|
Ireland–Claisen Rearrangement
The Ireland–Claisen rearrangement is a chemical reaction of an allylic ester with strong base to give an γ,δ-unsaturated carboxylic acid. Several reviews have been published. Mechanism The Ireland–Claisen rearrangement is a type of Claisen rearrangement. The mechanism is therefore a concerted ,3sigmatropic rearrangement which according to the Woodward–Hoffmann rules show a concerted, suprafacial, pericyclic reaction pathway. See also *Cope rearrangement *Overman rearrangement The Overman rearrangement is a chemical reaction that can be described as a Claisen rearrangement of allylic alcohols to give allylic trichloroacetamides through an imidate intermediate. The Overman rearrangement was discovered in 1974 by Larry Ove ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Ireland-Claisen rearrangement Rearrangement reactions Name reactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
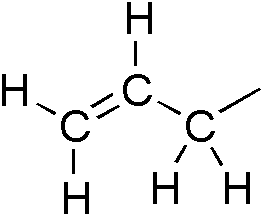
Allylic
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters typically have a pleasant smell; those of low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and are found in essential oils and pheromones. They perform as high-grade solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, and are one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. Polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties. '' Nomenclature Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Letters
''Organic Letters'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in organic chemistry. It was established in 1999 and is published by the American Chemical Society. In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. The founding editor-in-chief was Amos Smith. Since 2019, Erick M. Carreira serves as the editor-in-chief. The journal is abstracted and indexed in: the Science Citation Index Expanded, Scopus, Academic Search Premier, BIOSIS Previews, Chemical Abstracts Service, EMBASE, and MEDLINE MEDLINE (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online, or MEDLARS Online) is a bibliographic database of life sciences and biomedical information. It includes bibliographic information for articles from academic journals covering medic .... References External links * American Chemical Society academic journals Biweekly journals Organic chemistry journals Publications established in 1999 English-language journals {{chem-journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldrichimica Acta
''Aldrichimica Acta'' is a scientific journal published by Sigma-Aldrich. Established in 1968 in Milwaukee, Wi, ''Aldrichimica Acta'' publishes reviews in the field of synthetic organic chemistry, with each issue focusing on a special topic. The journal is open access. In 2015, the Acta was ranked #1 among journals in the field of organic chemistry by impact factor. History In 1968, Aldrich Chemical Company published Volume 1, Number 1 edition of ''Aldrichimica Acta''. The Acta both replaced ''Klarindex Sheets'' as a scientific journal meant specifically to keep chemists informed, as well as complemented the company's world-famous annual catalog, the Aldrich Handbook of Fine Chemicals. Aldrich founder Alfred Bader and created the journal with an emphasis on both the reliability of Aldrich, but also on art. Despite seeing mergers with Sigma Chemical Company of St. Louis in 1975 and Merck KGaA The Merck Group, branded and commonly known as Merck, is a German multinational sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron (journal)
''Tetrahedron'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of organic chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Tetrahedron'' has a 2020 impact factor of 2.457. ''Tetrahedron'' and Elsevier, its publisher, support an annual symposium. In 2010, complaints were raised over its high subscription cost. Notable papers , the Web of Science lists ten papers from ''Tetrahedron'' that have more than 1000 citations. The four articles that have been cited more than 2000 times are: * – cited 2228 times * – cited 2162 times * – cited 2124 times * – cited 2107 times See also * ''Tetrahedron Letters'' * ''Tetrahedron Computer Methodology'' * ''Polyhedron In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on th ...'' (journal) Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claisen Rearrangement
The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon–carbon bond-forming chemical reaction discovered by Rainer Ludwig Claisen. The heating of an allyl vinyl ether will initiate a ,3sigmatropic rearrangement to give a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl, driven by exergonically favored carbonyl CO bond formation (ΔΔHf = -327kcalmol−1). Mechanism The Claisen rearrangement is an exothermic, concerted (bond cleavage and recombination) pericyclic reaction. Woodward–Hoffmann rules show a suprafacial, stereospecific reaction pathway. The kinetics are of the first order and the whole transformation proceeds through a highly ordered cyclic transition state and is intramolecular. Crossover experiments eliminate the possibility of the rearrangement occurring via an intermolecular reaction mechanism and are consistent with an intramolecular process. There are substantial solvent effects observed in the Claisen rearrangement, where polar solvents tend to accelerate the reaction to a greater e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmatropic Rearrangement
A sigmatropic reaction in organic chemistry is a pericyclic reaction wherein the net result is one σ-bond is changed to another σ-bond in an uncatalyzed intramolecular reaction. The name ''sigmatropic'' is the result of a compounding of the long-established sigma designation from single carbon–carbon bonds and the Greek word ''tropos'', meaning turn. In this type of rearrangement reaction, a substituent moves from one part of a π-bonded system to another part in an intramolecular reaction with simultaneous rearrangement of the π system. True sigmatropic reactions are usually uncatalyzed, although Lewis acid catalysis is possible. Sigmatropic reactions often have transition-metal catalysts that form intermediates in analogous reactions. The most well-known of the sigmatropic rearrangements are the ,3Cope rearrangement, Claisen rearrangement, Carroll rearrangement, and the Fischer indole synthesis. Overview of sigmatropic shifts Woodward–Hoffman sigmatropic shift nomencla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodward–Hoffmann Rules
The Woodward–Hoffmann rules (or the pericyclic selection rules), devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules used to rationalize or predict certain aspects of the stereochemistry and activation energy of pericyclic reactions, an important class of reactions in organic chemistry. The rules are best understood in terms of the concept of ''the conservation of orbital symmetry'' using ''orbital correlation diagrams'' (see Section 3 below). The Woodward–Hoffmann rules are a consequence of the changes in electronic structure that occur during a pericyclic reaction and are predicated on the phasing of the interacting molecular orbitals. They are applicable to all classes of pericyclic reactions (and their microscopic reverse 'retro' processes), including (1) electrocyclic reaction, electrocyclizations, (2) cycloadditions, (3) sigmatropic reactions, (4) group transfer reactions, (5) ene reactions, (6) cheletropic reactions, and (7) dyotropic reactions. Due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprafacial
Antarafacial ( Woodward-Hoffmann symbol a) and suprafacial (s) are two topological concepts in organic chemistry describing the relationship between two simultaneous chemical bond making and/or bond breaking processes in or around a reaction center. The reaction center can be a p- or sp''n-''orbital (Woodward-Hoffmann symbol ω), a conjugated system (π) or even a sigma bond (σ). * The relationship is ''antarafacial'' when opposite faces of the π system or isolated orbital are involved in the process (think ''anti''). For a σ bond, it corresponds to involvement of one "interior" lobe and one "exterior" lobe of the bond. * The relationship is ''suprafacial'' when the same face of the π system or isolated orbital are involved in the process (think ''syn''). For a σ bond, it corresponds to involvement of two "interior" lobes or two "exterior" lobes of the bond. The components of all pericyclic reactions, including sigmatropic reactions and cycloadditions, and electrocyclizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |