|
Internal Rotary Inspection System
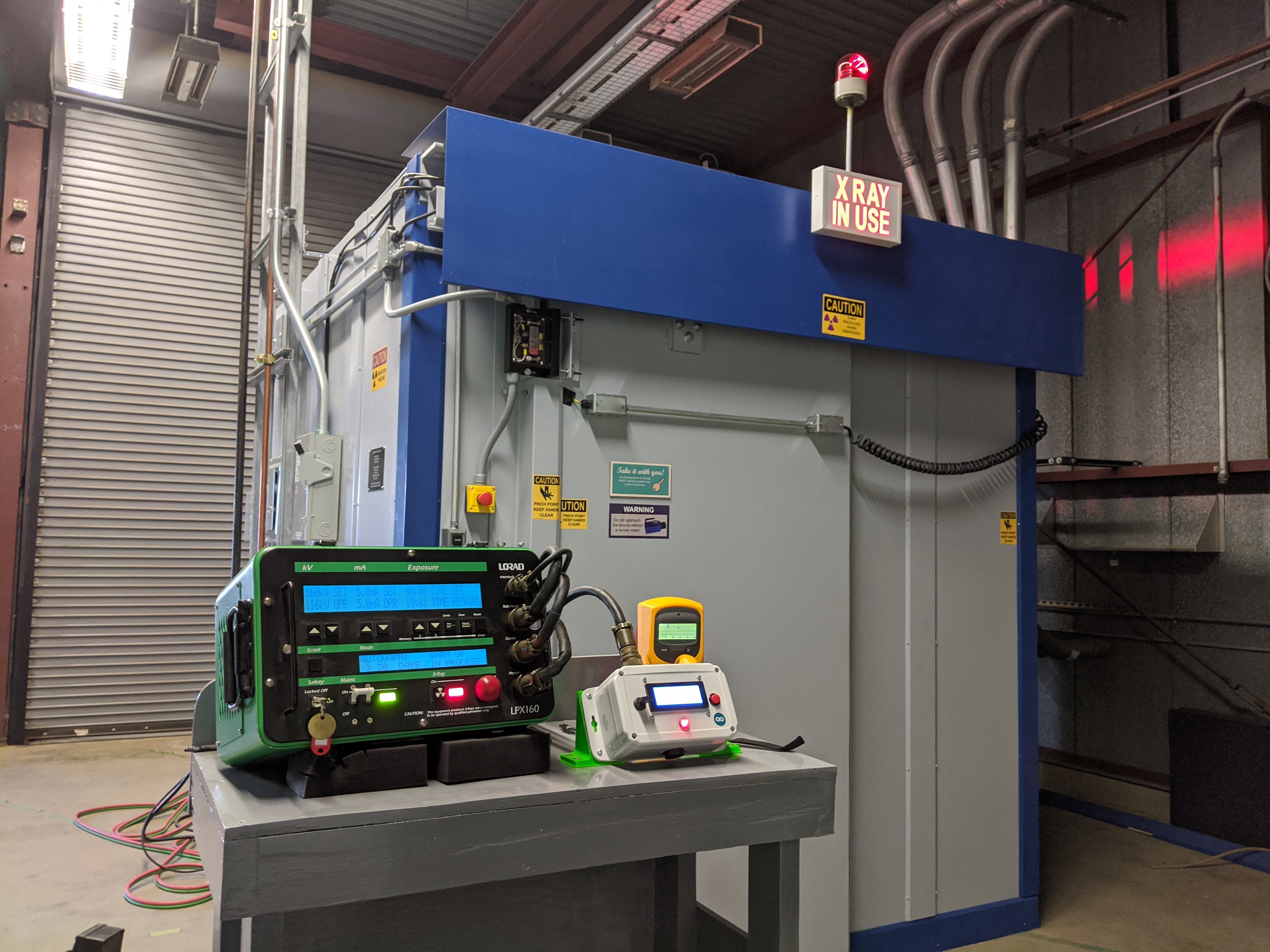
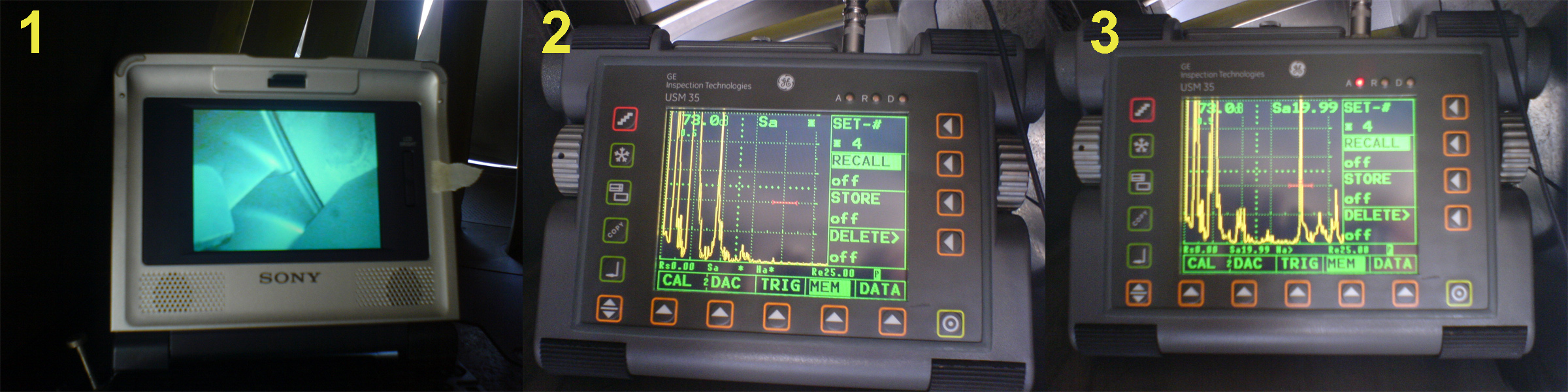
Internal rotary inspection system (IRIS) is an ultrasonic method for the nondestructive testing of pipes and tubes. The IRIS probe is inserted into a tube that is flooded with water, and the probe is pulled out slowly as the data is displayed and recorded. The ultrasonic beam allows detection of metal loss from the inside and outside of the tube wall. Principle of operation The IRIS probe consists of a rotating mirror that directs the ultrasonic beam into the tube wall. The mirror is driven by a small turbine that is rotated by the pressure of water being pumped in. As the probe is pulled the spinning motion of the mirror results in a helical Helical may refer to: * Helix, the mathematical concept for the shape * Helical engine, a proposed spacecraft propulsion drive * Helical spring, a coilspring * Helical plc, a British property company, once a maker of steel bar stock * Helicoil A t ... scan path. One of the key settings in the procedure is to ensure that the ultrasonic pulse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasonic Testing
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications, very short ultrasonic pulse-waves with center frequencies ranging from 0.1-15 MHz, and occasionally up to 50 MHz, are transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials. A common example is ultrasonic thickness measurement, which tests the thickness of the test object, for example, to monitor pipework corrosion. Ultrasonic testing is often performed on steel and other metals and alloys, though it can also be used on concrete, wood and composites, albeit with less resolution. It is used in many industries including steel and aluminium construction, metallurgy, manufacturing, aerospace, automotive and other transportation sectors. History The first efforts to use ultrasonic testing to detect flaws in solid material occurred in the 1930s.''Nondestructive F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nondestructive Testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, radiographic, ultrasonic, and visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, aeronautical engineering, medicine, and art. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipe (material)
A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than solid members. In common usage the words ''pipe'' and ''tube'' are usually interchangeable, but in industry and engineering, the terms are uniquely defined. Depending on the applicable standard to which it is manufactured, pipe is generally specified by a nominal diameter with a constant outside diameter (OD) and a schedule that defines the thickness. Tube is most often specified by the OD and wall thickness, but may be specified by any two of OD, inside diameter (ID), and wall thickness. Pipe is generally manufactured to one of several international and national industrial standards. While similar standards exist for specific industry applicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubing (material)
A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than solid members. In common usage the words ''pipe'' and '' tube'' are usually interchangeable, but in industry and engineering, the terms are uniquely defined. Depending on the applicable standard to which it is manufactured, pipe is generally specified by a nominal diameter with a constant outside diameter (OD) and a schedule that defines the thickness. Tube is most often specified by the OD and wall thickness, but may be specified by any two of OD, inside diameter (ID), and wall thickness. Pipe is generally manufactured to one of several international and national industrial standards. While similar standards exist for specific industry applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helix
A helix () is a shape like a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices. The word ''helix'' comes from the Greek word ''ἕλιξ'', "twisted, curved". A "filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is a surface called ''helicoid''. Properties and types The ''pitch'' of a helix is the height of one complete helix turn, measured parallel to the axis of the helix. A double helix consists of two (typically congruent) helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. A circular helix (i.e. one with constant radius) has constant band curvature and constant torsion. A ''conic helix'', also known as a ''conic spiral'', may be defined as a spiral on a conic surface, with the distance to the apex an expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Field Testing
Remote field testing (RFT) is a method of nondestructive testing using low-frequency AC. whose main application is finding defects in steel pipes and tubes. RFT is also referred to as remote field eddy current testing (RFEC or RFET). RFET is sometimes expanded as remote field electromagnetic technique, although a magnetic, rather than electromagnetic field is used. An RFT probe is moved down the inside of a pipe and is able to detect inside and outside defects with approximately equal sensitivity (although it can not discriminate between the two). Although RFT works in nonferromagnetic materials such as copper and brass, its sister technology eddy-current testing is preferred. The basic RFT probe consists of an exciter coil (also known as a transmit or send coil) which sends a signal to the detector (or receive coil). The exciter coil is pumped with an AC current and emits a magnetic field. The field travels outwards from the exciter coil, through the pipe wall, and along the pipe. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nondestructive Testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, radiographic, ultrasonic, and visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, aeronautical engineering, medicine, and art. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |