|
Invasion Of Trinidad (1797)
On 18 February 1797, a fleet of 18 British warships under the command of Sir Ralph Abercromby invaded and took the Island of Trinidad. Within a few days the last Spanish Governor, Don José María Chacón surrendered the island to Abercromby. Effected as a result of the signing of the second Treaty of San Ildefonso in 1796 by the governments of Spain and France and by virtue of which both nations became allies, turning Spain automatically into an enemy of Great Britain. In retaliation, this latter country sent a fleet to the Caribbean with the intention of invading the islands of Trinidad and Puerto Rico, obtaining the surrender of the first, but being repelled in the second. Background Spain, previously an ally of Great Britain, had been defeated in the War of the Pyrenees against France in 1795 and forced to sign the Peace of Basel. An alliance convention between France and Spain was signed the following year in 1796. British forces in the Caribbean in 1796 had already ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Britain, Austria, Prussia, Russia, and several other monarchies. They are divided in two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–97) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian Peninsula, the Low Countries and the Rhineland in Europe and abandoned Louisiana in North America. French success in these conflicts ensured the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe. As early as 1791, the other monarchies of Europe looked with outrage at the revolution and its upheavals; and they considered whether they should intervene, either in support of King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaspar Grande
Gaspar Grande or Gasparee is an island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago named for Gaspar de Percín. The island is in area and lies west of Port of Spain. It is one of the "Bocas Islands", which lie in the ''Bocas del Dragón'' (''Dragon's Mouth'') between Trinidad and Venezuela. Gaspar Grande is primarily limestone, and reaches a height of at its highest point. Gaspar Grande is home to the Gasparee Caves, a natural limestone cave system with a mysterious pool at its base. Other caves on the island include the White Cave, the Brioge Cavern and the Precipice Cavern. Vegetation on the island includes the Yellow Poui, Giant Cactus, Hog Plum, Silk Cotton, Agave, Manicou Fig, Naked Indian, Pelican Flower, Queen-of-the-Forest (Filipendula occidentalis), Cow Itch, Sugar Apple and Salt-fish Wood. Legend has it that another cave on the island, William Dampiers Tunnel, has a pirate's treasure chest which is easily accessible on certain days of the year. History In 1783, Gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaguaramas, Trinidad
Chaguaramas (pronounced, in the local English dialect, "shag-gah-rah-muss") lies in the Northwest Peninsula of Trinidad west of Port of Spain; the name is often applied to the entire peninsula, but is sometimes used to refer to its most developed area. The developed area in Chaguaramas starts at ALCOA and ends at the Army and Coast Guard camps on the mainland. In the description or context of "developed area" one excludes the five islands which are in various stages of development or redevelopment as of 2016. Most of the roadway in Chaguaramas lies close to the coastline and one can view the sea from the winding road. Chaguaramas is about 14 km from Port of Spain. Leasing of Chaguaramas to the United States The entire peninsula was leased to the United States in 1940 for the construction of a naval base, Naval Base Trinidad, under the '' Destroyers for Bases Agreement''. The base was also used during the early 1960s as a BMEWS early warning radar site, as well as a miss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
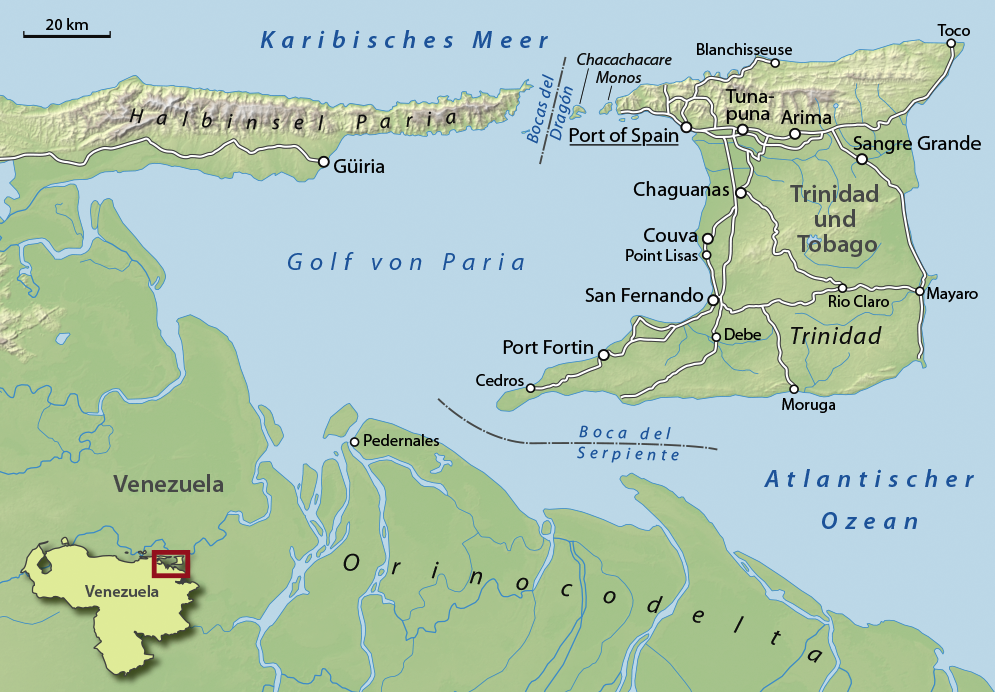
Gulf Of Paria
The Gulf of Paria ( ; es, Golfo de Paria) is a shallow (180 m at its deepest) semi-enclosed inland sea located between the island of Trinidad (Republic of Trinidad and Tobago) and the east coast of Venezuela. It separates the two countries by as little as 15 km at its narrowest and 120 km at its widest points. The tides within the Gulf are semi-diurnal in nature with a range of approximately 1m. The Gulf of Paria is considered to be one of the best natural harbors on the Atlantic coast of the Americas. The jurisdiction of the Gulf of Paria is split between Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela with Trinidad and Tobago having control over approximately (37.7%) and Venezuela the remainder (62.3%). It was originally named the Gulf of the Whale ( es, Golfo de la Ballena) by Christopher Columbus, but the 19th-century whaling industry eliminated whales from the area and populations have never recovered. Cartographic sources of the late 18th century repeatedly refer to it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventy-four (ship)
The "seventy-four" was a type of two- decked sailing ship of the line, which nominally carried 74 guns. It was developed by the French navy in the 1740s, replacing earlier classes of 60- and 62-gun ships, as a larger complement to the recently-developed 64-gun ships. Impressed with the performance of several captured French seventy-fours, the British Royal Navy quickly adopted similar designs, classing them as third rates. The type then spread to the Spanish, Dutch, Danish and Russian navies. The design was considered a good balance between firepower and sailing qualities. Hundreds of seventy-fours were constructed, becoming the dominant form of ship-of-the-line. They remained the mainstay of most major fleets into the early 19th century. From the 1820s, they began to be replaced by larger two-decked ships mounting more guns. However some seventy-fours remained in service until the late 19th century, when they were finally supplanted by ironclads. Standardising on a common shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carriacou And Petite Martinique
Carriacou and Petite Martinique, also known as the Southern Grenadines, is a dependency of Grenada, lying north of Grenada island and south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines in the Lesser Antilles. The islands of Carriacou and Petite Martinique belong to the sovereign state of Grenada. Together they all form the 3-island country of Grenada, Carriacou, and Petite Martinique. Carriacou Island is the largest island of the Grenadines, an archipelago in the Windward Islands chain. The island is with a population of 9,595 (2019 census). The main settlements on the island are Hillsborough, L'Esterre, Harvey Vale, and Windward. The neighbouring island of Petite Martinique is away from Carriacou, and also a part of Grenada. With its and population of 900, it is smaller than Carriacou. The residents of this island live by boat-building, fishing and seafaring. Carriacou and Petite Martinique are known for its Regatta and Village Maroon. Colonial history On 27 September 1650, Jacq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captaincy General Of Venezuela
The Captaincy General of Venezuela ( es, Capitanía General de Venezuela), also known as the Kingdom of Venezuela (), was an administrative district of colonial Spain, created on September 8, 1777, through the Royal Decree of Graces of 1777, to provide more autonomy for the provinces of Venezuela, previously under the jurisdiction of the Audiencia of Santo Domingo (and thus the Viceroyalty of New Spain) and then the Viceroyalty of New Granada. It established a unified government in political (governorship), military ( captaincy general), fiscal ( intendancy), ecclesiastical (archdiocese) and judicial ('' audiencia'') affairs. Its creation was part of the Bourbon Reforms and laid the groundwork for the future nation of Venezuela, in particular by orienting the province of Maracaibo towards the province of Caracas. History Antecedents The Bourbon dynasty had already taken steps towards reorganizing their overseas possessions and Venezuela, in particular. When the New Granadan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1777
Events January–March * January 2 – American Revolutionary War – Battle of the Assunpink Creek: American general George Washington's army repulses a British attack by Lieutenant General Charles Cornwallis, in a second battle at Trenton, New Jersey. * January 3 – American Revolutionary War – Battle of Princeton: American general George Washington's army defeats British troops. * January 13 – Mission Santa Clara de Asís is founded in what becomes Santa Clara, California. * January 15 – Vermont declares its independence from New York, becoming the Vermont Republic, an independent country, a status it retains until it joins the United States as the 14th state in 1791. * January 21 – The Continental Congress approves a resolution "that an unauthentic copy, with names of the signers of the Declaration of independence, be sent to each of the United States. *February 5 – Under the 1st Constitution of Georgia, 8 count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus * lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo * es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón * pt, Cristóvão Colombo * ca, Cristòfor (or ) * la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was an Italian explorer and navigator who completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, opening the way for the widespread European exploration and colonization of the Americas. His expeditions were the first known European contact with the Caribbean, Central America, and South America. The name ''Christopher Columbus'' is the anglicisation of the Latin . Scholars generally agree that Columbus was born in the Republic of Genoa and spoke a dialect of Ligurian as his first language. He went to sea at a young age and travelled widely, as far north as the British Isles and as far south as what is now Ghana. He married Portuguese noblewoman Filipa Moniz Perestrelo, who bore his son Diego, and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |