|
Instantaneously Trained Neural Networks
Instantaneously trained neural networks are feedforward artificial neural networks that create a new hidden neuron node for each novel training sample. The weights to this hidden neuron separate out not only this training sample but others that are near it, thus providing generalization. Kak, S. On training feedforward neural networks. Pramana, vol. 40, pp. 35-42, 199 This separation is done using the nearest hyperplane that can be written down instantaneously. In the two most important implementations the neighborhood of generalization either varies with the training sample (CC1 network) or remains constant (CC4 network). These networks use unary coding for an effective representation of the data sets. This type of network was first proposed in a 1993 paper of Subhash Kak. Since then, instantaneously trained neural networks have been proposed as models of short term learning and used in web search, and financial time series prediction applications. They have also been used in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons, which loosely model the neurons in a biological brain. Each connection, like the synapses in a biological brain, can transmit a signal to other neurons. An artificial neuron receives signals then processes them and can signal neurons connected to it. The "signal" at a connection is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs. The connections are called ''edges''. Neurons and edges typically have a '' weight'' that adjusts as learning proceeds. The weight increases or decreases the strength of the signal at a connection. Neurons may have a threshold such that a signal is sent only if the aggregate signal crosses that threshold. Typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unary Coding
Unary coding, or the unary numeral system and also sometimes called thermometer code, is an entropy encoding that represents a natural number, ''n'', with a code of length ''n'' + 1 ( or ''n'' ), usually ''n'' ones followed by a zero (if ''natural number'' is understood as ''non-negative integer'') or with ''n'' − 1 ones followed by a zero (if ''natural number'' is understood as ''strictly positive integer''). For example 5 is represented as 111110 or 11110. Some representations use ''n'' or ''n'' − 1 zeros followed by a one. The ones and zeros are interchangeable without loss of generality. Unary coding is both a prefix-free code and a self-synchronizing code. Unary coding is an optimally efficient encoding for the following discrete probability distribution :\operatorname(n) = 2^\, for n=1,2,3,.... In symbol-by-symbol coding, it is optimal for any geometric distribution :\operatorname(n) = (k-1)k^\, for which ''k'' ≥ φ = 1.6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subhash Kak
Subhash Kak is an Indian-American computer scientist and historical revisionist. He is the Regents Professor of Computer Science Department at Oklahoma State University–Stillwater, an honorary visiting professor of engineering at Jawaharlal Nehru University, and a member of the Indian Prime Minister's Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC). Kak has published on the history of science, the philosophy of science, ancient astronomy, and the history of mathematics. Kak has also published on archaeoastronomy, and advocated the idea of Indigenous Aryans. Many scholars have rejected his theories on these topics in entirety, and his writings have been heavily criticized. Kak has been associated with Hindu fanatics and many scholars do not take his opinion seriously. In 2019, the Government of India awarded him the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award in India, for his contributions on the history of mathematics, science, ancient astronomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of learning in certain plants. Some learning is immediate, induced by a single event (e.g. being burned by a hot stove), but much skill and knowledge accumulate from repeated experiences. The changes induced by learning often last a lifetime, and it is hard to distinguish learned material that seems to be "lost" from that which cannot be retrieved. Human learning starts at birth (it might even start before in terms of an embryo's need for both interaction with, and freedom within its environment within the womb.) and continues until death as a consequence of ongoing interactions between people and their environment. The nature and processes involved in learning are studied in many established fields (including educational psychology, neurop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Search
Web most often refers to: * Spider web, a silken structure created by the animal * World Wide Web or the Web, an Internet-based hypertext system Web, WEB, or the Web may also refer to: Computing * WEB, a literate programming system created by Donald Knuth * GNOME Web, a Web browser * Web.com, a web-design company * Webs (web hosting), a Web hosting and website building service Engineering * Web (manufacturing), continuous sheets of material passed over rollers ** Web, a roll of paper in offset printing * Web, the vertical element of an I-beam or a rail profile * Web, the interior beams of a truss Films * ''Web'' (2013 film), a documentary * ''Webs'' (film), a 2003 science-fiction movie * ''The Web'' (film), a 1947 film noir * Charlotte's Web (2006 film) Literature * ''Web'' (comics), a MLJ comicbook character (created 1942) * ''Web'' (novel), by John Wyndham (1979) * The Web (series), a science fiction series (1997–1999) * World English Bible, a public-domain Bible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Series Prediction
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Examples of time series are heights of ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. A time series is very frequently plotted via a run chart (which is a temporal line chart). Time series are used in statistics, signal processing, pattern recognition, econometrics, mathematical finance, weather forecasting, earthquake prediction, electroencephalography, control engineering, astronomy, communications engineering, and largely in any domain of applied Applied science, science and engineering which involves Time, temporal measurements. Time series ''analysis'' comprises methods for analyzing time series data in order to extract meaningful statistics and other characteristics of the data. Time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Document Classification
Document classification or document categorization is a problem in library science, information science and computer science. The task is to assign a document to one or more classes or categories. This may be done "manually" (or "intellectually") or algorithmically. The intellectual classification of documents has mostly been the province of library science, while the algorithmic classification of documents is mainly in information science and computer science. The problems are overlapping, however, and there is therefore interdisciplinary research on document classification. The documents to be classified may be texts, images, music, etc. Each kind of document possesses its special classification problems. When not otherwise specified, text classification is implied. Documents may be classified according to their subjects or according to other attributes (such as document type, author, printing year etc.). In the rest of this article only subject classification is considered. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecture Notes In Computer Science
''Lecture Notes in Computer Science'' is a series of computer science books published by Springer Science+Business Media since 1973. Overview The series contains proceedings, post- proceedings, monographs, and Festschrift In academia, a ''Festschrift'' (; plural, ''Festschriften'' ) is a book honoring a respected person, especially an academic, and presented during their lifetime. It generally takes the form of an edited volume, containing contributions from the ...s. In addition, tutorials, state-of-the-art surveys, and "hot topics" are increasingly being included. The series is indexed by DBLP. See also *'' Monographiae Biologicae'', another monograph series published by Springer Science+Business Media *'' Lecture Notes in Physics'' *'' Lecture Notes in Mathematics'' *'' Electronic Workshops in Computing'', published by the British Computer Society References External links * Publications established in 1973 Computer science books Series of non-fiction books ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
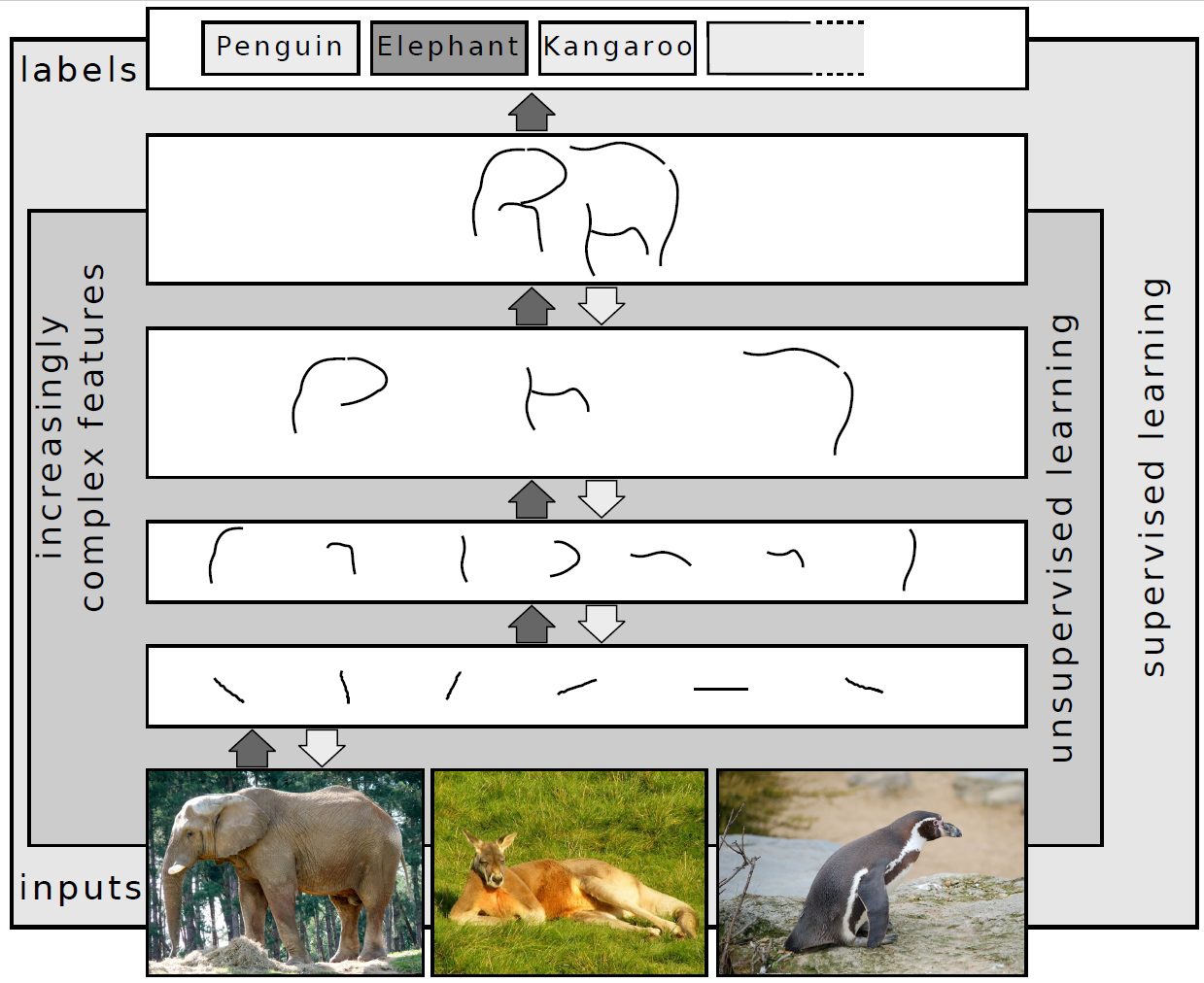
Deep Learning
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be Supervised learning, supervised, Semi-supervised learning, semi-supervised or Unsupervised learning, unsupervised. Deep-learning architectures such as #Deep_neural_networks, deep neural networks, deep belief networks, deep reinforcement learning, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks and Transformer (machine learning model), Transformers have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, Climatology, climate science, material inspection and board game programs, where they have produced results comparable to and in some cases surpassing human expert performance. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) were inspired by information processing and distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Neural Network
An optical neural network is a physical implementation of an artificial neural network with optical components. Early optical neural networks used a photorefractive Volume hologram to interconnect arrays of input neurons to arrays of output with synaptic weights in proportion to the multiplexed hologram's strength. Volume holograms were further multiplexed using spectral hole burning to add one dimension of wavelength to space to achieve four dimensional interconnects of two dimensional arrays of neural inputs and outputs. This research led to extensive research on alternative methods using the strength of the optical interconnect for implementing neuronal communications. Some artificial neural networks that have been implemented as optical neural networks include the Hopfield neural network and the Kohonen self-organizing map with liquid crystal spatial light modulators Optical neural networks can also be based on the principles of neuromorphic engineering, creating neuromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamming Weight
The Hamming weight of a string is the number of symbols that are different from the zero-symbol of the alphabet used. It is thus equivalent to the Hamming distance from the all-zero string of the same length. For the most typical case, a string of bits, this is the number of 1's in the string, or the digit sum of the binary representation of a given number and the ''ℓ''₁ norm of a bit vector. In this binary case, it is also called the population count, popcount, sideways sum, or bit summation. History and usage The Hamming weight is named after Richard Hamming although he did not originate the notion. The Hamming weight of binary numbers was already used in 1899 by James W. L. Glaisher to give a formula for the number of odd binomial coefficients in a single row of Pascal's triangle. Irving S. Reed introduced a concept, equivalent to Hamming weight in the binary case, in 1954. Hamming weight is used in several disciplines including information theory, coding theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |