|
Integrated Reception System
An integrated reception system (IRS) provides broadcast signals from multiple sources (typically terrestrial television Terrestrial television or over-the-air television (OTA) is a type of television broadcasting in which the signal transmission occurs via radio waves from the terrestrial (Earth-based) transmitter of a television station, TV station to a televis ..., FM radio, DAB digital radio and satellite TV) to multiple outlets, via a single aerial cluster and signal booster-distributor. The most obvious use for such a system is in communal housing blocks, where one aerial cluster can replace many aerials serving individual dwellings (e.g. flats or apartments). The predecessor to IRS was MATV- master aerial television- which provided communal housing with terrestrial TV signals only. Because the booster-distributor boxes within such systems usually need replacing to cope with digital terrestrial TV signals, many landlords are opting to replace the entire system with IRS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
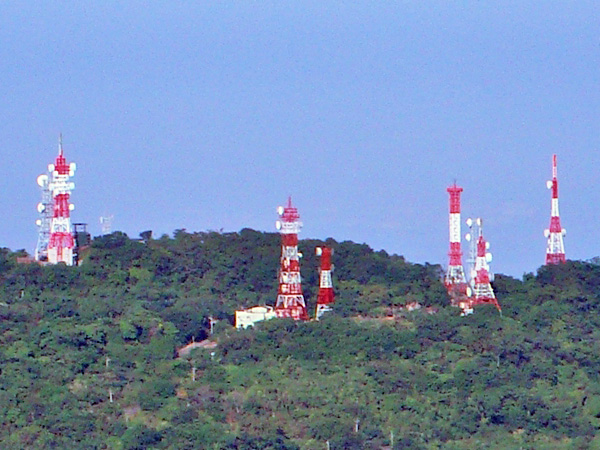
Terrestrial Television
Terrestrial television or over-the-air television (OTA) is a type of television broadcasting in which the signal transmission occurs via radio waves from the terrestrial (Earth-based) transmitter of a television station, TV station to a television set, TV receiver having an television antenna, antenna. The term ''terrestrial'' is more common in Europe and Latin America, while in Canada and the United States it is called ''over-the-air'' or simply ''broadcast''. This type of Television broadcasting, TV broadcast is distinguished from newer technologies, such as satellite television (direct broadcast satellite or DBS television), in which the signal is transmitted to the receiver from an overhead satellite; cable television, in which the signal is carried to the receiver through a coaxial cable, cable; and Internet Protocol television, in which the signal is received over an Internet stream or on a network utilizing the Internet Protocol. Terrestrial television stations broadcast o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FM Radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is capable of higher fidelity—that is, more accurate reproduction of the original program sound—than other broadcasting technologies, such as AM broadcasting. It is also less susceptible to common forms of interference, reducing static and popping sounds often heard on AM. Therefore, FM is used for most broadcasts of music or general audio (in the audio spectrum). FM radio stations use the very high frequency range of radio frequencies. Broadcast bands Throughout the world, the FM broadcast band falls within the VHF part of the radio spectrum. Usually 87.5 to 108.0 MHz is used, or some portion thereof, with few exceptions: * In the former Soviet republics, and some former Eastern Bloc countries, the older 65.8–74 M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DAB Digital Radio
Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services. Types In digital broadcasting systems, the analog audio signal is digital audio, digitized, Audio compression (data), compressed using an audio coding format such as AAC+ (MDCT) or MPEG-1 Audio Layer II, MP2, and transmitted using a digital modulation scheme. The aim is to increase the number of radio programs in a given spectrum, to improve the audio quality, to eliminate fading problems in mobile environments, to allow additional datacasting services, and to decrease the transmission power or the number of transmitters required to cover a region. However, analog radio (AM and FM) is still more popular and listening to radio over IP (Internet Protocol) is growing in popularity. In 2012 four digital wireless radio systems are recognized by the International Telecommunicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite TV
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter. A satellite receiver then decodes the desired television program for viewing on a television set. Receivers can be external set-top boxes, or a built-in television tuner. Satellite television provides a wide range of channels and services. It is usually the only television available in many remote geographic areas without terrestrial television or cable television service. Modern systems signals are relayed from a communications satellite on the X band (8–12 GHz) or Ku band (12–18 GHz) frequencies requiring only a small dish less than a meter in diameter. The first satellite TV systems were an obsolete type now known as television receive-only. These s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Terrestrial Television
Digital terrestrial television (DTTV or DTT, or DTTB with "broadcasting") is a technology for terrestrial television in which land-based (terrestrial) television stations broadcast television content by radio waves to televisions in consumers' residences in a digital format. DTTV is a major technological advance over the previous analog television, and has largely replaced analog which had been in common use since the middle of the 20th century. Test broadcasts began in 1998 with the changeover to DTTV (aka Analog Switchoff (ASO), or Digital Switchover (DSO)) beginning in 2006 and is now complete in many countries. The advantages of ''digital'' terrestrial television are similar to those obtained by digitising platforms such as cable TV, satellite, and telecommunications: more efficient use of limited radio spectrum bandwidth, provision of more television channels than analog, better quality images, and potentially lower operating costs for broadcasters (after the initia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Technology
Large-screen television technology (colloquially big-screen TV) developed rapidly in the late 1990s and 2000s. Prior to the development of thin-screen technologies, rear-projection television was standard for larger displays, and jumbotron, a non-projection video display technology, was used at stadiums and concerts. Various thin-screen technologies are being developed, but only liquid crystal display (LCD), plasma display (PDP) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) have been publicly released. Recent technologies like organic light-emitting diode (OLED) as well as not-yet-released technologies like surface-conduction electron-emitter display (SED) or field emission display (FED) are in development to replace earlier flat-screen technologies in picture quality. Large-screen technologies have almost completely displaced cathode-ray tubes (CRT) in television sales due to the necessary bulkiness of cathode-ray tubes. The diagonal screen size of a CRT television is limited to abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |