|
Iota Horologii
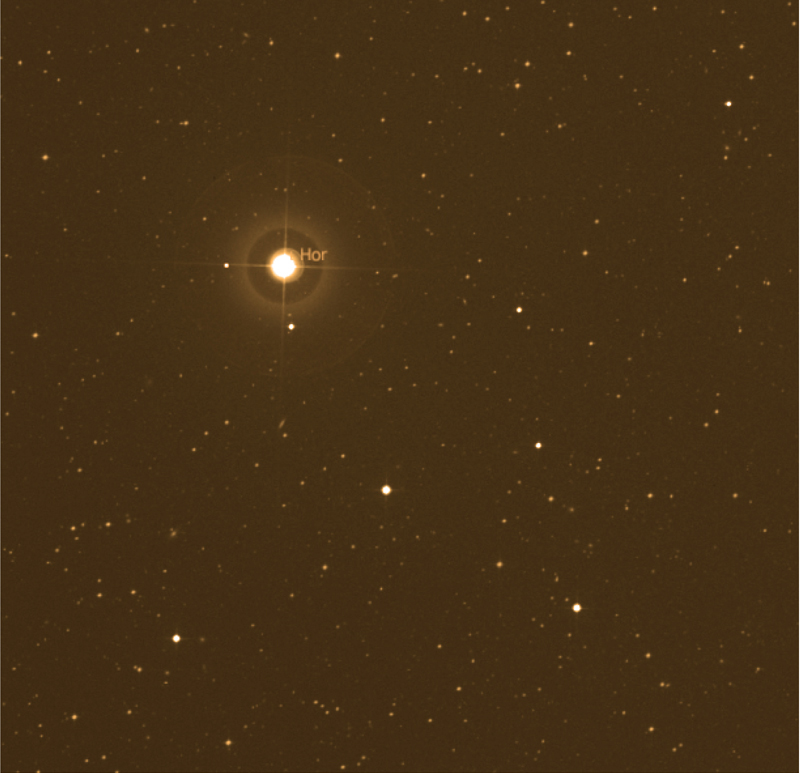
Iota Horologii, Latinized from ι Horologii, is a yellow-hued star approximately 56.5 light-years away in the Horologium constellation. The star is classified as a G0Vp yellow dwarf (it has previously been classified as G3 and a subgiant V. It has a mass and radius larger than the Sun, and is about 50% more luminous. In 1999, a planet of the star was discovered. Because the planet orbits in a near Earth orbit, Iota Horologii was ranked 69th in the list of candidates for NASA's planned Terrestrial Planet Finder mission. In 2000, a dust disc was announced around the star, but this was later determined to be an instrumental artifact. Distance and visibility Since Iota Horologii is in the minor constellation of Horologium and is quite dim in the sky, it has not been given a traditional name. It lies roughly between the stars Eta Horologii and R Horologii (though it is not close to them in real space). In its current position, Iota Horologii is closest to the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iota Horologii
Iota Horologii, Latinized from ι Horologii, is a yellow-hued star approximately 56.5 light-years away in the Horologium constellation. The star is classified as a G0Vp yellow dwarf (it has previously been classified as G3 and a subgiant V. It has a mass and radius larger than the Sun, and is about 50% more luminous. In 1999, a planet of the star was discovered. Because the planet orbits in a near Earth orbit, Iota Horologii was ranked 69th in the list of candidates for NASA's planned Terrestrial Planet Finder mission. In 2000, a dust disc was announced around the star, but this was later determined to be an instrumental artifact. Distance and visibility Since Iota Horologii is in the minor constellation of Horologium and is quite dim in the sky, it has not been given a traditional name. It lies roughly between the stars Eta Horologii and R Horologii (though it is not close to them in real space). In its current position, Iota Horologii is closest to the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary System
A planetary system is a set of gravitationally In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stron ... bound non-Star, stellar objects in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consist of bodies such as dwarf planets, asteroids, natural satellites, meteoroids, comets, planetesimals and circumstellar disks. The Sun together with the planetary system revolving around it, including Earth, forms the Solar System. The term exoplanetary system is sometimes used in reference to other planetary systems. Debris disks are also known to be common, though other objects are more difficult to observe. Of particular interest to astrobiology is the habitable zone of planetary sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccentricity (orbit)
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * circular orbit: ''e'' = 0 * elliptic orbit: 0 < ''e'' < 1 * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trojan Points
In astronomy, a trojan is a small celestial body (mostly asteroids) that shares the orbit of a larger body, remaining in a stable orbit approximately 60° ahead of or behind the main body near one of its Lagrangian points and . Trojans can share the orbits of planets or of large moons. Trojans are one type of co-orbital object. In this arrangement, a star and a planet orbit about their common barycenter, which is close to the center of the star because it is usually much more massive than the orbiting planet. In turn, a much smaller mass than both the star and the planet, located at one of the Lagrangian points of the star–planet system, is subject to a combined gravitational force that acts through this barycenter. Hence the smallest object orbits around the barycenter with the same orbital period as the planet, and the arrangement can remain stable over time. In the Solar System, most known trojans share the orbit of Jupiter. They are divided into the Greek camp at (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
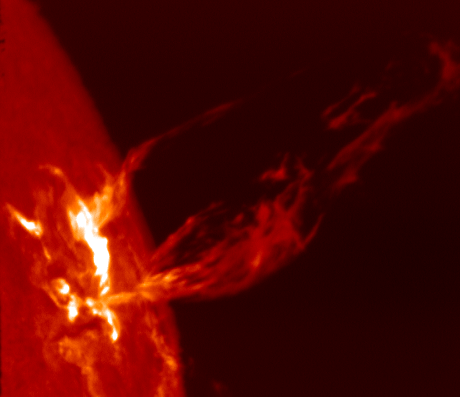
Solar Cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surface. Over the period of a solar cycle, levels of solar radiation and ejection of solar material, the number and size of sunspots, solar flares, and coronal loops all exhibit a synchronized fluctuation from a period of minimum activity to a period of a maximum activity back to a period of minimum activity. The magnetic field of the Sun flips during each solar cycle, with the flip occurring when the solar cycle is near its maximum. After two solar cycles, the Sun's magnetic field returns to its original state, completing what is known as a Hale cycle. This cycle has been observed for centuries by changes in the Sun's appearance and by terrestrial phenomena such as aurora but was not clearly identified until 1843. Solar activity, driven by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Activity
A stellar magnetic field is a magnetic field generated by the motion of conductive plasma inside a star. This motion is created through convection, which is a form of energy transport involving the physical movement of material. A localized magnetic field exerts a force on the plasma, effectively increasing the pressure without a comparable gain in density. As a result, the magnetized region rises relative to the remainder of the plasma, until it reaches the star's photosphere. This creates starspots on the surface, and the related phenomenon of coronal loops. Measurement The magnetic field of a star can be measured by means of the Zeeman effect. Normally the atoms in a star's atmosphere will absorb certain frequencies of energy in the electromagnetic spectrum, producing characteristic dark absorption lines in the spectrum. When the atoms are within a magnetic field, however, these lines become split into multiple, closely spaced lines. The energy also becomes polarized with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory
The Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) is an astronomical observatory located on Cerro Tololo in the Coquimbo Region of northern Chile, with additional facilities located on Cerro Pachón about to the southeast. It is approximately east of La Serena, where support facilities are located. The site was identified by a team of scientists from Chile and the United States in 1959, and it was selected in 1962. Construction began in 1963 and regular astronomical observations commenced in 1965. Construction of large buildings on Cerro Tololo ended with the completion of the Víctor Blanco Telescope in 1974, but smaller facilities have been built since then. Cerro Pachón is still under development, with two large telescopes (Gemini South and SOAR) inaugurated since 2000, and one in the early stages of construction (the Vera C. Rubin Observatory) The principal telescopes at CTIO are the 4 m Víctor M. Blanco Telescope, named after Puerto Rican astronomer Víctor Manuel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the abundance of elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal physical matter in the Universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''"metals"'' as a convenient short term for ''"all elements except hydrogen and helium"''. This word-use is distinct from the conventional chemical or physical definition of a metal as an electrically conducting solid. Stars and nebulae with relatively high abundances of heavier elements are called "metal-rich" in astrophysical terms, even though many of those elements are nonmetals in chemistry. The presence of heavier elements hails from stellar nucleosynthesis, where the majority of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium in the Universe (''metals'', hereafter) are formed in the cores of stars as they evolve. Over time, stellar winds and supernovae deposit the metals into the surrounding environment, enriching the interstellar medium and providing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyades Cluster
The Hyades (; Greek Ὑάδες, also known as Caldwell 41, Collinder 50, or Melotte 25) is the nearest open cluster and one of the best-studied star clusters. Located about away from the Sun, it consists of a roughly spherical group of hundreds of stars sharing the same age, place of origin, chemical characteristics, and motion through space.Bouvier J, Kendall T, Meeus G, Testi L, Moraux E, Stauffer JR, James D, Cuillandre J-C, Irwin J, McCaughrean MJ, Baraffe I, Bertin E. (2008) Brown dwarfs and very low mass stars in the Hyades cluster: a dynamically evolved mass function. ''Astronomy & Astrophysics'', 481: 661-672. Abstract at http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2008A%26A...481..661B. From the perspective of observers on Earth, the Hyades Cluster appears in the constellation Taurus, where its brightest stars form a "V" shape along with the still-brighter Aldebaran. However, Aldebaran is unrelated to the Hyades, as it is located much closer to Earth and merely happens to lie alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a unit directly proportional to the photon energy, such as reciprocal centimeters or electron volts, which has a reciprocal relationship to wavelength. A spectrometer is used in spectroscopy for producing spectral lines and measuring their wavelengths and intensities. Spectrometers may operate over a wide range of non-optical wavelengths, from gamma rays and X-rays into the far infrared. If the instrument is designed to measure the spectrum on an absolute scale rather than a relative one, then it is typically called a spectrophotometer. The majority o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Reticuli
Zeta Reticuli, Latinized from ζ Reticuli, is a wide binary star system in the southern constellation of Reticulum. From the southern hemisphere the pair can be seen with the naked eye as a double star in very dark skies. Based upon parallax measurements, this system is located at a distance of about from Earth. Both stars are solar analogs that have characteristics similar to those of the Sun. They belong to the Zeta Herculis Moving Group of stars that share a common origin. Nomenclature At a declination of −62°, the system is not visible from Britain's latitude of +53°, so it never received a Flamsteed designation in John Flamsteed's 1712 ''Historia Coelestis Britannica''. The Bayer designation for this star system, Zeta (ζ) Reticuli, originated in a 1756 star map by the French astronomer Abbé Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille. Subsequently, the two stars received separate designations in the Cape Photographic Durchmusterung, which was processed between 1859 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nu Phoenicis
Nu Phoenicis is a F-type main-sequence star in the southern constellation of Phoenix. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.95. This is a solar analogue, meaning its observed properties appear similar to the Sun, although it is somewhat more massive. At an estimated distance of around 49.5 light years, this star is located relatively near the Sun. Based on observations of excess infrared radiation from this star, it may possess a dust ring that extends outward several AU from an inner edge starting at 10 AU. Properties This is an F-type main-sequence star with a spectral type of F9V Fe+0.4, indicating it is similar to the Sun but somewhat hotter and more luminous. The notation 'Fe+0.4' indicates strong iron absorption lines; the star is indeed metal-rich, with an iron abundance 45% greater than the Sun's. Nu Phoenicis has an estimated mass of 1.17 times the solar mass and a radius of 1.26 times the solar radius. It is shinin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |