economically important substance as it is the sugar source for honey. It is also useful in agriculture and horticulture because the adult stages of some predatory insects feed on nectar. For example, a number of parasitoid wasps (e.g. the social wasp species ''Apoica flavissima'') rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenoptera Of Australia
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic. Females typically have a special ovipositor for inserting eggs into hosts or places that are otherwise inaccessible. This ovipositor is often modified into a stinger. The young develop through holometabolism (complete metamorphosis)—that is, they have a wormlike larval stage and an inactive pupal stage before they mature. Etymology The name Hymenoptera refers to the wings of the insects, but the original derivation is ambiguous. All references agree that the derivation involves the Ancient Greek πτερόν (''pteron'') for wing. The Ancient Greek ὑμήν (''hymen'') for membrane provides a plausible etymology for the term because species in this order have membranous wings. However, a key characteristic of this order is that the hindwings are con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canberra
Canberra ( ) is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The city is located at the northern end of the Australian Capital Territory at the northern tip of the Australian Alps, the country's highest mountain range. As of June 2021, Canberra's estimated population was 453,558. The area chosen for the capital had been inhabited by Indigenous Australians for up to 21,000 years, with the principal group being the Ngunnawal people. European settlement commenced in the first half of the 19th century, as evidenced by surviving landmarks such as St John's Anglican Church and Blundells Cottage. On 1 January 1901, federation of the colonies of Australia was achieved. Following a long dispute over whether Sydney or Melbourne should be the national capital, a compromise was reached: the new capital would be buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptospermum
''Leptospermum'' is a genus of shrubs and small trees in the myrtle family Myrtaceae commonly known as tea trees, although this name is sometimes also used for some species of ''Melaleuca''. Most species are endemic to Australia, with the greatest diversity in the south of the continent, but some are native to other parts of the world, including New Zealand and Southeast Asia. Leptospermums all have five conspicuous petals and five groups of stamens which alternate with the petals. There is a single style in the centre of the flower and the fruit is a woody capsule. The first formal description of a leptospermum was published in 1776 by the German botanists Johann Reinhold Forster and his son Johann Georg Adam Forster, but an unambiguous definition of individual species in the genus was not achieved until 1979. Leptospermums grow in a wide range of habitats but are most commonly found in moist, low-nutrient soils. They have important uses in horticulture, in the production of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jalmenus Icilius
''Jalmenus icilius'', the Icilius blue or amethyst hairstreak, is a butterfly of the family Lycaenidae. It is found in all mainland states of Australia, throughout much of the subtropical areas of the inland, from the Selwyn Range and from Carnarvon to Kalgoorlie. It is generally common except in the south-eastern end of its range in central and western Victoria, where it is now very scarce. The wingspan is about 30 mm. The larvae feed on a wide range of plants, including '' Cassia artemisioides'', '' Cassia nemophila'', ''Daviesia benthamii'', and the ''Acacia'' species: '' A. acuminata'', '' A. anceps'', '' A. aneura'', '' A. dealbata'', '' A. deanei'', '' A. harpophylla'', '' A. mearnsii'', '' A. parramattensis'', '' A. pendula'', '' A. pycnantha'', '' A. rubida'', '' A. saligna'' and '' A. victoriae''. The caterpillars are attended by the ant species ''Iridomyrmex rufoniger ''Iridomyrmex rufoniger'' is a species of ant in the genus ''Iridomyrmex''. It was described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jalmenus Evagoras
''Jalmenus evagoras,'' the imperial hairstreak, imperial blue, or common imperial blue, is a small, metallic blue butterfly of the family Lycaenidae. It is commonly found in eastern coastal regions of Australia. This species is notable for its unique Mutualism (biology), mutualism with ants of the genus ''Iridomyrmex.'' The ants provide protection for juveniles and cues for adult mating behavior. They are compensated with food secreted from ''J. evagoras'' larvae. The ants greatly enhance the survival and reproductive success of the butterflies. ''J. evagoras'' lives and feeds on ''Acacia'' plants, so butterfly populations are localized to areas with preferred species of both host plants and ants. Description The wings of ''Jalmenus evagoras'' are metallic blue outlined with black. The hindwings have tails and orange spots towards the bottom. On the ventral side, wings are buff-colored with black streaks and orange hindwing spots similar to the dorsal side. The butterfly has a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jalmenus Daemeli
''Jalmenus daemeli'', the Daemel's blue, Dämel's blue or emerald hairstreak, is a butterfly of the family Lycaenidae, and was first described in 1879 by Georg SemperSemper, G. 1879. Beitrag zur Rhopalocerenfauna von Australien. Journal des Museum Godeffroy, Hamburg V(14): 138-194 pls 8, 9 ated 1878 66 It is endemic to the Australian states of New South Wales and Queensland, where it is found in coastal areas. The wingspan is about 2 cm. The larvae feed on a wide range of plants, including ''Acacia'' species, ''Eucalyptus melanophloia'' and '' Heterodendrum diversifolium.'' The caterpillars are attended by the ant species ''Iridomyrmex rufoniger ''Iridomyrmex rufoniger'' is a species of ant in the genus ''Iridomyrmex''. It was described by Lowne in 1865. The species is endemic to Australia and introduced to several other countries. Taxonomy The species was first described by Lowne in 18 ...''. References External links''Jalmenus daemeli'' at the Butterfly House Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphis Hederae
''Aphis'' is a genus of insects in the family Aphididae containing at least 600 species of aphids. It includes many notorious agricultural pests, such as the soybean aphid '' Aphis glycines''. Many species of ''Aphis'', such as '' A. coreopsidis'' and '' A. fabae'', are myrmecophiles, forming close associations with ants. Selected Species *''Aphis affinis'' *'' Aphis asclepiadis'' — milkweed aphid *'' Aphis craccae'' — tufted vetch aphid *''Aphis craccivora'' — cowpea aphid *''Aphis fabae'' — black bean aphid *'' Aphis genistae'' *''Aphis gossypii'' — cotton aphid *'' Aphis glycines'' — soybean aphid *'' Aphis helianthi'' — sunflower aphid *''Aphis nerii'' — oleander aphid *'' Aphis pomi'' — apple aphid *''Aphis rubicola'' — small raspberry aphid *''Aphis spiraecola'' — spirea aphid (syn. ''Aphis citricola'' — citrus aphid) *''Aphis valerianae'' — black valerian aphid See also * List of Aphis species Photos Image:Aphis citricola1.jpg, ''Aphis cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving live birth to female nymphs—who may also be already pregnant, an adaptation scientists call telescoping generations—without the involvement of males. Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonize new plants. In temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn, with the insects often overwintering as eggs. The life cycle of some species involves an alternation between two species of host plants, for example between an annual crop and a woody plant. Some species feed on only one type of plant, while others are generalists, coloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |