|
Iran Space Agency
The Iranian Space Agency (ISA, Persian: ''Sāzmān-e Fazāi-ye Irān'') is Iran's governmental space agency. Iran became an orbital-launch-capable nation in 2009. Iran is one of the 24 founding members of the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS), which was set up on 13 December 1958. History ISA was established on 28 February 2004, according to the Article 9 of the Law for Tasks and Authorizations of the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology passed on 10 December 2003 by the Parliament of Iran. Based on the approved statute ISA mandated to cover and support all the activities in Iran concerning the peaceful applications of space science and technology under the leadership of a Supreme Council of Space chaired by the President of Iran. The council's main goals included policy making for the application of space technologies aiming peaceful uses of outer space, manufacturing, launching and use of the national research satellit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imam Khomeini Spaceport
Imam Khomeini Space Launch Terminal(Persian:) is an Iranian space vehicle launch facility, consisting of the service tower and launch pad used to launch the Simorgh launch vehicle. it is a part of the Semnan Space Center located south-east of the provincial capital of Semnan in Semnan Province. Launch history See also *Iranian Space Agency *Semnan Space Center *Simorgh (rocket) References External links ;VideosIman Khomeini Space Launch CenterNuclear Threat Initiative The Nuclear Threat Initiative, generally referred to as NTI, is a non-profit organization located in Washington, D.C. The American foreign policy think tank was founded in 2001 by former U.S. Senator Sam Nunn and describes itself as a "nonprofit ... (2017) {{Spaceport Rocket launch sites Space program of Iran 2017 establishments in Iran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Calendars
The Iranian calendars or Iranian chronology ( fa, گاهشماری ایرانی, ) are a succession of calendars invented or used for over two millennia in Iran, also known as Persia. One of the longest chronological records in human history, the Iranian calendar has been modified time and again during its history to suit administrative, climatic, and religious purposes. The most influential person in laying the frameworks for the calendar and its precision was the 11th century Persian polymath, hakim Omar Khayyam. The modern Iranian calendar is currently the official civil calendar in Iran and Afghanistan. The Iranian new year begins at the midnight nearest to the instant of the northern spring equinox, as determined by astronomic calculations for the meridian (52.5°E). It is, therefore, an observation-based calendar, unlike the Gregorian, which is rule-based. This equinox occurs on or about 20 March of the Gregorian calendar. The time zone of Iran is Iran Standard Time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soroush
Soroush ( fa, سروش), is an Iranian name and may refer to: ;First name * Soroush Ahmadi, Iranian taekwondo competitor * Soroush Eskandari, Iranian badminton player * Soroush Omoumi, Iranian musician * Soroush Rafiei, Iranian footballer * Soroush Saeidi, Iranian footballer * Soroush Sehhat, Iranian director, screenwriter and actor ;Last name * Abdolkarim Soroush, Iranian philosopher and writer * Abolfazl Soroush, Iranian physician and reformist politician * Bahram Soroush, Iranian activist * Tajuden Soroush, Afghan journalist ;Others * Soroush, publishing center of the Islamic Republic of Iran Broadcasting (IRIB) * Soroush (messenger), Iranian instant messaging application * Soroush Cinema Soroush Cinema ( fa, سینما سروش; formerly known as: Moulin Rouge Cinema ( fa, سینما مولن روژ) is one of the old cinema of Tehran which opened on October 15, 1956. The first movie showed in this cinema was Trapeze. Moulin Ro ... (formerly known as "Moulin Rouge Cinem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zuljanah
{{unreferenced, date=October 2015 Zuljanah ( ar, ذو الجناح) was a grey Arabian Stallion that belonged to Husayn ibn Ali. He was bred and raised by Muhammad. Zuljanah was known to be very loyal and was famous for his strength, endurance and devotion. It is said that he shielded Husayn ibn Ali with his body and was injured taking an arrow meant for his master during the Battle of Karbala. When Husayn ibn Ali Abū ʿAbd Allāh al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, أبو عبد الله الحسين بن علي بن أبي طالب; 10 January 626 – 10 October 680) was a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a son of Ali ibn Abi ... succumbed to his injuries, Zuljanah returned bloodied to his family, alerting them to the ambush and died after discharging his final duty. During the Moharram procession, a decorated riderless horse representing the historic sacrifice is honoured by the devotees. External linksDhuljanah - A brief introduction Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times Of Israel
''The Times of Israel'' is an Israeli multi-language online newspaper that was launched in 2012. It was co-founded by Israeli journalist David Horovitz, who is also the founding editor, and American billionaire investor Seth Klarman.Forbes: The World's Billionaires: Seth Klarman April 2014 Based in , it "documents developments in Israel, the Middle East and around the ." Along with its original English site, ''The Times of Israel'' publishes in |
Attitude Control
Attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of an aerospace vehicle with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc. Controlling vehicle attitude requires sensors to measure vehicle orientation, actuators to apply the torques needed to orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, and algorithms to command the actuators based on (1) sensor measurements of the current attitude and (2) specification of a desired attitude. The integrated field that studies the combination of sensors, actuators and algorithms is called guidance, navigation and control (GNC). Aircraft attitude control An aircraft's attitude is stabilized in three directions: ''Yaw (rotation), yaw'', nose left or right about an axis running up and down; ''pitch'', nose up or down about an axis running from wing to wing; and ''roll'', rotation about an axis running from nose to tail. Elevator (aeronautics), Elevat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simorgh (rocket)
Simorgh ( fa, ماهوارهبر سیمرغ, ''Phoenix''), also called Safir-2, is an Iranian expendable launch vehicle under development. It is the successor of the Safir, Iran's first space launch vehicle. Its mission is to carry heavier satellites into higher orbit than Safir. The project was unveiled by Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad on 3 February 2010, as part of celebrations of the first anniversary of the launch of Omid, the first indigenously launched Iranian satellite, and was launched for the first time on 19 April 2016. Design Simorgh is a two-stage liquid-fueled rocket developed from the Safir rocket. It is be able to place a payload into a circular low Earth orbit (LEO). It is also the first Iranian rocket that can place multiple payloads into orbit (e.g., one main payload and several secondary cubesats). In comparison, the Safir was only able to place a 50 kg payload into a 250x375 km elliptic orbit. The Simorgh rocket is long, and has a launch mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
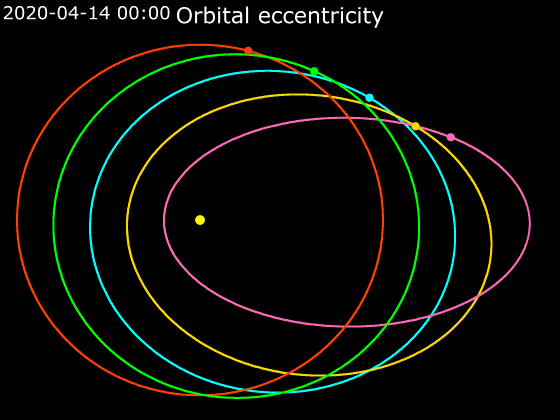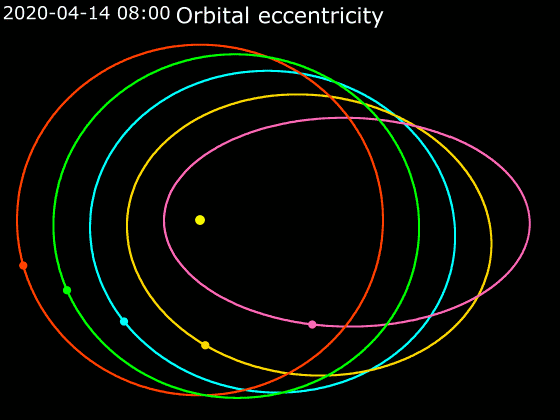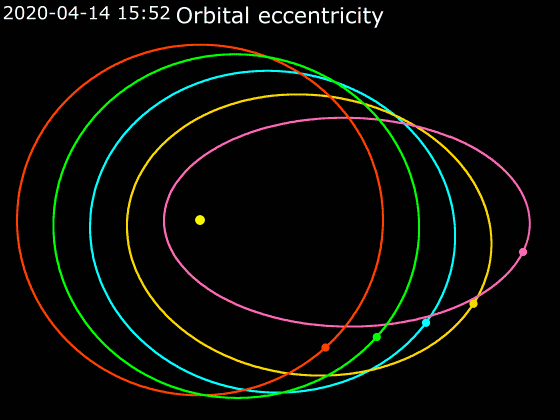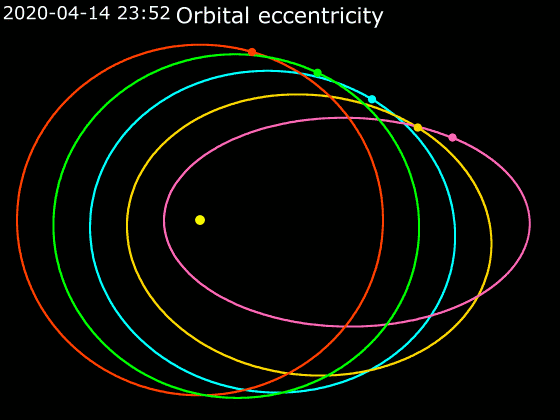
Elliptic Orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptic orbit or elliptical orbit is a Kepler orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. In a stricter sense, it is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity greater than 0 and less than 1 (thus excluding the circular orbit). In a wider sense, it is a Kepler's orbit with negative energy. This includes the radial elliptic orbit, with eccentricity equal to 1. In a gravitational two-body problem with negative energy, both bodies follow similar elliptic orbits with the same orbital period around their common barycenter. Also the relative position of one body with respect to the other follows an elliptic orbit. Examples of elliptic orbits include: Hohmann transfer orbit, Molniya orbit, and tundra orbit. Velocity Under standard assumptions, no other forces acting except two spherically symmetrical bodies m1 and m2, the orbital speed (v\,) of one body trave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Office For Outer Space Affairs
The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) is an office of the U.N. Secretariat that promotes and facilitates peaceful international cooperation in outer space. It works to establish or strengthen the legal and regulatory frameworks for space activities, and assists developing countries in using space science and technology for sustainable socioeconomic development. The Office was established in 1958 to assist and advise the ''ad hoc'' Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS), which was established by the UN General Assembly to discuss the scientific and legal aspects of exploring and using outer space to benefit humankind. The Committee became permanent the following year, with UNOOSA undergoing several structural changes before its relocation in 1993 to the United Nations Office in Vienna, Austria. As the secretariat of COPUOS, the Office is responsible for helping implement the major international treaties, legal principles, and General Assembl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahab-3C
The Shahab-3 ( fa, شهاب ۳, Šahâb 3; meaning "meteor-3") is a liquid-propelled medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) developed by Iran and based on the North Korean Nodong-1. The Shahab-3 has a range of ; a MRBM variant can now reach (can hit targets as far as Israel, Egypt, Romania, Bulgaria and Greece). It was tested from 1998 to 2003 and added to the military arsenal on 7 July 2003, with an official unveiling by Ayatollah Khamenei on July 20. With an accuracy of 140 m CEP, the Shahab-3 missile is primarily effective against large, soft targets (like military airfields). Given the Shahab-3’s payload capacity, it would likely be capable of delivering nuclear warheads. According to the IAEA, Iran in the early 2000s may have explored various fuzing, arming and firing systems to make the Shahab-3 more capable of reliably delivering a nuclear warhead. The forerunners to this missile include the Shahab-1 and Shahab-2. In 2007, the then- Iranian Defence Minister Admiral Sham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safir (rocket)
The Safir ( fa, سفیر, meaning "ambassador") was the first Iranian expendable launch vehicle able to place a satellite in orbit. The first successful orbital launch using the Safir launch system took place on 2 February 2009 when a Safir carrier rocket placed the Omid satellite into an orbit with a apogee. Making Iran the ninth nation capable of producing and launching a satellite. The Simorgh is a larger orbital launcher based on Safir technology which has since replaced the Safir, and is sometimes called the Safir-2. Design and specifications The Safir measures 1.25 meters in diameter, 22 meters in height and has a launching mass of 26 tons. The rocket consists of two stages; The first stage utilizes an upgraded Nodong/Shahab-3 type engine which burns a hypergolic combination of UDMH as fuel and nitrogen tetroxide as oxidant, producing 37 tons (363 kN; 82,500 lbf) of thrust. The second stage utilizes a pair of smaller engines (originally the Vernier engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noor Satellite
Noor or Nour may refer to: People *Noor (name) *Queen Noor of Jordan Fiction * ''Noor'' (film), a 2017 Bollywood film * ''Noor'' (play), a 2009 play by Akbar Ahmed *''Noor'', a 2020 Pakistani television series with Usama Khan * ''Noor'' (novel), a 2022 Africanfuturist novel by Nnedi Okorafor *''Noor'', an album by the metal band Adorned Brood *''Noor'', the Arabic title for Turkish soap opera '' Gümüş'' and a character in the series Places *Noor (Meuse), a river in the Netherlands and Belgium *Noor, Iran, a city in northern Iran and capital of the Noor county *Noor County, a county in Mazandaran Province in Iran *Noor Palace, Sweden Other uses *Noor (horse), an Irish-bred Thoroughbred racehorse *Nūr (Islam), a concept in Islam * Noor (missile), a version of C-802 *Noor (satellite), a series of satellites; included the first Iranian military satellite *NOOR photo agency, a documentary photography collective and foundation *Ouarzazate solar power station (Noor 1), a concentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |