|
Intef II
Wahankh Intef II (also Inyotef II and Antef II) was the third ruler of the Eleventh Dynasty of Egypt during the First Intermediate Period. He reigned for almost fifty years from 2112 BC to 2063 BC. His capital was located at Thebes. In his time, Egypt was split between several local dynasties. He was buried in a saff tomb at El-Tarif. Family Intef's parents were Mentuhotep I and Neferu I. His predecessor Intef I may have been his brother. Intef was succeeded by his son Intef III. Reign After the death of the nomarch Ankhtifi, Intef was able to unite all the southern nomes down to the First Cataract. After this he clashed with his main rivals, the kings of Herakleopolis Magna for the possession of Abydos. The city changed hands several times, but Intef II was eventually victorious, extending his rule north to the thirteenth nome. After these wars, more friendly relations were established and the rest of Intef's reign was peaceful. The discovery of a statue of Intef II, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neferu I
Neferu I ("the beauty") was the first queen of Ancient Egyptian Eleventh dynasty. She was a wife of the Pharaoh Mentuhotep I. Her sons were Intef I and Intef II and she was a grandmother of Intef III Intef III was the third pharaoh of the Eleventh Dynasty of Egypt during the late First Intermediate Period in the 21st century BC, at a time when Egypt was divided in two kingdoms. The son of his predecessor Intef II and father of his successo ... and Queen Iah, his wife. She was also a great-grandmother of Neferu II. She is mentioned on one stela. It is possible that she is the same as the Queen Neferukayet, who is thought to be wife of Intef II. Her titles would be then: "King's wife, his beloved", "King's daughter" and "Royal Ornament". References Queens consort of the Eleventh Dynasty of Egypt Mentuhotep I {{Africa-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Museum Of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 Fifth Avenue, along the Museum Mile on the eastern edge of Central Park on Manhattan's Upper East Side, is by area one of the world's largest art museums. The first portion of the approximately building was built in 1880. A much smaller second location, The Cloisters at Fort Tryon Park in Upper Manhattan, contains an extensive collection of art, architecture, and artifacts from medieval Europe. The Metropolitan Museum of Art was founded in 1870 with its mission to bring art and art education to the American people. The museum's permanent collection consists of works of art from classical antiquity and ancient Egypt, paintings, and sculptures from nearly all the European masters, and an extensive collection of America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
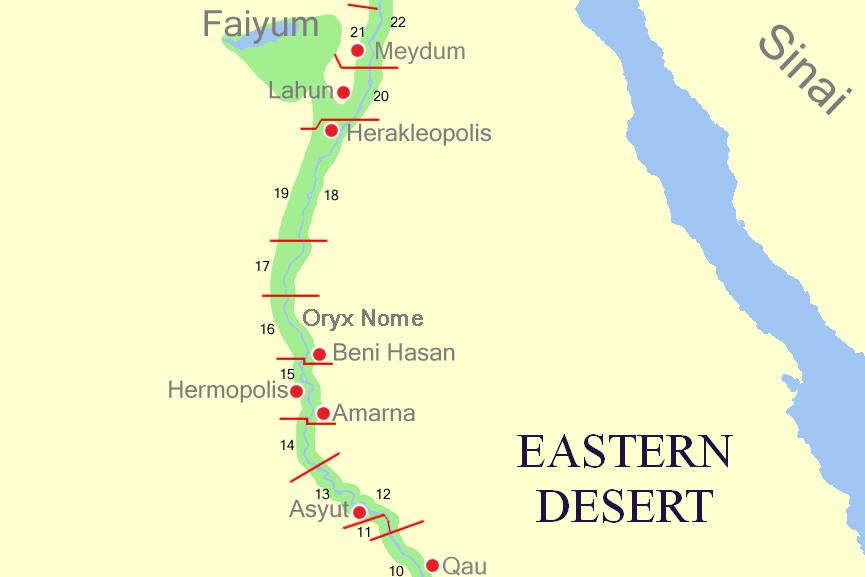
Abydos, Egypt
Abydos ( ar, أبيدوس, Abīdūs or ; Sahidic cop, Ⲉⲃⲱⲧ ') is one of the oldest cities of ancient Egypt, and also of the eighth nome in Upper Egypt. It is located about west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of El Araba El Madfuna and El Balyana. In the ancient Egyptian language, the city was called Abdju (''ꜣbḏw'' or ''AbDw''). The English name ''Abydos'' comes from the Greek , a name borrowed by Greek geographers from the unrelated city of Abydos on the Hellespont. Considered one of the most important archaeological sites in Egypt, the sacred city of Abydos was the site of many ancient temples, including Umm el-Qa'ab, a royal necropolis where early pharaohs were entombed. These tombs began to be seen as extremely significant burials and in later times it became desirable to be buried in the area, leading to the growth of the town's importance as a cult site. Today, Abydos is notable for the memorial temple of Seti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idudju-iker
Idudju-iker was an ancient Egyptian high official who lived around 2050 BC in the 11th Dynasty. His title ''foremost one of the chiefs of Lower Nubia'' demonstrates his important position in the administration of Lower Nubia. Idudju-iker is only known from the fragments of a stela found reused in the Second Intermediate Period tomb of king Senebkay at Abydos. On the stela Idudju-iker bears the titles ''sole friend'', ''count'' and ''hereditary prince'' (smr waty, haty-a, iry-pat) but is also called ''foremost one of the chiefs of Lower Nubia'' (HAt HqAw nw wAtwAt). The first three titles place him high in the social hierarchy, while the latter title is so far unique. He was evidently the highest official in charge of Lower Nubia. The stela contains an autobiography of Idudju-iker that is heavily destroyed. Lower Nubia and the land of the Medjay are mentioned and the text also refers to many rituals that Idudju-iker performed at Abydos. On stylistic grounds, the stela can be dated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Kab
El Kab (or better Elkab) is an Upper Egyptian site on the east bank of the Nile at the mouth of the Wadi Hillal about south of Luxor (ancient Thebes). El Kab was called Nekheb in the Egyptian language ( , Late Coptic: ), a name that refers to Nekhbet, the goddess depicted as a white vulture.Limme, Luc. "Elkab, 1937–2007: Seventy Years of Belgian Archaeological Research." British Museum Studies in Ancient Egypt and Sudan (2008): 15-50. The British Museum. Web. 24 Oct. 2012. . In Greek it was called Eileithyias polis, "city of the goddess Eileithyia". El Kab consists of prehistoric and ancient Egyptian settlements, rock-cut tombs of the early Eighteenth Dynasty (1550–1295 BC), remains of temples dating from the Early Dynastic period (3100–2686 BC) to the Ptolemaic Kingdom (332–30 BC), as well as part of the walls of a Coptic monastery. This site was first scientifically excavated by James Quibell at the end of the nineteenth century, but other archaeologists have sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thinis
Thinis (Greek: Θίνις ''Thinis'', Θίς ''This'' ; Egyptian: Tjenu; cop, Ⲧⲓⲛ; ar, ثينيس) was the capital city of the first dynasties of ancient Egypt. Thinis remains undiscovered but is well attested by ancient writers, including the classical historian Manetho, who cites it as the centre of the Thinite Confederacy, a tribal confederation whose leader, Menes (or Narmer), united Egypt and was its first pharaoh. Thinis began a steep decline in importance from Dynasty III, when the capital was relocated to Memphis, which was thought to be the first true and stable capital after the unification of old Egypt by Menes. Thinis's location on the border of the competing Heracleopolitan and Theban dynasties of the First Intermediate Period and its proximity to certain oases of possible military importance ensured Thinis some continued significance in the Old and New Kingdoms. This was a brief respite and Thinis eventually lost its position as a regional admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Egypt
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the 19th century that archaeologists felt the need to divide Upper Egypt in two. As a result, they coined the term "Middle Egypt" for the stretch of river between Cairo and the Qena Bend. It was also associated with a region termed " Heptanomis" (; Greek: , in Ptol. iv. 5. § 55; more properly or , in Dionysius Periegetes 251; and sometimes ; meaning "Seven Nomes", a " nome" being a subdivision of ancient Egypt), generally as the district which separates the Thebaïd from the Delta. Middle Egypt today can be identified as the part of the Nile Valley that, while geographically part of Upper Egypt, is culturally closer to Lower Egypt. For instance, in terms of language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Concept Of The Soul
The ancient Egyptians believed that a soul ( kꜣ and bꜣ; Egypt. pron. ka/ba) was made up of many parts. In addition to these components of the soul, there was the human body (called the ''ḥꜥ'', occasionally a plural '' ḥꜥw'', meaning approximately "sum of bodily parts"). According to ancient Egyptian creation myths, the god Atum created the world out of chaos, utilizing his own magic ( ḥkꜣ). Because the earth was created with magic, Egyptians believed that the world was imbued with magic and so was every living thing upon it. When humans were created, that magic took the form of the soul, an eternal force which resided in and with every human. The concept of the soul and the parts which encompass it has varied from the Old Kingdom to the New Kingdom, at times changing from one dynasty to another, from five parts to more. Most ancient Egyptian funerary texts reference numerous parts of the soul: Collectively, these spirits of a dead person were called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephantine
Elephantine ( ; ; arz, جزيرة الفنتين; el, Ἐλεφαντίνη ''Elephantíne''; , ) is an island on the Nile, forming part of the city of Aswan in Upper Egypt. The archaeological sites on the island were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979 along with other examples of Upper Egyptian architecture, as part of the " Nubian Monuments from Abu Simbel to Philae" (despite Elephantine being neither Nubian, nor between Abu Simbel and Philae). Geography Elephantine is from north to south, and is across at its widest point. The layout of this and other nearby islands in Aswan can be seen from west bank hillsides along the Nile. The island is located just downstream of the First Cataract, at the southern border of Upper Egypt with Lower Nubia. This region above is referred to as Upper Egypt because it is further up the Nile. The island may have received its name after its shape, which in aerial views is similar to that of an elephant tusk, or from the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. The British Museum was the first public national museum to cover all fields of knowledge. The museum was established in 1753, largely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods (followed by the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom), which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley. The concept of an "Old Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by the German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and the 20th centuries. Not only was the last king of the Early Dynastic Period related to the first two kings of the Old Kingdom, but the "cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)