|
Inspection Time
Inspection time refers to the exposure duration required for a human subject to reliably identify a simple stimulus. Typically a stimulus made up of two parallel lines differing in length and joined at the tops by a cross bar is presented (similar to the Greek letter Pi). The ability to quickly detect the identity of a stimulus is moderately heritable and correlates with the subject's IQ. Overview If asked which of the two lines in the figure below is longer; the left or the right, almost all non-visually impaired subjects can answer correctly 100% of the time. If, however, the stimulus is backward masked after a short period of time, the proportion of correct responses declines as the exposure duration reduces, and reliable individual differences emerge in the percent identified correctly at different intervals. The task itself was proposed by Doug Vickers as a measure of the rate of accumulation of information. Ted Nettelbeck, Chris Brand and others demonstrated it related q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi (letter)
Pi (uppercase Π, lowercase π and ϖ; el, πι ) is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiceless bilabial plosive . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 80. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Pe (). Letters that arose from pi include Latin P, Cyrillic Pe (П, п), Coptic pi (Ⲡ, ⲡ), and Gothic pairthra (𐍀). Uppercase Pi The uppercase letter Π is used as a symbol for: * In textual criticism, '' Codex Petropolitanus'', a 9th-century uncial codex of the Gospels, now located in St. Petersburg, Russia. * In legal shorthand, it represents a plaintiff. In science and engineering: * The product operator in mathematics, indicated with capital pi notation (in analogy to the use of the capital Sigma as summation symbol). * The osmotic pressure in chemistry. * The viscous stress tensor in continuum mechanics and fluid dynamics. Lowercase Pi The lowercase letter π is used as a symbol for: * The mathematical re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritability
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of Animal husbandry, breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of ''variation'' in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. The concept of heritability can be expressed in the form of the following question: "What is the proportion of the variation in a given trait within a population that is ''not'' explained by the environment or random chance?" Other causes of measured variation in a trait are characterized as environment (biophysical), environmental factors, including observational error. In human studies of heritability these are often apportioned into factors from "shared environment" and "non-shared environment" based on whether they tend to result in persons brought up in the same household being more or less similar to persons who were not. Heritability is estimated by comparing individual phenotypic variation among related individuals in a population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backward Masking
The concept of backward masking originated in psychoacoustics, referring to temporal masking of quiet sounds that occur moments before a louder sound. In cognitive psychology, visual backward masking involves presenting one visual stimulus (a "mask" or "masking stimulus") immediately after a brief (usually 30 ms) "target" visual stimulus resulting in a failure to consciously perceive the first stimulus.Breitmeyer, B.G. and Ogmen, H. (2007''Visual masking'' Scholarpedia, 2(7):3330. It is widely used in psychophysiological studies on fear and phobias that investigate the preattentive nonconscious reactions to fear-relevant stimuli. It is unknown how a later stimulus is able to block an earlier one. However, one theory for this phenomenon, known as the ''dual channel interaction'' theory, proposes that a fast signal created by the second stimulus is able to catch up to and overcome a slower signal sent from the first impulse. A similar phenomenon can occur when a masking stimulus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doug Vickers
Doug is a male personal name (or, depending on which definition of "personal name" one uses, part of a personal name). It is sometimes a given name (or "first name"), but more often it is hypocorism (affectionate variation of a personal name) which takes the place of a given name, usually Douglas. Notable people with the name include: Douglas Grosch, ex. People A–C * Doug Allison (1846–1916), American baseball player * Doug Anderson (other), multiple people * Doug Applegate (other), multiple people * Doug Armstrong (born 1964), Canadian National Hockey League team general manager * Doug Armstrong (broadcaster) (1931–2015), New Zealand cricketer, television sports broadcaster and politician * Doug Baldwin (born 1988), American football player * Doug Baldwin (ice hockey) (1922–2007), Canadian ice hockey player * Doug Bennett (other), multiple people * Doug Bereuter (born 1939), American former politician * Doug Bing (born 1950/51), Canadian polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ted Nettelbeck
Theodore Nettelbeck is an Australian psychologist and jazz pianist who is emeritus professor in the School of Psychology at the University of Adelaide. He is active in researching human intelligence and inspection time Inspection time refers to the exposure duration required for a human subject to reliably identify a simple stimulus. Typically a stimulus made up of two parallel lines differing in length and joined at the tops by a cross bar is presented (similar .... References External linksFaculty page Living people Australian psychologists Intelligence researchers University of Adelaide faculty Australian jazz pianists Year of birth missing (living people) {{Australia-academic-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chris Brand
Christopher Richard Brand (1 June 1943 – 28 May 2017) was a British psychological and psychometric researcher who gained media attention for his statements on race and intelligence and paedophilia. Brand was a proponent of IQ testing and the general intelligence factor, and was "a major influence in the spread of influence of inspection time as a theoretically interesting correlate of psychometric intelligence," according to Ian Deary and Pauline Smith. Life and career Brand was born in Preston, England on 1 June 1943. He went to Queen Elizabeth's Grammar School for Boys, and was a graduate of The Queen's College, Oxford, and a 1968–1970 Fellow of Nuffield College, Oxford. He was a Lecturer at University of Edinburgh, from 1970 to 1997, teaching in personality, psychopathology and philosophical problems and researching in factorial psychology. In the 1980s he served on the United Kingdom's Council for National Academic Awards. His 1996 book ''The g Factor'' garne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
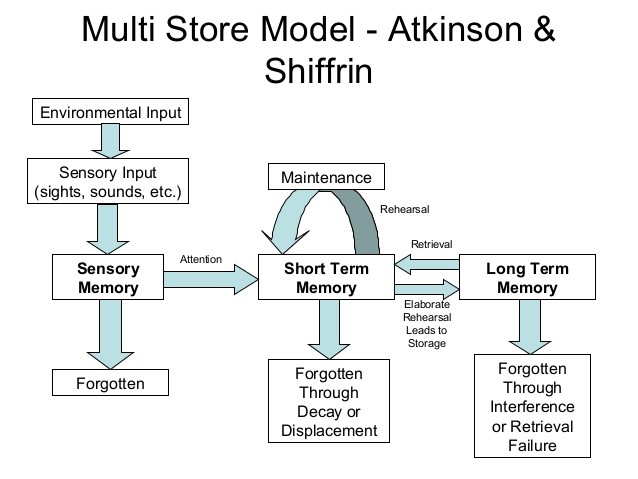
Information Processing
Information processing is the change (processing) of information in any manner detectable by an observer. As such, it is a process that ''describes'' everything that happens (changes) in the universe, from the falling of a rock (a change in position) to the printing of a text file from a digital computer system. In the latter case, an information processor (the printer) is changing the form of presentation of that text file (from bytes to glyphs). The computers up to this period function on the basis of programs saved in the memory, having no intelligence of their own. In cognitive psychology Within the field of cognitive psychology, information processing is an approach to the goal of understanding human thinking in relation to how they process the same kind of information as computers (Shannon & Weaver, 1963). It arose in the 1940s and 1950s, after World War II (Sternberg & Sternberg, 2012). The approach treats cognition as essentially computational in nature, with ''mind'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Jensen
Arthur Robert Jensen (August 24, 1923 – October 22, 2012) was an American psychologist and writer. He was a professor of educational psychology at the University of California, Berkeley. Jensen was known for his work in psychometrics and differential psychology, the study of how and why individuals differ behaviorally from one another. He was a major proponent of the hereditarian position in the nature and nurture debate, the position that genetics play a significant role in behavioral traits, such as intelligence and personality. He was the author of over 400 scientific papers published in refereed journals and sat on the editorial boards of the scientific journals ''Intelligence'' and ''Personality and Individual Differences''. Jensen was controversial, largely for his conclusions regarding the causes of race-based differences in IQ. A 2019 study found him to be the most controversial intelligence researcher among 55 persons covered. Early life Jensen was born Augu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illustration Of Inspection Time Stimulus
An illustration is a decoration, interpretation or visual explanation of a text, concept or process, designed for integration in print and digital published media, such as posters, flyers, magazines, books, teaching materials, animations, video games and films. An illustration is typically created by an illustrator. Digital illustrations are often used to make websites and apps more user-friendly, such as the use of emojis to accompany digital type. llustration also means providing an example; either in writing or in picture form. The origin of the word "illustration" is late Middle English (in the sense ‘illumination; spiritual or intellectual enlightenment’): via Old French from Latin ''illustratio''(n-), from the verb ''illustrare''. Illustration styles Contemporary illustration uses a wide range of styles and techniques, including drawing, painting, printmaking, collage, montage, digital design, multimedia, 3D modelling. Depending on the purpose, illustration ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nick Martin (scientist)
Nicholas Gordon Martin (born 14 February 1950) is an Australian behavior geneticist who has published over 1300 peer-reviewed articles on topics including the heritability of religion and intelligence and medical disorders such as endometriosis. Martin is among the most cited medical scientists in the Southern Hemisphere, with a number of citation classics including "''Genes, culture and personality: An empirical approach''" that he co-authored with Lindon Eaves and Hans Eysenck, "''Analysis of the p16 gene (CDKN2) as a candidate for the chromosome 9p melanoma susceptibility locus''" ( ''Nature'', and "''Genetic and environmental contributions to alcohol dependence risk in a national twin sample''". Early life Martin studied at the University of Adelaide. In 1972 he established a sample of twins in Adelaide while completing his honours thesis. Academic career Martin moved to the United Kingdom to complete a PhD in 1977 under Lindon Eaves at the University of Birmingham. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information; and to retain it as knowledge to be applied to adaptive behaviors within an environment or context. The term rose to prominence during the early 1900s. Most psychologists believe that intelligence can be divided into various domains or competencies. Intelligence has been long-studied in humans, and across numerous disciplines. It has also been observed in the Animal cognition, cognition of non-human animals. Some researchers have suggested that Plant, plants exhibit forms of intelligence, though this remains controversial. Intelligence in computers or other machines is called artificial intelligence. Etymology The word ''wikt:intelligence#English, intelligence'' derives from the Latin nouns ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
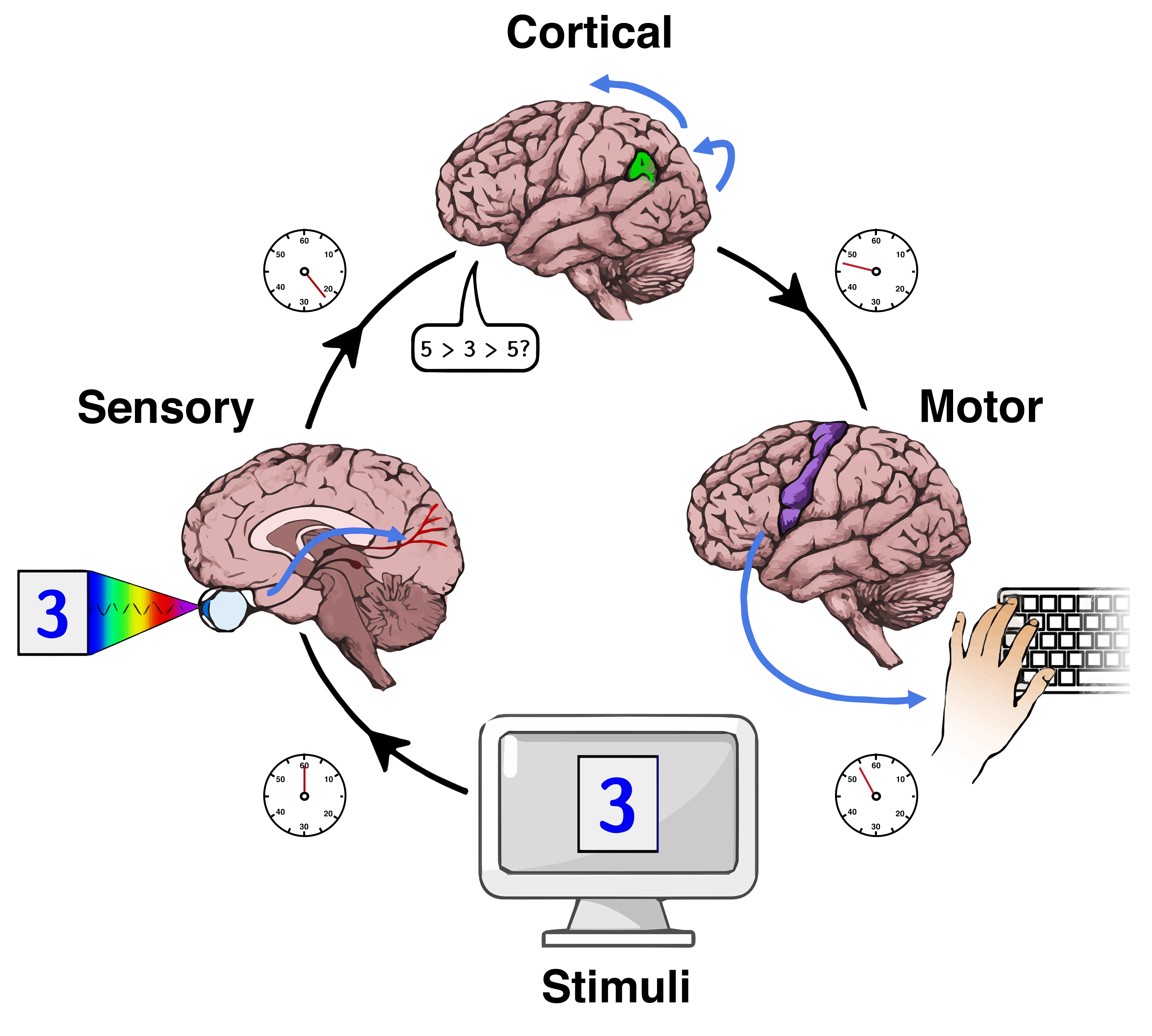
Mental Chronometry
Mental chronometry is the scientific study of processing speed or reaction time on cognitive tasks to infer the content, duration, and temporal sequencing of mental operations. Reaction time (RT; sometimes referred to as "response time") is measured by the elapsed time between stimulus onset and an individual's response on elementary cognitive tasks (ETCs), which are relatively simple perceptual-motor tasks typically administered in a laboratory setting. Mental chronometry is one of the core methodological paradigms of human experimental, cognitive, and differential psychology, but is also commonly analyzed in psychophysiology, cognitive neuroscience, and behavioral neuroscience to help elucidate the biological mechanisms underlying perception, attention, and decision-making in humans and other species. Mental chronometry uses measurements of elapsed time between sensory stimulus onsets and subsequent behavioral responses to study the time course of information processing in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |