|
Interdiction Assault Ship
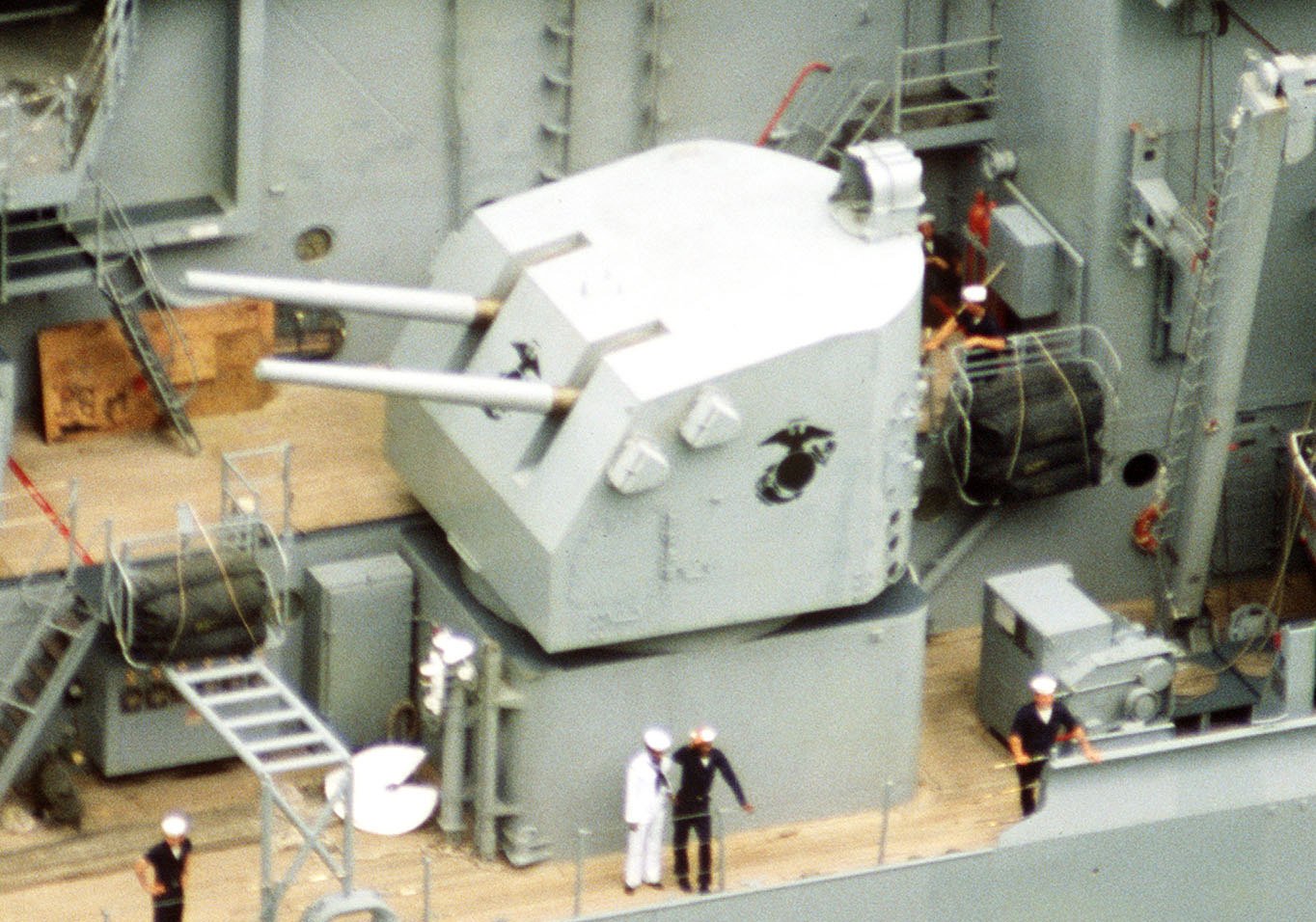
The Interdiction Assault Ship (IAS) was an aircraft cruiser conversion project in 1980 for the ''Iowa''-class battleships that would have removed the aft main gun turret. This would free up space for a V-shaped ramped flight deck (the base of the V would have been on the ship's stern, while each leg of the V would extend forward, so that planes taking off would fly past the ship's exhaust stacks and conning tower), while a new hangar would be added with two elevators, which would support up to twelve McDonnell Douglas AV-8B Harrier II jump-jets. These aviation facilities could also support helicopters, SEAL teams and up to 500 Marines for an air assault. In the empty space between the V flight deck would be up to 320 missile silos accommodating a mixture of Tomahawk land attack missiles, ASROC anti-submarine rockets and Standard surface-to-air missiles. The existing five-inch gun turrets would be replaced with 155-millimeter howitzers for naval gunfire support. These modifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Cruiser
The aircraft cruiser (also known as aviation cruiser or cruiser-carrier) is a warship that combines the features of the aircraft carrier and a surface warship such as a cruiser or battleship. Early types The first aircraft cruiser was originally a 1930s experimental concept of creating an all-around warship. The early aircraft cruisers were usually armed with relatively heavy artillery, mines and a number of aircraft fitted with floats (making the ship a kind of seaplane tender/ fighter catapult ship). The early aircraft cruiser turned out to be an unsuccessful design. The rapid development of naval aircraft in the 1930s quickly rendered the vessels obsolete, and they were rebuilt e.g. as anti-aircraft cruisers. A United States design for a flight deck cruiser from 1930,Friedman 1983, p.179. was described as "a light cruiser forwards ndone half of a aft". Although not built, similar ships were created during and after World War II as reconstructions and later from the kee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iowa-class Battleship
The ''Iowa'' class was a class of six fast battleships ordered by the United States Navy in 1939 and 1940. They were initially intended to intercept fast capital ships such as the Japanese while also being capable of serving in a traditional battle line alongside slower battleships and act as its "fast wing". The ''Iowa'' class was designed to meet the Second London Naval Treaty's "escalator clause" limit of standard displacement. Four vessels, , , , and , were completed; two more, and , were laid down but canceled in 1945 and 1958, respectively, before completion, and both hulls were scrapped in 1958–1959. The four ''Iowa''-class ships were the last battleships commissioned in the US Navy. All older US battleships were decommissioned by 1947 and stricken from the ''Naval Vessel Register'' (NVR) by 1963. Between the mid-1940s and the early 1990s, the ''Iowa''-class battleships fought in four major US wars. In the Pacific Theater of World War II, they served primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Deck
The flight deck of an aircraft carrier is the surface from which its aircraft take off and land, essentially a miniature airfield at sea. On smaller naval ships which do not have aviation as a primary mission, the landing area for helicopters and other VTOL aircraft is also referred to as the flight deck. The official U.S. Navy term for these vessels is "air-capable ships". Flight decks have been in use upon ships since 1910, the American pilot Eugene Ely being the first individual to take off from a warship. Initially consisting of wooden ramps built over the forecastle of capital ships, a number of battlecruisers, including the British and , the American and , and the Japanese Akagi and battleship Kaga, were converted to aircraft carriers during the interwar period. The first aircraft carrier to feature a full-length flight deck, akin to the configuration of the modern vessels, was the converted liner . The armoured flight deck was another innovation pioneered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
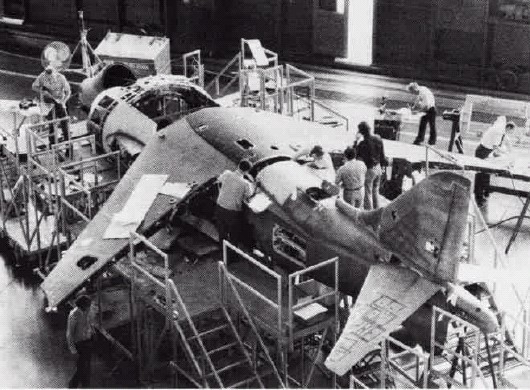
McDonnell Douglas AV-8B Harrier II
The McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) AV-8B Harrier II is a single-engine ground-attack aircraft that constitutes the second generation of the Harrier family, capable of vertical or short takeoff and landing (V/STOL). The aircraft is primarily employed on light attack or multi-role missions, ranging from close air support of ground troops to armed reconnaissance. The AV-8B is used by the United States Marine Corps (USMC), the Spanish Navy, and the Italian Navy. A variant of the AV-8B, the British Aerospace Harrier II, was developed for the British military, while another, the TAV-8B, is a dedicated two-seat trainer. The project that eventually led to the AV-8B's creation started in the early 1970s as a cooperative effort between the United States and United Kingdom, aimed at addressing the operational inadequacies of the first-generation Hawker Siddeley Harrier. Early efforts centered on a larger, more powerful Pegasus engine to dramatically improve the capabilities of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy SEALs
The United States Navy Sea, Air, and Land (SEAL) Teams, commonly known as Navy SEALs, are the U.S. Navy's primary special operations force and a component of the Naval Special Warfare Command. Among the SEALs' main functions are conducting small-unit special operation missions in maritime, jungle, urban, arctic, mountainous, and desert environments. SEALs are typically ordered to capture or to kill high level targets, or to gather intelligence behind enemy lines. All active SEALs are members of the U.S. Navy. The CIA's highly secretive and elite Special Operations Group (SOG) recruits operators from SEAL Teams, with joint operations going back to the MACV-SOG during the Vietnam War. This cooperation still exists today, as evidenced by military operations in Iraq and Afghanistan. History Origins Although not formally founded until 1962, the modern-day U.S. Navy SEALs trace their roots to World War II. The United States Military recognized the need for the covert reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
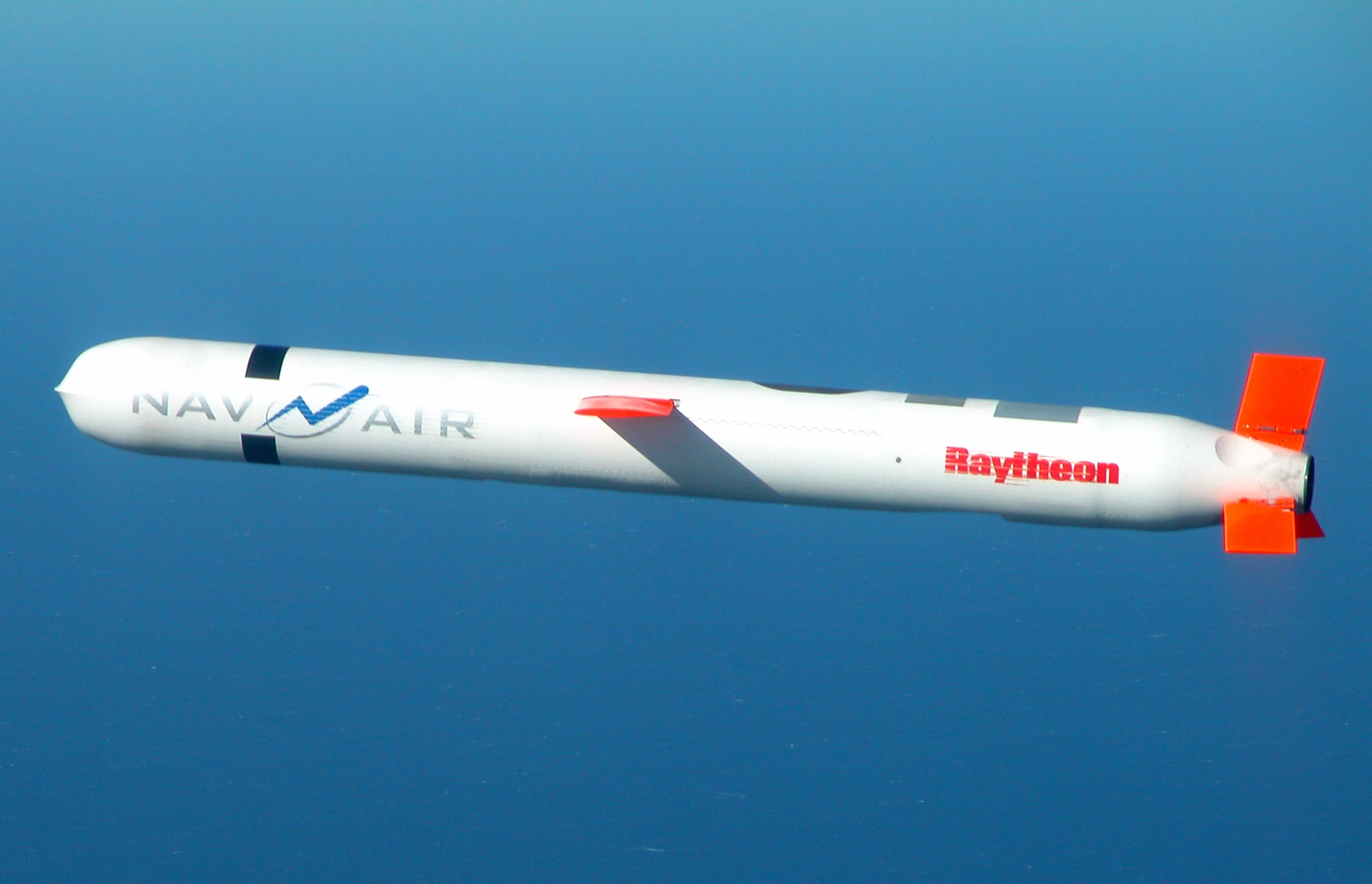
Tomahawk (missile)
The Tomahawk () Land Attack Missile (TLAM) is a long-range, all-weather, jet-powered, subsonic cruise missile that is primarily used by the United States Navy and Royal Navy in ship and submarine-based land-attack operations. Under contract from the U.S. Navy, the Tomahawk was designed at the APL/JHU in a project led by James Walker near Laurel, Maryland, and was first manufactured by General Dynamics in the 1970s. It was intended to fill the role of a medium- to long-range, low-altitude missile that could be launched from a naval surface warfare platform, and featured a modular design accommodating a wide variety of warhead, guidance, and range capabilities. At least six variants and multiple upgraded versions of the TLAM have been added since the original design was introduced, including air-, sub-, and ground-launched variants with conventional and nuclear armaments. In 1992–1994, McDonnell Douglas Corporation was the sole supplier of Tomahawk Missiles and produced Block I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASROC
The RUR-5 ASROC (for "Anti-Submarine Rocket") is an all-weather, all sea-conditions anti-submarine missile system. Developed by the United States Navy in the 1950s, it was deployed in the 1960s, updated in the 1990s, and eventually installed on over 200 USN surface ships, specifically cruisers, destroyers, and frigates. The ASROC has been deployed on scores of warships of many other navies, including Canada, Germany, Italy, Japan, the Republic of China, Greece, Pakistan and others. History ASROC started development as the Rocket Assisted Torpedo (RAT) program by the Naval Ordnance Test Station at China Lake in the early 1950s to develop a surface warship ASW weapon to counter the new post-World War II submarines which ran quieter, at much higher speed and could attack from much longer range with high speed homing torpedoes. In addition, the goal was to take advantage of modern sonars with a much larger detection range. An extended range torpedo delivered by parachute from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
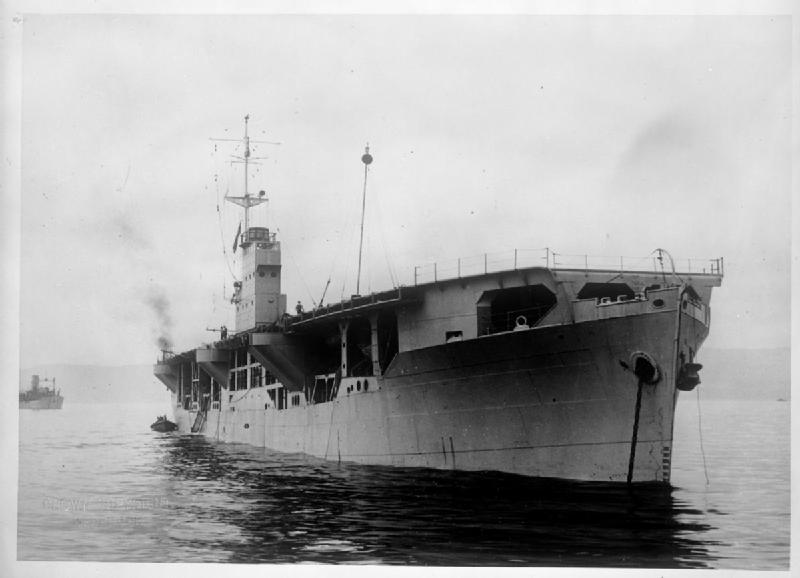
Fighter Catapult Ship
Fighter catapult ships also known as Catapult Armed Ships were an attempt by the Royal Navy to provide air cover at sea. Five ships were acquired and commissioned as Naval vessels early in the Second World War, and these were used to accompany convoys. The concept was extended to merchant ships which were also equipped with rocket assisted launch systems and known as Catapult Aircraft Merchantmen ( CAM ships). Both classes could launch a disposable fighter (usually a Hawker Hurricane) to fight off a threat, with the pilot expected to be rescued after either ditching the aircraft or bailing out close to the launching ship. The ships There were five fighter catapult ships, collectively known as the ''Pegasus'' class. Two, ''Patia'' and ''Springbank'', were lost during the war. They were each equipped with a single Fairey Fulmar or "Hurricat" (an adapted Hawker Hurricane Mk.1A). See also * List of ships of the Second World War * List of aircraft carriers of the Second World War * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merchant Aircraft Carrier
A merchant aircraft carrier (also known as a MAC ship, the Admiralty's official 'short name') was a limited-purpose aircraft carrier operated under British and Dutch civilian registry during World War II. MAC ships were adapted by adding a flight deck to a bulk grain ship or oil tanker enabling it to operate anti-submarine aircraft in support of Allied convoys during the Battle of the Atlantic. Despite their quasi-military function, MAC ships retained their mercantile status, continued to carry cargo and operated under civilian command. MAC ships entered service from May 1943 when they began to supplement and supplant escort carriers, and remained operational until the end of the war in Europe. Development In 1940, Captain M. S. Slattery RN, Director of Air Material at the Admiralty, proposed a scheme for converting merchant ships into aircraft carriers as a follow-up to the CAM ship project. Slattery proposed fitting a flight deck equipped with two arrester wires and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaplane Tender
A seaplane tender is a boat or ship that supports the operation of seaplanes. Some of these vessels, known as seaplane carriers, could not only carry seaplanes but also provided all the facilities needed for their operation; these ships are regarded by some as the first aircraft carriers and appeared just before the First World War. Terminology In maritime parlance a tender is a vessel that is used to support the operation of other vessels. In British usage, the term tender was used for small craft, with the term depot ship being used for large seagoing vessels. Flying boats and float planes even when based at home in ports and harbour had a need for small support vessels to operate.p British tenders were small craft of launch to pinnace size. These were used to ferry crews, stores and supplies between shore and the aircraft, to maintain the buoys used to mark out "taxiways" and "runways" and to keep these clear of debris to prevent foreign object damage, and in the case o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Cruiser Classes
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_1936.jpg)