|
Intragovernmental Holdings
In public finance, intragovernmental holdings (also known as intragovernmental debt or intragovernmental obligations) are debt obligations that a government owes to its own agencies. These agencies may receive or spend money unevenly throughout the year, or receive it for payout at a future date, as in the case of a pension fund. Lending the excess funds to the government, typically on the accounts of its treasury, enables the government to calculate its net cash requirements over time. United States In the United States, intragovernmental holdings are primarily composed of the Medicare trust funds, the Social Security Trust Fund, and Federal Financing Bank securities. A small amount of marketable securities are held by government accounts. See also * Government debt US specific: * United States public debt * United States Treasury security * Federal Financing Bank * Bureau of Public Debt * Federal Reserve System * Office of Management and Budget (OMB) References Externa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Finance
Public finance is the study of the role of the government in the economy. It is the branch of economics that assesses the government revenue and government expenditure of the public authorities and the adjustment of one or the other to achieve desirable effects and avoid undesirable ones. The purview of public finance is considered to be threefold, consisting of governmental effects on: # The efficient allocation of available resources; # The distribution of income among citizens; and # The stability of the economy. Economist Jonathan Gruber has put forth a framework to assess the broad field of public finance. Gruber suggests public finance should be thought of in terms of four central questions: # When should the government intervene in the economy? To which there are two central motivations for government intervention, Market failure and redistribution of income and wealth. # How might the government intervene? Once the decision is made to intervene the government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasury
A treasury is either *A government department related to finance and taxation, a finance ministry. *A place or location where treasure, such as currency or precious items are kept. These can be state or royal property, church treasure or in private ownership. The head of a treasury is typically known as a treasurer. This position may not necessarily have the final control over the actions of the treasury, particularly if they are not an elected representative. The adjective for a treasury is normally treasurial. The adjective "tresorial" can also be used, but this normally means pertaining to a ''treasurer''. History The earliest found artefacts made of silver and gold are from Lake Varna in Bulgaria dated 4250–4000 BC, the earliest of copper are dated 9000–7000 BC. The term ''treasury'' was first used in Classical times to describe the votive buildings erected to house gifts to the gods, such as the Siphnian Treasury in Delphi or many similar buildings er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicare (United States)
Medicare is a government national health insurance program in the United States, begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration (SSA) and now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). It primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, but also for some younger people with disability status as determined by the SSA, including people with end stage renal disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease). In 2018, according to the 2019 Medicare Trustees Report, Medicare provided health insurance for over 59.9 million individuals—more than 52 million people aged 65 and older and about 8 million younger people. According to annual Medicare Trustees reports and research by the government's MedPAC group, Medicare covers about half of healthcare expenses of those enrolled. Enrollees almost always cover most of the remaining costs by taking additional private insurance and/or by joining a public Part C o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
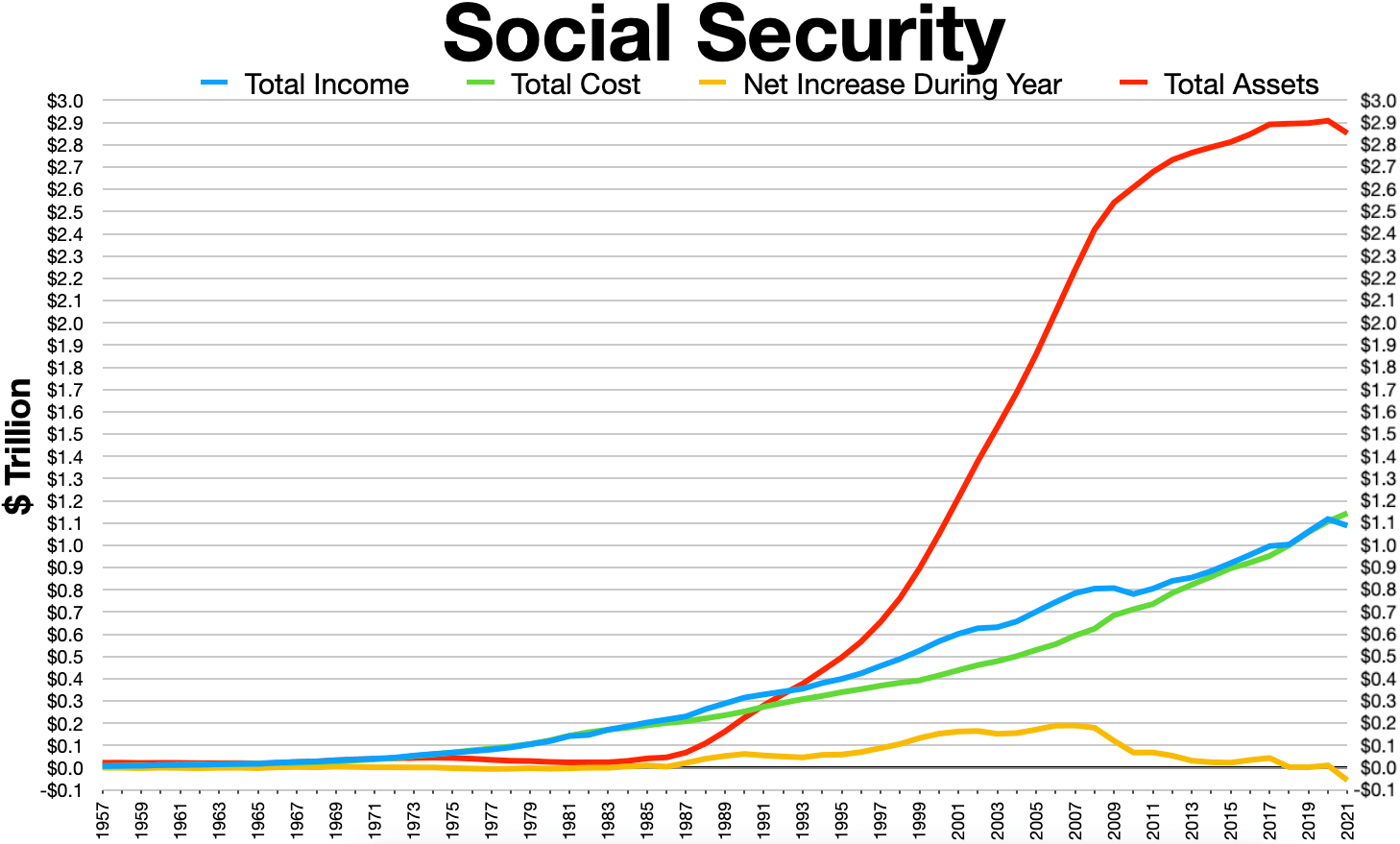
Social Security Trust Fund
The Federal Old-Age and Survivors Insurance Trust Fund and Federal Disability Insurance Trust Fund (collectively, the Social Security Trust Fund or Trust Funds) are trust funds that provide for payment of Social Security (Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance; OASDI) benefits administered by the United States Social Security Administration. The Social Security Administration collects payroll taxes and uses the money collected to pay Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance benefits by way of trust funds. When the program runs a surplus, the excess funds increase the value of the Trust Fund. As of 2021, the Trust Fund contained (or alternatively, was owed) $2.908 trillion The Trust Fund is required by law to be invested in non-marketable securities issued and guaranteed by the "full faith and credit" of the federal government. These securities earn a market rate of interest. Excess funds are used by the government for non-Social Security purposes, creating the obligatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Financing Bank
The Federal Financing Bank (FFB) is a United States government corporation created by Congress in 1973 under the general supervision of the Secretary of the Treasury.Federal Financing Bank Act of 1973 (12 USC 2281, the Act) The FFB was established to centralize and reduce the cost of federal borrowing, as well as federally assisted borrowing from the public. The FFB was also established to deal with federal budget management issues which occurred when off-budget financing flooded the government securities market with offers of a variety of government-backed securities that were competing with Treasury securities. Today the FFB has statutory authority to purchase any obligation issued, sold, or guaranteed by a federal agency to ensure that fully guaranteed obligations are financed efficiently. the FFB had $74.2 billion in assets and $69.6 billion in liabilities, for a net position of $4.6 billion. See also * Title 12 of the Code of Federal Regulations * United States Department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit occurs when a government's expenditures exceed revenues. Government debt may be owed to domestic residents, as well as to foreign residents. If owed to foreign residents, that quantity is included in the country's external debt. In 2020, the value of government debt worldwide was $87.4 US trillion, or 99% measured as a share of gross domestic product (GDP). Government debt accounted for almost 40% of all debt (which includes corporate and household debt), the highest share since the 1960s. The rise in government debt since 2007 is largely attributable to the global financial crisis of 2007–2008, and the COVID-19 pandemic. The ability of government to issue debt has been central to state formation and to state building. Public deb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Public Debt
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt: * "Debt held b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Treasury Security
United States Treasury securities, also called Treasuries or Treasurys, are government debt instruments issued by the United States Department of the Treasury to finance government spending as an alternative to taxation. Since 2012, U.S. government debt has been managed by the Bureau of the Fiscal Service, succeeding the Bureau of the Public Debt. There are four types of marketable Treasury securities: Treasury bills, Treasury notes, Treasury bonds, and Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (TIPS). The government sells these securities in auctions conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, after which they can be traded in secondary markets. Non-marketable securities include savings bonds, issued to the public and transferable only as gifts; the State and Local Government Series (SLGS), purchaseable only with the proceeds of state and municipal bond sales; and the Government Account Series, purchased by units of the federal government. Treasury securities are ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of The Public Debt
The Bureau of the Public Debt was an agency within the Fiscal Service of the United States Department of the Treasury. United States Secretary of the Treasury Timothy Geithner issued a directive that the Bureau be combined with the Financial Management Service to form the Bureau of the Fiscal Service in 2012. Under authority derived from Article I, section 8 of the Constitution, the Bureau of Public Debt was responsible for borrowing the money needed to operate the federal government, and is where donations to reduce the debt were made. It also accounted for the resulting debt and more recently, provides administrative and IT services to federal agencies. Principal operations were conducted in Washington, D.C. and Parkersburg, West Virginia. Additionally, Federal Reserve Banks, acting as Treasury's fiscal agents, operate critical systems in support of Public Debt Programs and perform a variety of processing and customer service functions in marketable and savings securities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics (particularly the panic of 1907) led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises. Over the years, events such as the Great Depression in the 1930s and the Great Recession during the 2000s have led to the expansion of the roles and responsibilities of the Federal Reserve System. Congress established three key objectives for monetary policy in the Federal Reserve Act: maximizing employment, stabilizing prices, and moderating long-term interest rates. The first two objectives are sometimes referred to as the Federal Reserve's dual mandate. Its duties have expanded over the years, and currently also include supervising and regulating banks, maintaining the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Management And Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, policies, and procedures to see whether they comply with the president's policies and coordinates inter-agency policy initiatives. Shalanda Young became OMB's acting director in March 2021, and was Senate confirmation, confirmed by the Senate in March 2022. History The Bureau of the Budget, OMB's predecessor, was established in 1921 as a part of the Department of the Treasury by the Budget and Accounting Act of 1921, which President Warren G. Harding signed into law. The Bureau of the Budget was moved to the Executive Office of the President of the United States, Executive Office of the President in 1939 and was run by Harold D. Smith during the government's rapid expansion of spending during World War II. James L. Sundquist, a staffer at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |