|
Inflammatory Fibroid Polyp
An inflammatory fibroid polyp (IFP) is an uncommon digestive system tumor. J. Vanek initially identified it as a separate pathological entity in 1949 when he reported six case reports of eosinophilic infiltration in gastric submucosal granulomas. It is a single, non-encapsulated polypoid lesion that is typically submucosal. It is characterized by a large number of small blood vessels, oedematous connective tissue, and an inflammatory eosinophilic infiltrate. Inflammatory fibroid polyp has also been referred to as polypoid myo-endothelioma, fibroma with eosinophilic infiltration, inflammatory pseudotumour, myxoma, haemangiopericytoma, eosinophilic granuloma, Vanek's tumour, and gastric eosinophilic submucosal granuloma. When the lesions are symptomatic, they typically measure less than 3 cm in size and are linked to symptoms such as iron deficiency anemia, bleeding, weight loss, and dyspeptic symptoms. Significant complications like obstruction, intussusception, and even hyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamina Propria
The lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings known as mucous membranes or mucosae, which line various tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, and the urogenital tract. The lamina propria is a thin layer of loose (areolar) connective tissue, which lies beneath the epithelium, and together with the epithelium and basement membrane constitutes the mucosa. As its Latin name indicates, it is a characteristic component of the mucosa, or the mucosa's "own special layer." Thus, the term mucosa or mucous membrane refers to the combination of the epithelium and the lamina propria. The connective tissue of the lamina propria is loose and rich in cells. The cells of the lamina propria are variable and can include fibroblasts, lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, eosinophilic leukocytes, and mast cells. It provides support and nutrition to the epithelium, as well as the means to bind to the underlying t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
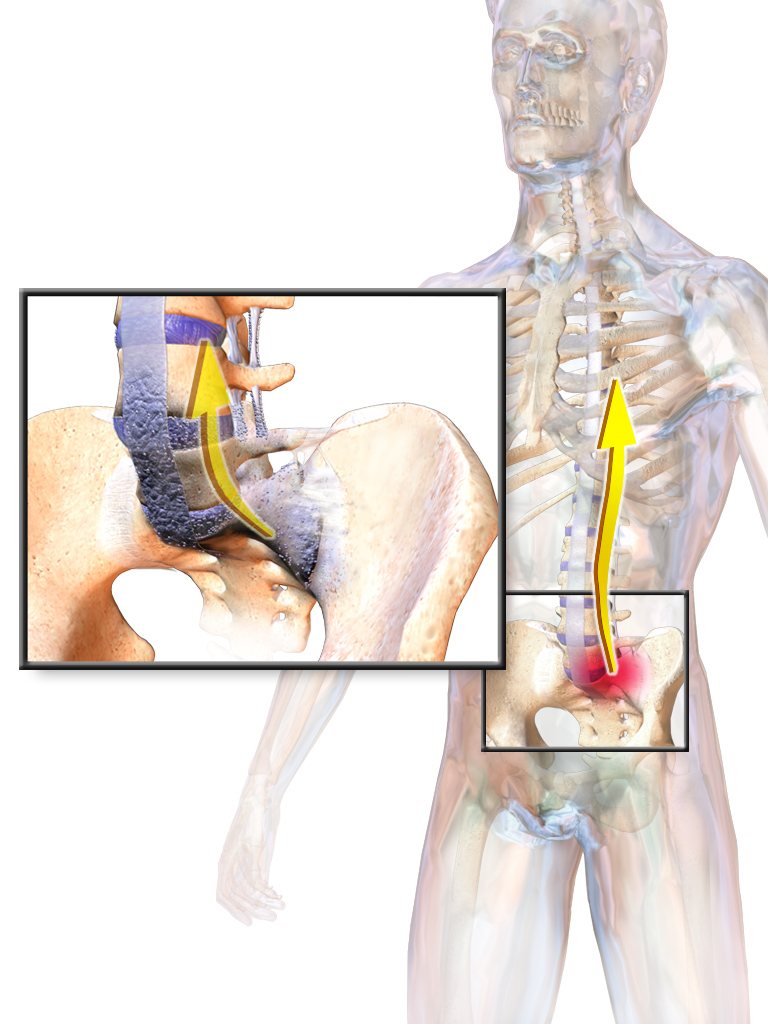
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis from the disease spectrum of axial spondyloarthritis. It is characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine, typically where the spine joins the pelvis. With AS, eye and bowel problems—as well as back pain—may occur. Joint mobility in the affected areas sometimes worsens over time. Ankylosing spondylitis is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. More than 90% of people affected in the UK have a specific human leukocyte antigen known as the HLA-B27 antigen. The underlying mechanism is believed to be autoimmune or autoinflammatory. Diagnosis is based on symptoms with support from medical imaging and blood tests. AS is a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy, meaning that tests show no presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) antibodies. There is no cure for AS. Treatments may include medication, physical therapy, and surgery. Medication therapy focuses on relieving the pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
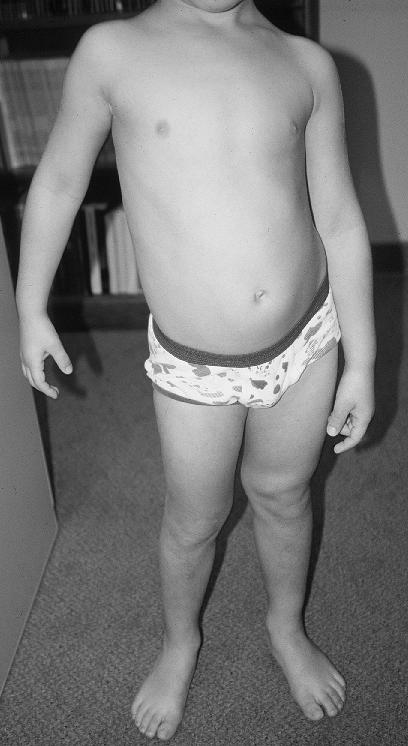
Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis (NF) refers to a group of three distinct genetic conditions in which tumors grow in the nervous system. The tumors are non-cancerous (benign) and often involve the skin or surrounding bone. Although symptoms are often mild, each condition presents differently. neurofibromatosis type I, Neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) is typically characterized by Café au lait spot, café au lait spots (light-brown flat patches of skin), Neurofibroma, neurofibromas (small bumps in or under the skin), scoliosis (side-way curvature of the back), and Headache, headaches. neurofibromatosis type II, Neurofibromatosis type II (NF2), on the other hand, may present with early-onset hearing loss, cataracts, tinnitus, difficulty walking or maintaining balance, and muscle atrophy. The third type is called schwannomatosis and often presents in early adulthood with widespread pain, numbness, or tingling due to nerve compression. The cause is a genetic mutation in certain oncogenes. These c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic worms, and also objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy biological tissue, tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use humoral immunity, molecules and cell-mediated immunity, cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage, viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granular Cell Tumor
Granular cell tumor is a tumor that can develop on any skin or mucosal surface, but occurs on the tongue 40% of the time. It is also known as Abrikossoff's tumor, granular cell myoblastoma, granular cell nerve sheath tumor, and granular cell schwannoma. Granular cell tumors (GCTs) affect females more often than males. Pathology Granular cell tumors are derived from neural tissue, as can be demonstrated by immunohistochemistry and ultrastructural evidence using electron microscopy. These lesions characteristically consist of polygonal cells with bland nuclei, abundant cytoplasm and fine eosinophilic cytoplasmic granules. The tumor cells stain positively for S-100 as they are of Schwann cell origin. Both malignant and benign versions of the tumor exist, where malignant tumors are characterized histologically by features such as spindling, high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratios, pleomorphism, and necrosis. Multiple granular cell tumors may seen in the context of '' LEOPARD syndrome'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stromal Cell
Stromal cells, or mesenchymal stromal cells, are differentiating cells found in abundance within bone marrow but can also be seen all around the body. Stromal cells can become connective tissue cells of any organ, for example in the uterine mucosa (endometrium), prostate, bone marrow, lymph node and the ovary. They are cells that support the function of the parenchymal cells of that organ. The most common stromal cells include fibroblasts and pericytes. The term ''stromal'' comes from Latin , "bed covering", and Ancient Greek , , "bed". Stromal cells are an important part of the body's immune response and modulate inflammation through multiple pathways. They also aid in differentiation of hematopoietic cells and forming necessary blood elements. The interaction between stromal cells and tumor cells is known to play a major role in cancer growth and progression. In addition, by regulating local cytokine networks (e.g. M-CSF, LIF), bone marrow stromal cells have been describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of Tissue (biology), organic tissue that results from cell proliferation. It may lead to the Gross anatomy, gross enlargement of an organ, and the term is sometimes confused with benign neoplasia or benign tumor. Hyperplasia is a common preneoplastic response to stimulus. Microscopically, cells resemble normal cells but are increased in numbers. Sometimes cells may also be increased in size (hypertrophy). Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy in that the Cellular adaptation, adaptive cell change in hypertrophy is an increase in the cell size, ''size'' of cells, whereas hyperplasia involves an increase in the ''number'' of cells. Causes Hyperplasia may be due to any number of causes, including proliferation of basal layer of epidermis to compensate skin loss, Chronic inflammation, chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
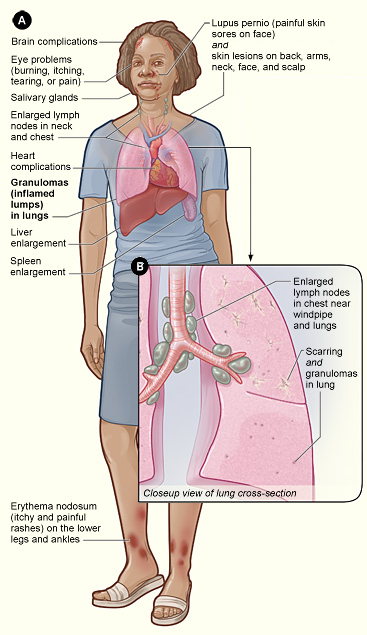
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and Human brain, brain, though any Organ (anatomy), organ can be affected. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no symptoms or only mild symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, enlarged hilar lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, uveitis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue (medical), fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections, as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer. Although the precise causes of Crohn's disease (CD) are unknown, it is believed to be caused by a combination of environmental, Immunity (medical), immune, and bacterial factors in genetically susceptible individuals. It results in a Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, chronic inflammatory disorder, in which the body's immune system defends the gastrointesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
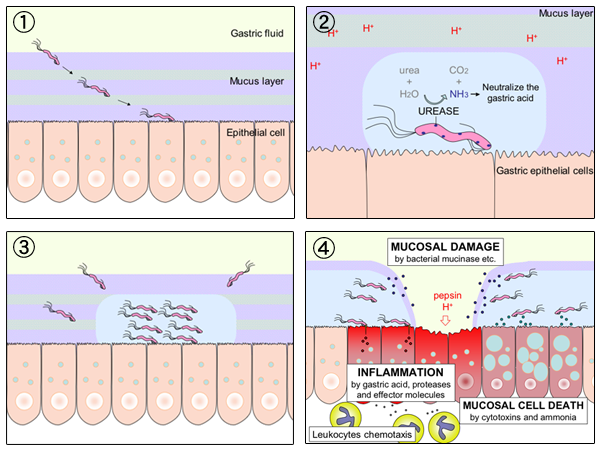
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, Flagellum#bacterial, flagellated, Bacterial cellular morphologies#Helical, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape that exhibits less virulence. Its Helix, helical body (from which the genus name ''Helicobacter'' derives) is thought to have evolved to penetrate the gastric mucosa, mucous lining of the stomach, helped by its flagella, and thereby establish infection. While many earlier reports of an association between bacteria and the ulcers had existed, such as the works of John Lykoudis, it was only in 1983 when the bacterium was formally described for the first time in the English-language Western literature as the causal agent of peptic ulcer, gastric ulcers by Australian physician-scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. In 2005, the pair was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery. Infection of the stomach with ''H. pylori'' doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |