|
Investment Style
Investment style, is a term in investment management (and more generally, in finance), referring to how a characteristic investment philosophy is employed by an investor or fund manager. Investment Philosophies Aswath Damodaran Here, for example, one manager favors Small capitalization, small cap stocks, while another prefers large blue-chip stocks. The classification extends across asset classes — Stock, equities, Bond (finance), bonds or financial derivatives — and within each further weighs factors such as Leverage (finance), leverage, momentum investing, momentum, diversification (finance), diversification benefits, value stock, relative value or growth stock, growth prospects. Major style choices include the following: *Active vs. Passive: acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment Management
Investment management (sometimes referred to more generally as financial asset management) is the professional asset management of various Security (finance), securities, including shareholdings, Bond (finance), bonds, and other assets, such as real estate, to meet specified investment goals for the benefit of investors. Investors may be institutions, such as insurance companies, pension funds, corporations, charities, educational establishments, or private investors, either directly via investment contract, contracts/mandates or via collective investment schemes like mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, or REIT, Real estate investment trusts. The term ''investment management'' is often used to refer to the management of investment funds, most often specializing in private equity, private and public equity, real assets, alternative assets, and/or bonds. The more generic term ''asset management'' may refer to management of assets not necessarily primarily held for investment purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Management
Passive management (also called passive investing) is an investing strategy that tracks a market-weighted index or portfolio. Passive management is most common on the equity market, where index funds track a stock market index, but it is becoming more common in other investment types, including bonds, commodities and hedge funds.Burton G. Malkiel, A Random Walk Down Wall Street, W. W. Norton, 1996, There has been a substantial increase in passive investing over the last twenty years. The most popular method is to mimic the performance of an externally specified index by buying an index fund. By tracking an index, an investment portfolio typically gets good diversification, low turnover (good for keeping down internal transaction costs), and low management fees. With low fees, an investor in such a fund would have higher returns than a similar fund with similar investments but higher management fees and/or turnover/transaction costs.William F. SharpeIndexed Investing: A Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Size Premium
The size premium is the historical tendency for the stocks of firms with smaller market capitalizations to outperform the stocks of firms with larger market capitalizations. It is one of the factors in the Fama–French three-factor model. See also * Liquidity premium *Risk premium
A risk premium is a measure of excess return that is required by an individual to compensate being sub ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Capitalization
Market capitalization, sometimes referred to as market cap, is the total value of a publicly traded company's outstanding common shares owned by stockholders. Market capitalization is equal to the market price per common share multiplied by the number of common shares outstanding. Description Market capitalization is sometimes used to rank the size of companies. It measures only the equity component of a company's capital structure, and does not reflect management's decision as to how much debt (or leverage) is used to finance the firm. A more comprehensive measure of a firm's size is enterprise value (EV), which gives effect to outstanding debt, preferred stock, and other factors. For insurance firms, a value called the embedded value (EV) has been used. It is also used in ranking the relative size of stock exchanges, being a measure of the sum of the market capitalizations of all companies listed on each stock exchange. The total capitalization of stock markets or eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquidation Value
Liquidation value is the likely price of an asset when it is allowed insufficient time to sell on the open market, thereby reducing its exposure to potential buyers. Liquidation value is typically lower than fair market value. Unlike cash or other available liquid assets, certain illiquid assets, like real estate, often require a period of several months in order to obtain their fair market value in a sale, and will generally sell for a significantly lower price if a sale is forced to occur in a shorter time period. The liquidation value may be either the result of a ''forced liquidation'' or an ''orderly liquidation''. Either value assumes that the sale is consummated by a seller who is compelled to sell and assumes an exposure period which is less than market normal. The most common definition used by real estate appraisers is as followsDictionary of Real Estate Appraisal, 4th ed., Appraisal Institute, 2002 The most probable price that a specified interest in real property is lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Value
In accounting, book value (or carrying value) is the value of an asset according to its balance sheet account balance. For assets, the value is based on the original cost of the asset less any depreciation, amortization or impairment costs made against the asset. Traditionally, a company's book value is its minus intangible assets and liabilities. However, in practice, depending on the source of the calculation, book value may variably include goodwill, intangible assets, or both.Graham and Dodd's ''Security Analysis'', Fifth Edition, pp 318 – 319 The value inherent in its workforce, part of the intellectual capital of a company, is always ignored. When intangible assets and goodwill are explicitly excluded, the metric is often specified to be ''tangible book value''. In the United Kingdom, the term net asset value may refer to the book value of a company. Asset book value An asset's initial book value is its actual cash value or its acquisition cost. Cash assets are record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valuation (finance)
In finance, valuation is the process of determining the value of a (potential) investment, asset, or security. Generally, there are three approaches taken, namely discounted cashflow valuation, relative valuation, and contingent claim valuation. Valuations can be done for assets (for example, investments in marketable securities such as companies' shares and related rights, business enterprises, or intangible assets such as patents, data and trademarks) or for liabilities (e.g., bonds issued by a company). Valuation is a subjective exercise, and in fact, the process of valuation itself can also affect the value of the asset in question. Valuations may be needed for various reasons such as investment analysis, capital budgeting, merger and acquisition transactions, financial reporting, taxable events to determine the proper tax liability. In a business valuation context, various techniques are used to determine the (hypothetical) price that a third party would pay for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Cycle
Business cycles are intervals of general expansion followed by recession in economic performance. The changes in economic activity that characterize business cycles have important implications for the welfare of the general population, government institutions, and private sector firms. There are many definitions of a business cycle. The simplest defines recessions as two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth. More satisfactory classifications are provided by, first including more economic indicators and second by looking for more data patterns than the two quarter definition. In the United States, the National Bureau of Economic Research oversees a Business Cycle Dating Committee that defines a recession as "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the market, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales." Business cycles are usually thought of as medium-term ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
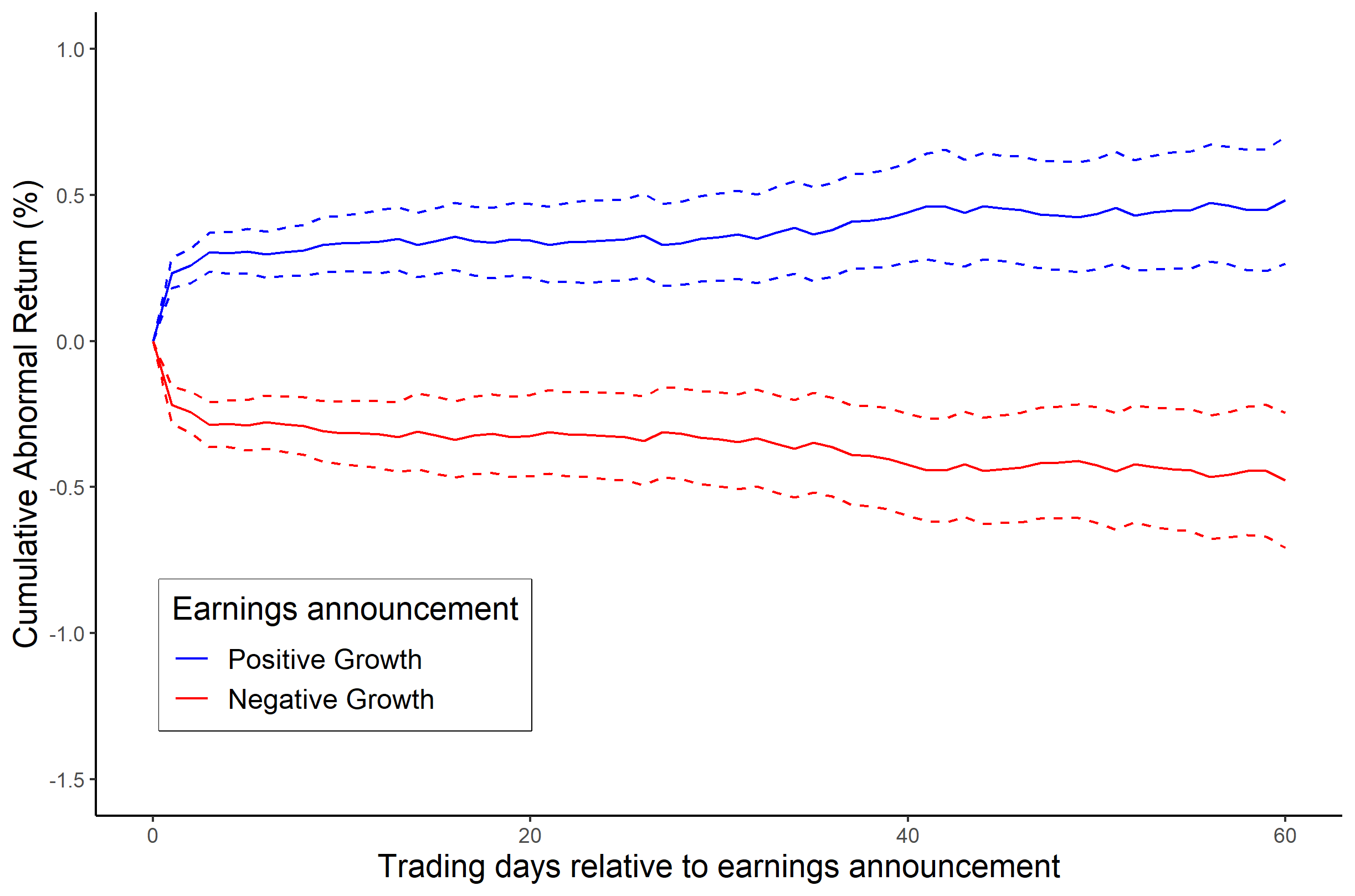
Growth Investing
Growth investing is a type of investment strategy focused on capital appreciation. Those who follow this style, known as ''growth investors'', invest in companies that exhibit signs of above-average growth, even if the share price appears expensive in terms of metrics such as price-to-earnings or price-to-book ratios. In typical usage, the term "growth investing" contrasts with the strategy known as value investing. However, some notable investors such as Warren Buffett have stated that there is no theoretical difference between the concepts of value and growth: "the two approaches are joined at the hip: Growth is ''always'' a component in the calculation of value, constituting a variable whose importance can range from negligible to enormous and whose impact can be negative as well as positive. In addition, we think the very term 'value investing' is redundant. What is 'investing' if it is not the act of seeking value at least sufficient to justify the amount paid?" Buf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core & Satellite
Core & Satellite Portfolio Management is an investment strategy that incorporates traditional fixed-income and equity-based securities (i.e., index funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), passive mutual funds, etc.), known as the "core" portion of the portfolio, with a percentage of selected individual securities in the fixed-income and equity-based side of the port folio known as the "satellite" portion. Core portfolio The "core" is made of passively managed securities and uses a traditional benchmark (e.g., Russell 3000 or the S&P 1500) to benchmark performance. The positions may have more small cap stocks over mid/large cap companies, more value positions over growth positions, higher or lower concentration in developed international market Global marketing is defined as “marketing on a worldwide scale reconciling or taking global operational differences, similarities and opportunities to reach global objectives". Global marketing is also a field of study in general busi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Efficiency
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted basis since market prices should only react to new information. Because the EMH is formulated in terms of risk adjustment, it only makes testable predictions when coupled with a particular model of risk. As a result, research in financial economics since at least the 1990s has focused on market anomalies, that is, deviations from specific models of risk. The idea that financial market returns are difficult to predict goes back to Bachelier, Mandelbrot, and Samuelson, but is closely associated with Eugene Fama, in part due to his influential 1970 review of the theoretical and empirical research. The EMH provides the basic logic for modern risk-based theories of asset prices, and frameworks such as consumption-based asset pricing and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |