|
Intrusion (orthodontics)
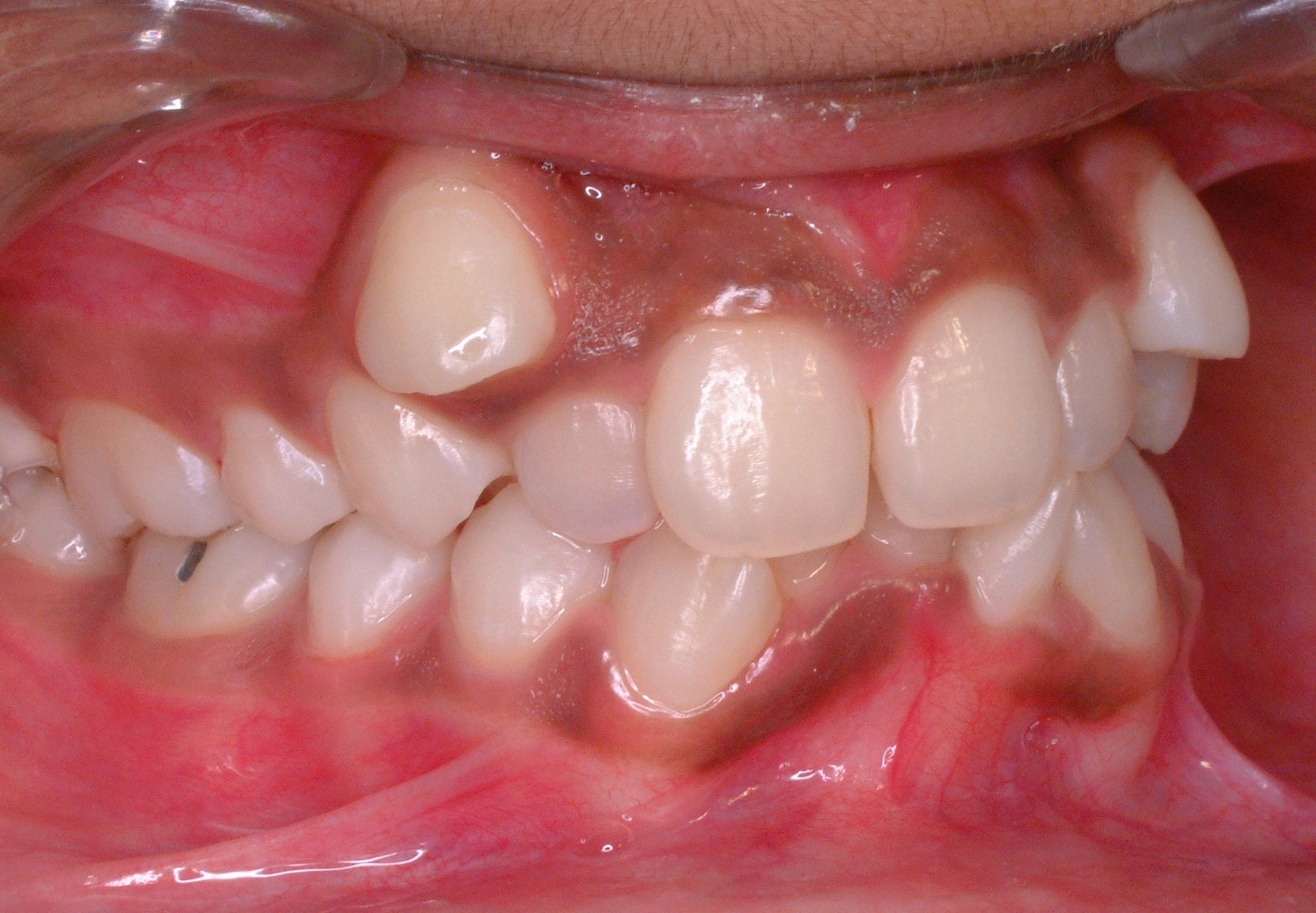
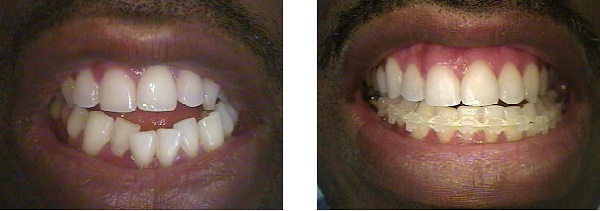
Intrusion is a movement in the field of orthodontics where a tooth is moved partially into the bone. Intrusion is done in orthodontics to correct an anterior deep bite or in some cases intrusion of the over-erupted posterior teeth with no opposing tooth. Intrusion can be done in many ways and consists of many different types. Intrusion, in orthodontic history, was initially defined as problematic in early 1900s and was known to cause periodontal effects such as root resorption and recession. However, in mid 1950s successful intrusion with light continuous forces was demonstrated. Charles J. Burstone defined intrusion to be "the apical movement of the geometric center of the root (centroid) in respect to the occlusal plane or plane based on the long axis of tooth". Types True Intrusion This type of intrusion consists of true intrusion of incisors without any extrusion of the posterior teeth. The incisors in the anterior teeth (depending on the arch) move towards the bone and no mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodontics
Orthodontics is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, management, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, and misaligned bite patterns. It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial orthopedics. Abnormal alignment of the teeth and jaws is very common. Nearly 50% of the developed world's population, according to the American Association of Orthodontics, has malocclusions severe enough to benefit from orthodontic treatment: although this figure decreases to less than 10% according to the same AAO statement when referring to medically necessary orthodontics. However, conclusive scientific evidence for the health benefits of orthodontic treatment is lacking, although patients with completed orthodontic treatment have reported a higher quality of life than that of untreated patients undergoing orthodontic treatment. Treatment may require several months to a few years, and entails using dental braces and other appliances t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontal
Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek , – 'around'; and , – 'tooth', genitive , ) is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants. The periodontium The term ''periodontium'' is used to describe the group of structures that directly surround, support and protect the teeth. The periodontium is composed largely of the gingival tissue and the supporting bone. Gingivae Normal gingiva may range in color from light coral pink to heavily pigmented. The soft tissues and connective fibres that cover and protect the underlying cementum, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone are known as the gingivae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Resorption
Resorption of the root of the tooth, or root resorption, is the progressive loss of dentin and cementum by the action of odontoclasts. Root resorption is a normal physiological process that occurs in the exfoliation of the primary dentition. However, pathological root resorption occurs in the permanent or secondary dentition and sometimes in the primary dentition. Causes While resorption of bone is a normal physiological response to stimuli throughout the body, root resorption in permanent dentition and sometimes in the primary dentition is pathological. The root is protected internally (endodontium) by pre-dentin and externally on the root surface by cementum and the periodontal ligament. Chronic stimuli that damage these protective layers expose underlying dentin to the action of osteoclasts. Root resorption most commonly occurs due to inflammation caused by: pulp necrosis, trauma, periodontal treatment, orthodontic tooth movement and tooth whitening. Less common causes incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles J
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Some Germanic languages, for example Dutch and German, have retained the word in two separate senses. In the particular case of Dutch, ''Karel'' refers to the given name, whereas the noun ''kerel'' means "a bloke, fellow, man". Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (< Old English ''ċeorl''), which developed its depr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisor are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typically, the mandibular central incisors erupt first, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curve Of Spee
In anatomy, the Curve of Spee (called also von Spee's curve or Spee's curvature) is defined as the curvature of the mandibular occlusal plane beginning at the canine and following the buccal cusps of the posterior teeth, continuing to the terminal molar. According to another definition the curve of Spee is an anatomic curvature of the occlusal alignment of the teeth, beginning at the tip of the lower incisor, following the buccal cusps of the natural premolars and molars and continuing to the anterior border of the ramus. It is named for the German embryologist Ferdinand Graf von Spee (1855–1937), who was first to describe the anatomic relations of human teeth in the sagittal plane. Details The pull of the main muscle of mastication, the masseter, is at a perpendicular angle with the curve of Spee to adapt for favorable loading of force on the teeth. The long axis of each lower tooth is aligned nearly parallel to their individual arch of closure. The Curve of Spee is, essentiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Block Appliance
A twin block is an orthodontic appliance developed by William J. Clark whose purpose is to lengthen the lower jaw by posturing it forward. If the jaw is growing during treatment, it naturally grows at a faster rate; otherwise the appliance is useless. Treatment time varies, but is generally around 9 months. Twin Blocks can also be used to cure an overbite Overbite is the extent of vertical ( superior-inferior) overlap of the maxillary central incisors over the mandibular central incisors, measured relative to the incisal ridges. The term overbite does not refer to a specific condition, nor i ..., which can mean treatment may be slightly longer. If this is the case, treatment can vary from 6 to 11 months. References Orthodontic appliances {{Dentistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Bite
In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855-1930), the "father of modern orthodontics", popularised it. The word "malocclusion" derives from ''occlusion'', and refers to the manner in which opposing teeth meet ('' mal-'' + ''occlusion'' = "incorrect closure"). The malocclusion classification is based on the relationship of the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar and the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar. If this molar relationship exists, then the teeth can align into normal occlusion. According to Angle, malocclusion is any deviation of the occlusion from the ideal. However, assessment for malocclusion should also take into account aesthetics and the impact on functionality. If these aspects are acceptable to the patient despite meeting the formal definition of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert M
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malocclusion
In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855-1930), the "father of modern orthodontics", popularised it. The word "malocclusion" derives from ''occlusion'', and refers to the manner in which opposing teeth meet ('' mal-'' + ''occlusion'' = "incorrect closure"). The malocclusion classification is based on the relationship of the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar and the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar. If this molar relationship exists, then the teeth can align into normal occlusion. According to Angle, malocclusion is any deviation of the occlusion from the ideal. However, assessment for malocclusion should also take into account aesthetics and the impact on functionality. If these aspects are acceptable to the patient despite meeting the formal definition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |