|
Inversion Of Series
Inversion or inversions may refer to: Arts * , a French gay magazine (1924/1925) * ''Inversion'' (artwork), a 2005 temporary sculpture in Houston, Texas * Inversion (music), a term with various meanings in music theory and musical set theory * ''Inversions'' (novel) by Iain M. Banks * ''Inversion'' (video game), a 2012 third person shooter for Xbox 360, PlayStation 3, and PC * ''Inversions'' (EP), the 2014 extended play album by American rock music ensemble The Colourist * ''Inversions'' (album), a 2019 album by Belinda O'Hooley * ''Inversion'' (film), a 2016 Iranian film Linguistics and language * Inversion (linguistics), grammatical constructions where two expressions switch their order of appearance * Inversion (prosody), the reversal of the order of a foot's elements in poetry * Anastrophe, a figure of speech also known as an ''inversion'' Mathematics and logic * Involution (mathematics), a function that is its own inverse (when applied twice, the starting value is obt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversion (artwork)
''Inversion'' was a 2005 artwork by sculptors Dan Havel and Dean Ruck of Houston Alternative Art. Havel and Ruck altered two buildings owned by the Art League of Houston on the corner of Montrose Boulevard and Willard Street. The exterior skins of the houses were peeled off and used to create a large vortex that funneled into the small central hallway connecting the two buildings and eventually exited through a small hole into an adjacent courtyard. ''Inversion'' has become one of Houston's most well-known, albeit vanished, sculptures. The structure was later demolished to make way for a new Art League building. Art League Houston owned the two houses and had used them for art classes and exhibitions for over 30 years. The organisation commissioned Havel and Ruck to transform them into an artwork in demolition. The sculpture was opened on May 21, 2005, and was visible from Montrose Boulevard until its demolition the next month. Years later, the artwork continues to be cited on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplicative Inverse
In mathematics, a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal for a number ''x'', denoted by 1/''x'' or ''x''−1, is a number which when Multiplication, multiplied by ''x'' yields the multiplicative identity, 1. The multiplicative inverse of a rational number, fraction ''a''/''b'' is ''b''/''a''. For the multiplicative inverse of a real number, divide 1 by the number. For example, the reciprocal of 5 is one fifth (1/5 or 0.2), and the reciprocal of 0.25 is 1 divided by 0.25, or 4. The reciprocal function, the Function (mathematics), function ''f''(''x'') that maps ''x'' to 1/''x'', is one of the simplest examples of a function which is its own inverse (an Involution (mathematics), involution). Multiplying by a number is the same as Division (mathematics), dividing by its reciprocal and vice versa. For example, multiplication by 4/5 (or 0.8) will give the same result as division by 5/4 (or 1.25). Therefore, multiplication by a number followed by multiplication by its reciprocal yiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Inversion
In science, specifically statistical mechanics, a population inversion occurs while a system (such as a group of atoms or molecules) exists in a state in which more members of the system are in higher, excited states than in lower, unexcited energy states. It is called an "inversion" because in many familiar and commonly encountered physical systems, this is not possible. This concept is of fundamental importance in laser science because the production of a population inversion is a necessary step in the workings of a standard laser. Boltzmann distributions and thermal equilibrium To understand the concept of a population inversion, it is necessary to understand some thermodynamics and the way that light interacts with matter. To do so, it is useful to consider a very simple assembly of atoms forming a laser medium. Assume there is a group of ''N'' atoms, each of which is capable of being in one of two energy states: either #The ''ground state'', with energy ''E''1; or #The ''exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Inversion
In chemistry, pyramidal inversion (also umbrella inversion) is a fluxional process in compounds with a pyramidal molecule, such as ammonia (NH3) "turns inside out". It is a rapid oscillation of the atom and substituents, the molecule or ion passing through a planar transition state. For a compound that would otherwise be chiral due to a stereocenter, pyramidal inversion allows its enantiomers to racemize. The general phenomenon of pyramidal inversion applies to many types of molecules, including carbanions, amines, phosphines, arsines, stibines, and sulfoxides. Energy barrier The identity of the inverting atom has a dominating influence on the barrier. Inversion of ammonia is rapid at room temperature. In contrast, phosphine (PH3) inverts very slowly at room temperature (energy barrier: 132 kJ/mol). Consequently, amines of the type RR′R"N usually are not optically stable (enantiomers racemize rapidly at room temperature), but ''P''-chiral phosphines are. Appropriately s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Of Inversion
An island of inversion is a region of the chart of nuclides that contains isotopes with a non-standard ordering of single particle levels in the nuclear shell model. Such an area was first described in 1975 by French physicists carrying out spectroscopic mass measurements of exotic isotopes of lithium and sodium. Since then further studies have shown that five such regions exist within the known table of nuclides. These are centered at neutron-rich isotopes of five elements, namely 11Li, 20C, 31Na, 42Si, and 64Cr. Because there are five known islands of inversion, physicists have suggested renaming the phenomenon as an "archipelago of islands of shell breaking". Studies with the purpose of defining the edges of this region are still ongoing. See also * Table of nuclides * Periodic table and Periodic table (extended) * Island of stability References External links Abstract and references for the original paperArticle on archipelago of shell-breaking with map of nuclide ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Inversion
In geophysics (primarily in oil-and-gas exploration/development), seismic inversion is the process of transforming seismic reflection data into a quantitative rock-property description of a reservoir. Seismic inversion may be pre- or post- stack, deterministic, random or geostatistical; it typically includes other reservoir measurements such as well logs and cores. Introduction Geophysicists routinely perform seismic surveys to gather information about the geology of an oil or gas field. These surveys record sound waves which have traveled through the layers of rock and fluid in the earth. The amplitude and frequency of these waves can be estimated so that any side-lobe and tuning effects introduced by the wavelet may be removed. Seismic data may be inspected and interpreted on its own without inversion, but this does not provide the most detailed view of the subsurface and can be misleading under certain conditions. Because of its efficiency and quality, most oil and gas compani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverted Relief
Inverted relief, inverted topography, or topographic inversion refers to landscape features that have reversed their elevation relative to other features. It most often occurs when low areas of a landscape become filled with lava or sediment that hardens into material that is more resistant to erosion than the material that surrounds it. ''Differential erosion'' then removes the less resistant surrounding material, leaving behind the younger resistant material, which may then appear as a ridge where previously there was a valley. Terms such as "inverted valley" or "inverted channel" are used to describe such features.Pain, C.F., and C.D. Ollier, 1995, ''Inversion of relief - a component of landscape evolution.'' Geomorphology. 12(2):151-165. Inverted relief has been observed on the surfaces of other planets as well as on Earth. For example, well-documented inverted topographies have been discovered on Mars.Pain, C.F., J.D.A. Clarke, and M. Thomas, 2007, ''Inversion of relief on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversion (geology)
In structural geology inversion or basin inversion relates to the relative uplift of a sedimentary basin or similar structure as a result of crustal shortening. This normally excludes uplift developed in the footwalls of later extensional faults, or uplift caused by mantle plumes. "Inversion" can also refer to individual faults, where an extensional fault is reactivated in the opposite direction to its original movement. The term ''negative inversion'' is also occasionally used to describe the reactivation of reverse faults and thrusts during extension. The term "inversion" simply refers to the fact that a relatively low-lying area is uplifted – the rock sequence itself is not normally inverted. Formation Many inversion structures are caused by the direct reactivation of pre-existing extensional faults. In some cases only the deeper parts of the fault are reactivated and the shortening is accommodated over a much broader area in the shallow part of the section. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversion Therapy
Inversion therapy, or simply inversion, is the process of seeking therapeutic benefits from hanging by the legs, ankles, or feet in an inverted angle or entirely upside down. It is a form of spinal traction. Spinal Traction can be useful for effects of decreasing muscle spasm, stretching muscles/ligaments of the back, increasing the space between vertebral bodies and thus rehydrating the intervertebral discs, decreasing disc bulging and decreasing pressure on nerve roots and the spinal cord. In turn, these effects can help for the reduction of pain and increasing tissue repair. Gravity boots are ankle supports designed for inversion therapy. Some people use gravity boots to add an extra challenge to workouts, doing inverted crunches or squats. People who have heart disease, high blood pressure, eye diseases (such as glaucoma), or are pregnant are at higher risk for the dangers related to inversion therapy and should consult their doctors about it first. The first time anyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
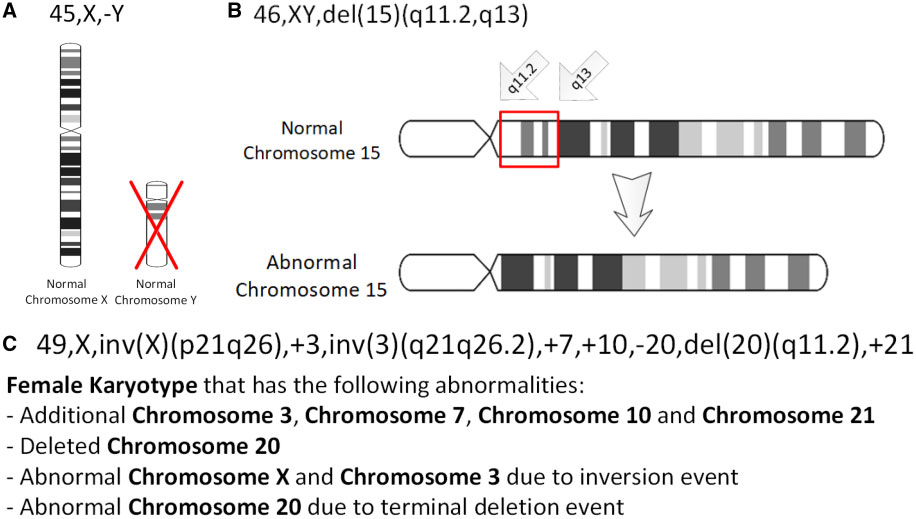
Chromosomal Inversion
An inversion is a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome becomes inverted within its original position. An inversion occurs when a chromosome undergoes a two breaks within the chromosomal arm, and the segment between the two breaks inserts itself in the opposite direction in the same chromosome arm. The breakpoints of inversions often happen in regions of repetitive nucleotides, and the regions may be reused in other inversions. Chromosomal segments in inversions can be as small as 100 kilobases or as large as 100 megabases. The number of genes captured by an inversion can range from a handful of genes to hundreds of genes. Inversions can happen either through ectopic recombination, chromosomal breakage and repair, or non-homologous end joining. Inversions are of two types: paracentric and pericentric. Paracentric inversions do not include the centromere, and both breakpoints occur in one arm of the chromosome. Pericentric inversions span the centromere, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversion (kinesiology)
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
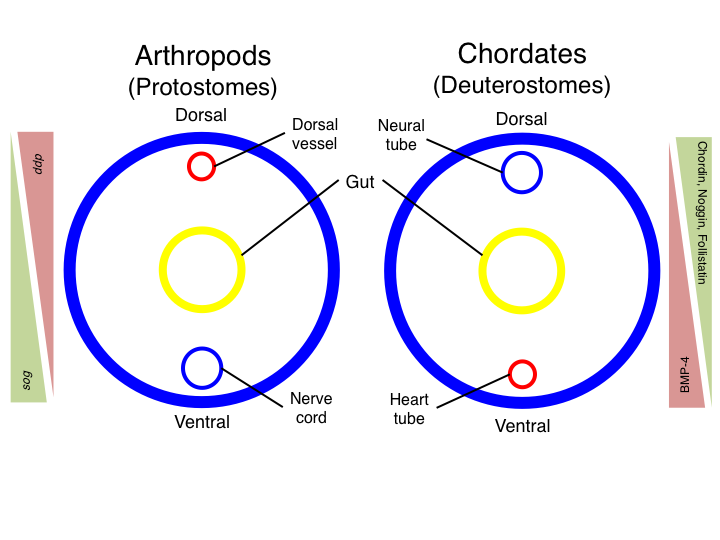
Inversion (evolutionary Biology)
In evolutionary developmental biology, inversion refers to the hypothesis that during the course of animal evolution, the structures along the dorsoventral (DV) axis have taken on an orientation opposite that of the ancestral form. Inversion was first noted in 1822 by the French zoologist Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, when he dissected a crayfish (an arthropod) and compared it with the vertebrate body plan. The idea was heavily criticised, but periodically resurfaced, and is now supported by some molecular embryologists. History As early as 1822, the French zoologist Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire noted that the organization of dorsal and ventral structures in arthropods is opposite that of mammals. Five decades later, in light of Darwin's theory of "descent with modification", German zoologist Anton Dohrn proposed that these groups arose from a common ancestor which possessed a body plan similar to that of modern annelids with a ventral nerve cord and dorsal heart. Where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |