|
Iodine (125I) CC49-monoclonal Antibody
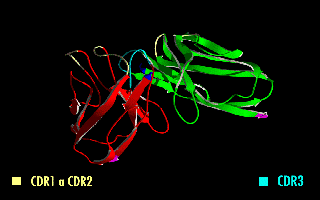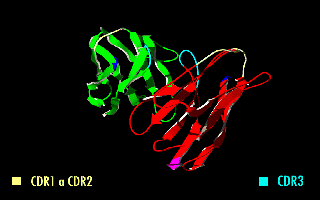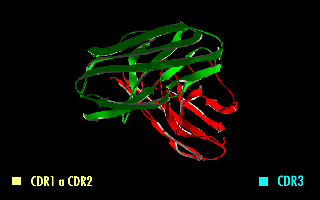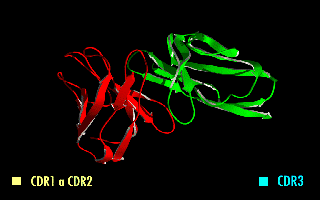
Minretumomab (CC49) is a mouse monoclonal antibody that was designed for the treatment of cancers that express the TAG-72 antigen. This includes breast, colon, lung, and pancreatic cancers. Apparently, it never got past Phase I clinical trials for this purpose. Derivatives A wide range of derivatives has been used in pharmaceutical research. Examples include chimeric and humanized minretumomab, as well as a fusion protein of a minretumomab single-chain variable fragment and the enzyme beta-lactamase. Radiopharmaceuticals Iodine (125I) minretumomab is an iodine-125 radiolabelled derivative that was developed for the detection of tumours in radioimmunoassays such as CA 72-4. Radiolabelled minretumomab has also been tested for the treatment of solid tumours, but without success. Iodine ( 131I) and lutetium ( 177Lu) minretumomab, for example, were shown to induce human anti-mouse antibodies; no tumour response was observed in Phase I and II clinical trials Clinical tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TAG-72
Tumor-associated glycoprotein 72 (TAG-72) is a glycoprotein found on the surface of many cancer cells, including ovary, breast, colon, lung, and pancreatic cancers. It is a mucin-like molecule with a molar mass of over 1000 kDa. TAG-72 is a tumor marker measured with radioimmunoassays like CA 72-4, which uses the monoclonal antibodies indium (111In) satumomab pendetide and iodine (125I) minretumomab. This assay has a good specificity for gastric cancer Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymph ..., with a correlation to the neoplasia's extension. It is used to identify relapses of the disease and to follow up the treatment. TAG-72 is also the target of the anti-cancer drugs anatumomab mafenatox and minretumomab. References Glycoproteins Tumor markers {{On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
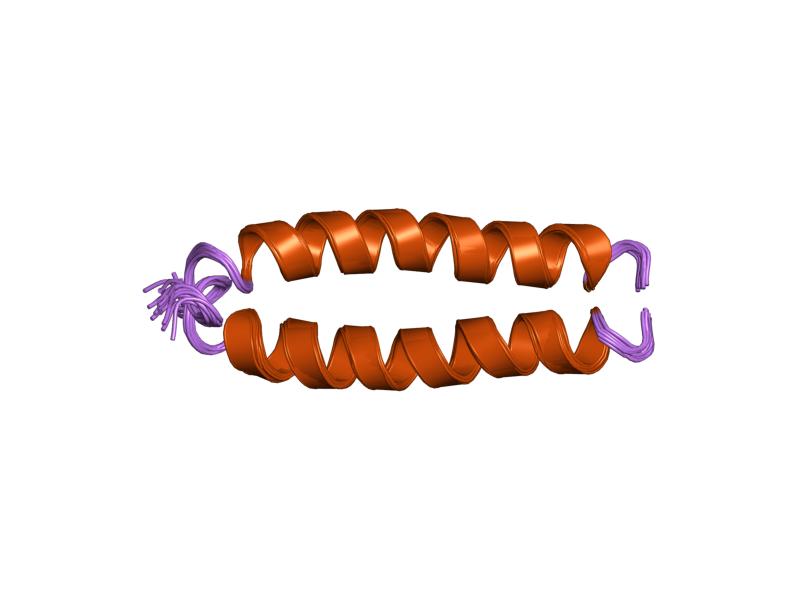
Single-chain Variable Fragment
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of ten to about 25 amino acids. The linker is usually rich in glycine for flexibility, as well as serine or threonine for solubility, and can either connect the N-terminus of the VH with the C-terminus of the VL, or ''vice versa''. This protein retains the specificity of the original immunoglobulin, despite removal of the constant regions and the introduction of the linker. The image to the right shows how this modification usually leaves the specificity unaltered. These molecules were created to facilitate phage display, where it is highly convenient to express the antigen-binding domain as a single peptide. As an alternative, scFv can be created directly from subcloned heavy and light chains derived from a hybridoma. ScFvs have many use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Anti-mouse Antibodies
Human anti-mouse antibody or human anti-murine antibody (HAMA) is an antibody found in humans which reacts to immunoglobins found in mice. The HAMA response Antibody treatment is a type of therapy that is used to treat certain types of cancer and immune disorders. Antibodies are proteins which are naturally formed by the body in response to a foreign substance, known as an antigen. Antibodies can also be grown outside of the patient’s body and injected into them to help aid the immune system to fight disease. These types of antibodies are typically called monoclonal antibodies because they are created to target one specific antigen. Herceptin and Avastin, two widely used cancer fighting drugs, are examples of monoclonal antibodies. For several decades, and until recently, mice were used extensively in the production of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). But the treatments were not as effective as doctors had hoped. One problem was that patients reacted to the mouse antibodies as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutetium-177
Naturally occurring lutetium (71Lu) is composed of one stable isotope 175Lu (97.41% natural abundance) and one long-lived radioisotope, 176Lu with a half-life of 3.78 × 1010 years (2.59% natural abundance). Thirty-five radioisotopes have been characterized, with the most stable, besides 176Lu, being 174Lu with a half-life of 3.31 years, and 173Lu with a half-life of 1.37 years. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 9 days, and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than half an hour. This element also has 18 meta states, with the most stable being 177mLu (t1/2 160.4 days), 174mLu (t1/2 142 days) and 178mLu (t1/2 23.1 minutes). The isotopes of lutetium range in mass number from 149 to 184. The primary decay mode before the most abundant stable isotope, 175Lu, is electron capture (with some alpha and positron emission), and the primary mode after is beta emission. The primary decay products before 175Lu are isotopes of ytterbium a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine-131
Iodine-131 (131I, I-131) is an important radioisotope of iodine discovered by Glenn Seaborg and John Livingood in 1938 at the University of California, Berkeley. It has a radioactive decay half-life of about eight days. It is associated with nuclear energy, medical diagnostic and treatment procedures, and natural gas production. It also plays a major role as a radioactive isotope present in nuclear fission products, and was a significant contributor to the health hazards from open-air atomic bomb testing in the 1950s, and from the Chernobyl disaster, as well as being a large fraction of the contamination hazard in the first weeks in the Fukushima nuclear crisis. This is because 131I is a major fission product of uranium and plutonium, comprising nearly 3% of the total products of fission (by weight). See fission product yield for a comparison with other radioactive fission products. 131I is also a major fission product of uranium-233, produced from thorium. Due to its mode of be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CA 72-4
Tumor-associated glycoprotein 72 (TAG-72) is a glycoprotein found on the surface of many cancer cells, including ovary, breast, colon, lung, and pancreatic cancers. It is a mucin-like molecule with a molar mass of over 1000 kDa. TAG-72 is a tumor marker measured with radioimmunoassays like CA 72-4, which uses the monoclonal antibodies indium (111In) satumomab pendetide and iodine (125I) minretumomab. This assay has a good specificity for gastric cancer Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymph ..., with a correlation to the neoplasia's extension. It is used to identify relapses of the disease and to follow up the treatment. TAG-72 is also the target of the anti-cancer drugs anatumomab mafenatox and minretumomab. References Glycoproteins Tumor markers {{On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioimmunoassay
A radioimmunoassay (RIA) is an immunoassay that uses radiolabeled molecules in a stepwise formation of immune complexes. A RIA is a very sensitive in vitro assay technique used to measure concentrations of substances, usually measuring antigen concentrations (for example, hormone levels in blood) by use of antibodies. Although the RIA technique is extremely sensitive and extremely specific, requiring specialized equipment, it remains among the least expensive methods to perform such measurements. It requires special precautions and licensing, since radioactive substances are used. In contrast, an immunoradiometric assay (IRMA) is an immunoassay that uses radiolabeled molecules but in an immediate rather than stepwise way. A radioallergosorbent test (RAST) is an example of radioimmunoassay. It is used to detect the causative allergen for an allergy. Method Classically, to perform a radioimmunoassay, a known quantity of an antigen is made radioactive, frequently by labeling it wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumour
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine-125
Iodine-125 (125I) is a radioisotope of iodine which has uses in biological assays, nuclear medicine imaging and in radiation therapy as brachytherapy to treat a number of conditions, including prostate cancer, uveal melanomas, and brain tumors. It is the second longest-lived radioisotope of iodine, after iodine-129. Its half-life is 59.49 days and it decays by electron capture to an excited state of tellurium-125. This state is not the metastable 125mTe, but rather a lower energy state that decays immediately by gamma decay with a maximum energy of 35 keV. Some of the excess energy of the excited 125Te may be internally converted ejected electrons (also at 35 keV), or to x-rays (from electron bremsstrahlung), and also a total of 21 Auger electrons, which are produced at the low energies of 50 to 500 electron volts. Eventually, stable ground state 125Te is produced as the final decay product. In medical applications, the internal conversion and Auger electrons cause little dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases, (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties. Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to target a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment. Structure The structure of a '' Streptomyces'' serine β-lactamase (SBLs) is given by . The alpha-beta fold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Protein
Fusion proteins or chimeric (kī-ˈmir-ik) proteins (literally, made of parts from different sources) are proteins created through the joining of two or more genes that originally coded for separate proteins. Translation of this ''fusion gene'' results in a single or multiple polypeptides with functional properties derived from each of the original proteins. ''Recombinant fusion proteins'' are created artificially by recombinant DNA technology for use in biological research or therapeutics. '' Chimeric'' or ''chimera'' usually designate hybrid proteins made of polypeptides having different functions or physico-chemical patterns. ''Chimeric mutant proteins'' occur naturally when a complex mutation, such as a chromosomal translocation, tandem duplication, or retrotransposition creates a novel coding sequence containing parts of the coding sequences from two different genes. Naturally occurring fusion proteins are commonly found in cancer cells, where they may function as oncoproteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine-125
Iodine-125 (125I) is a radioisotope of iodine which has uses in biological assays, nuclear medicine imaging and in radiation therapy as brachytherapy to treat a number of conditions, including prostate cancer, uveal melanomas, and brain tumors. It is the second longest-lived radioisotope of iodine, after iodine-129. Its half-life is 59.49 days and it decays by electron capture to an excited state of tellurium-125. This state is not the metastable 125mTe, but rather a lower energy state that decays immediately by gamma decay with a maximum energy of 35 keV. Some of the excess energy of the excited 125Te may be internally converted ejected electrons (also at 35 keV), or to x-rays (from electron bremsstrahlung), and also a total of 21 Auger electrons, which are produced at the low energies of 50 to 500 electron volts. Eventually, stable ground state 125Te is produced as the final decay product. In medical applications, the internal conversion and Auger electrons cause little dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |