|
Initiative Für Frieden Und Menschenrechte
The Initiative for Peace and Human Rights (german: Initiative für Frieden und Menschenrechte, IFM) was the oldest opposition group in East Germany. It was founded on 24 January 1986 and was independent of the churches and state. On 7 February 1990 it joined with New Forum and Democracy Now to form the electoral Alliance 90 and merged with them to form the Alliance 90 party on 21 September 1991. Before the Peaceful Revolution The Initiative emerged from a human rights seminar in East Berlin that was planned for 16 November 1985 but was cancelled by the Berlin-Brandenburg state church due to Stasi pressure. At first, it had a loose organizational structure and about 30 members. People involved in the IFM included Bärbel Bohley, Werner Fischer, Peter Grimm, Ralf Hirsch, Gerd Poppe, Ulrike Poppe, Martin Böttger, Wolfgang Templin and Ibrahim Böhme. It cooperated with the churches but was independent from them. The Initiative campaigned for disarmament and demilitarization and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initiative Für Frieden Und Menschenrechte
The Initiative for Peace and Human Rights (german: Initiative für Frieden und Menschenrechte, IFM) was the oldest opposition group in East Germany. It was founded on 24 January 1986 and was independent of the churches and state. On 7 February 1990 it joined with New Forum and Democracy Now to form the electoral Alliance 90 and merged with them to form the Alliance 90 party on 21 September 1991. Before the Peaceful Revolution The Initiative emerged from a human rights seminar in East Berlin that was planned for 16 November 1985 but was cancelled by the Berlin-Brandenburg state church due to Stasi pressure. At first, it had a loose organizational structure and about 30 members. People involved in the IFM included Bärbel Bohley, Werner Fischer, Peter Grimm, Ralf Hirsch, Gerd Poppe, Ulrike Poppe, Martin Böttger, Wolfgang Templin and Ibrahim Böhme. It cooperated with the churches but was independent from them. The Initiative campaigned for disarmament and demilitarization and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Templin
Wolfgang Templin (born in 1948) – politician of the democratic opposition in Eastern Germany, publicist, concerned with the history of the GDR, the former Eastern Bloc and the German reunification. From 1973 to 1975, he was a Stasi informer under the codename "Peter". Later, Templin was a victim of the Stasi's psychological warfare program, which he sought to expose to the public with modest success. In 1985 he co-founded the Initiative for Peace and Human Rights. He published in the underground journal “Grenzfall”, cooperated with opposition in Eastern Europe and integrated environmental and pacifist groups in the GDR. After the fall of the Berlin Wall, he took part in the Round Table discussions. He was a member of the Alliance 90 faction in the People's Chamber and a co-founder of the Alliance 90 party. 1994-96 he was a research worker at the Berlin Wall Museum, whereas 1996 he became a co-founder of the Federal Foundation for the Reconciliation of the SED Dictato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissent
Dissent is an opinion, philosophy or sentiment of non-agreement or opposition to a prevailing idea or policy enforced under the authority of a government, political party or other entity or individual. A dissenting person may be referred to as a ''dissenter''. The term's antonyms include ''agreement'', '' consensus'' (when all or nearly all parties agree on something) and ''consent'' (when one party agrees to a proposition made by another). Philosophical In philosophical skepticism, particularly that of Pyrrhonism, the existence of dissent is a rationale for suspending judgment regarding the issue associated with the dissent. Dissent in this respect appears as one of the tropes in the Five Modes of Agrippa, pointing to the uncertainty demonstrated by the differences of opinions among philosophers and people in general. Political Political dissent is a dissatisfaction with or opposition to the policies of a governing body. Expressions of dissent may take forms from voca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkskammer
__NOTOC__ The Volkskammer (, ''People's Chamber'') was the unicameral legislature of the German Democratic Republic (colloquially known as East Germany). The Volkskammer was initially the lower house of a bicameral legislature. The upper house was the Chamber of States, or ''Länderkammer'', but in 1952 the states of East Germany were dissolved, and the Chamber was abolished in 1958. Constitutionally, the Volkskammer was the highest organ of state power in the GDR, and both constitutions vested it with great lawmaking powers. All other branches of government, including the judiciary, were responsible to it. By 1960, the chamber appointed the Council of the State, the Council of Ministers, and the National Defence Council. In practice, however, it was a pseudo-parliament that did little more than rubber-stamp decisions already made by the SED — always by unanimous consent — and listen to the General Secretary's speeches. Membership In October 1949 the ''Volksrat'' charged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
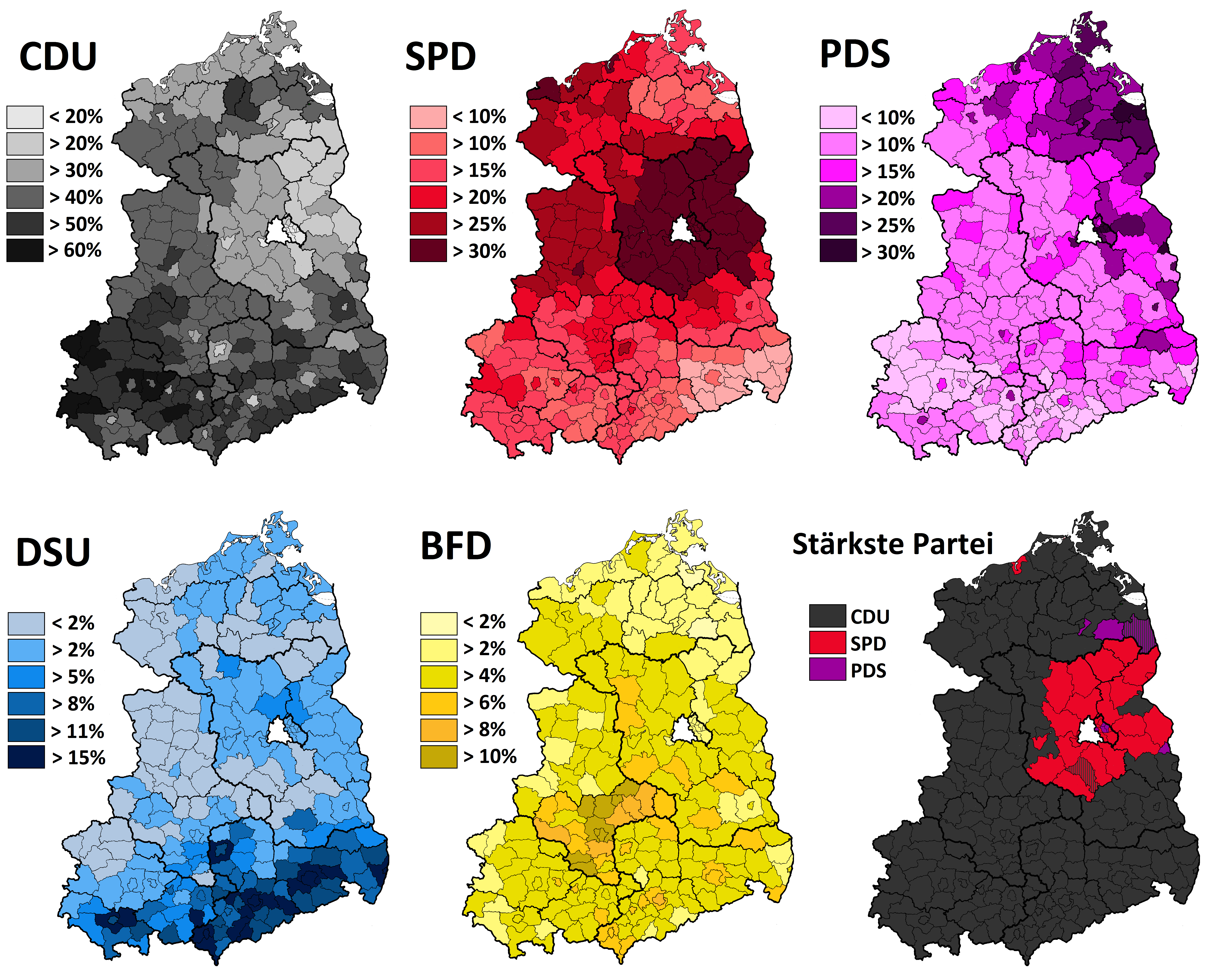
1990 East German General Election
General elections were held in East Germany on 18 March 1990. They were the only free and fair parliamentary elections in the history of the country, and the first free and fair election held in that part of Germany since November 1932. The Alliance for Germany, led by the East German branch of the Christian Democratic Union, won 192 seats and emerged as the largest bloc in the 400-seat Volkskammer, having run on a platform of speedy reunification with West Germany. The East German branch of the Social Democratic Party, which had been dissolved in 1946 and refounded only six months before the elections, finished second with 88 seats. The former Socialist Unity Party of Germany, renamed the Party of Democratic Socialism, running in a free election for the first time, finished third with 66 seats. The Alliance was just short of the 201 seats needed to govern alone. Lothar de Maizière of the CDU invited the SPD to join his Alliance partners – the German Social Union (DSU) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Modrow
Hans Modrow (; born 27 January 1928) is a German politician best known as the last communist premier of East Germany. Taking office in the middle of the Peaceful Revolution, he was the ''de facto'' leader of the country for much of the winter of 1989 and 1990. He was a transitional figure, paving the way to the first and only free elections in East Germany and including many opposition politicians in his cabinet. He had previously been a collaborator in the communist regime, even downplaying its role in the deaths at the Berlin Wall, and attempted to delay German reunification. After the end of Communist rule and reunification of Germany, he was convicted of electoral fraud and perjury by the Dresden District Court in 1995, on the basis that he had been the SED official nominally in charge of the electoral process. He was later convicted of abuse of office and was given a nine month suspended sentence. One of the few high-ranking former SED officials to not have been expelle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East German Round Table
Round table primarily refers to the Central Round Table (''Zentraler Runder Tisch''), a series of meetings during the Peaceful Revolution in East Germany in late-1989 and early-1990. The Round table first convened in East Berlin on 7 December 1989, the day after Egon Krenz had resigned as the head of the Socialist Unity Party (SED) government. This Round Table, modeled after the Polish Round Table convened in April 1989, was initiated by the group Democracy Now. "Round table" was to be understood in a metaphorical sense, meaning that the participants were on a par with each other. Physically, the table was rectangular (unlike the Polish model which was literally round). It was set up as a forum in which members of East German government-aligned organizations (such as the so-called bloc parties, trade unions, etc.) came together with representatives of the new citizens’ movements (such as Democracy Now, Democratic Awakening, and New Forum) to discuss and advance reforms in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as well as the second most populous city in the area of the former East Germany after (East) Berlin. Together with Halle (Saale), the city forms the polycentric Leipzig-Halle Conurbation. Between the two cities (in Schkeuditz) lies Leipzig/Halle Airport. Leipzig is located about southwest of Berlin, in the southernmost part of the North German Plain (known as Leipzig Bay), at the confluence of the White Elster River (progression: ) and two of its tributaries: the Pleiße and the Parthe. The name of the city and those of many of its boroughs are of Slavic origin. Leipzig has been a trade city since at least the time of the Holy Roman Empire. The city sits at the intersection of the Via Regia and the Via Imperii, two important medieval trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peaceful Revolution
The Peaceful Revolution (german: Friedliche Revolution), as a part of the Revolutions of 1989, was the process of sociopolitical change that led to the opening of East Germany's borders with the West, the end of the ruling of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) (communist regime) in the German Democratic Republic (GDR or "East Germany") in 1989 and the transition to a parliamentary democracy, which later enabled the reunification of Germany in October 1990. This happened through non-violent initiatives and demonstrations. This period of change is referred to in German as ' (, "the turning point"). These events were closely linked to Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev's decision to abandon Soviet hegemony in Eastern Europe as well as the reformist movements that spread through Eastern Bloc countries. In addition to the Soviet Union's shift in foreign policy, the GDR's lack of competitiveness in the global market, as well as its sharply rising national debt, hastened the des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zersetzung
''Zersetzung'' (, German language, German for "decomposition" and "disruption") was a psychological warfare technique used by the Ministry for State Security (East Germany), Ministry for State Security (''Stasi'') to repress political opponents in East Germany during the 1970s and 1980s. ''Zersetzung'' served to combat alleged and actual dissidents through covert means, using secret methods of Abusive power and control, abusive control and psychological manipulation to prevent anti-government activities. People were commonly targeted on a pre-emptive and preventative basis, to limit or stop politically incorrect activities that they may have gone on to perform, and not on the basis of crimes they had actually committed. ''Zersetzung'' methods were designed to break down, undermine, and paralyze people behind "a facade of social normality" in a form of "silent repression". Erich Honecker's succession to Walter Ulbricht as Leadership of East Germany, First Secretary of the Social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gethsemane Church
Gethsemane Church (german: link=no, Gethsemanekirche) is one of four church buildings of the Lutheran Northern Prenzlauer Berg Evangelical Congregation (german: link=no, Evangelische Kirchengemeinde Prenzlauer Berg-Nord), within the Evangelical Church of Berlin-Brandenburg-Silesian Upper Lusatia, an umbrella organisation which includes Lutheran, Reformed, and United Protestant Calvinist congregations. Gethsemane Church is the best known church in the locality of Prenzlauer Berg, in Berlin's borough of Pankow. The church was named after the Garden of Gethsemane (Old Aramaic גת שמנא, transliterated ''Gath Šmānê'', he, גת שמנים, translit. ''Gath Šmānîm'', lit. "oil press", transliteration in ''Gethsēmanḗ'') at the foot of the Mount of Olives in Jerusalem. Christians revere the place as it was where the Twelve Apostles and Jesus of Nazareth prayed on the eve of his crucifixion. The church and its congregation played a crucial role before and during the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolae Ceaușescu
Nicolae Ceaușescu ( , ; – 25 December 1989) was a Romanian communist politician and dictator. He was the general secretary of the Romanian Communist Party from 1965 to 1989, and the second and last Communist leader of Romania. He was also the country's head of state from 1967, serving as President of the State Council and from 1974 concurrently as President of the Republic, until his overthrow and execution in the Romanian Revolution in December 1989, part of a series of anti-Communist uprisings in Eastern Europe that year. Born in 1918 in Scornicești, Ceaușescu was a member of the Romanian Communist youth movement. Ceaușescu rose up through the ranks of Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej's Socialist government and, upon Gheorghiu-Dej's death in 1965, he succeeded to the leadership of the Romanian Communist Party as general secretary. Upon his rise to power, he eased press censorship and openly condemned the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia in his speech on 21 August ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)