|
Infection Rate
An infection rate (or incident rate) is the probability or risk of an infection in a population. It is used to measure the frequency of occurrence of new instances of infection within a population during a specific time period. \text = K \times \frac The number of infections equals the cases identified in the study or observed. An example would be HIV infection during a specific time period in the defined population. The population at risk are the cases appearing in the population during the same time period. An example would be all the people in a city during a specific time period. The constant, or K is assigned a value of 100 to represent a percentage. An example would be to find the percentage of people in a city who are infected with HIV: 6,000 cases in March divided by the population of a city (one million) multiplied by the constant (K) would give an infection rate of 0.6%. Calculating the infection rate is used to analyze trends for the purpose of infection and disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an Event (probability theory), event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speaking, 0 indicates impossibility of the event and 1 indicates certainty."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th Ed, (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', (Vol 1), 3rd Ed, (1968), Wiley, . The higher the probability of an event, the more likely it is that the event will occur. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicare (United States)
Medicare is a government national health insurance program in the United States, begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration (SSA) and now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). It primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, but also for some younger people with disability status as determined by the SSA, including people with end stage renal disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease). In 2018, according to the 2019 Medicare Trustees Report, Medicare provided health insurance for over 59.9 million individuals—more than 52 million people aged 65 and older and about 8 million younger people. According to annual Medicare Trustees reports and research by the government's MedPAC group, Medicare covers about half of healthcare expenses of those enrolled. Enrollees almost always cover most of the remaining costs by taking additional private insurance and/or by joining a public Part C or P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, screening, biomonitoring, and comparisons of treatment effects such as in clinical trials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Health And Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is "Improving the health, safety, and well-being of America". Before the separate federal Department of Education was created in 1979, it was called the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (HEW). HHS is administered by the Secretary of Health and Human Services, who is appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the United States Senate. The position is currently held by Xavier Becerra. The United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, the uniformed service of the PHS, is led by the Surgeon General who is responsible for addressing matters concerning public health as authorized by the secretary or by the assistant secretary for Health in addition to his or her primary mission of administering the Commission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridium Difficile (bacteria)
''Clostridioides difficile'' ( syn. ''Clostridium difficile'') is a bacterium that is well known for causing serious diarrheal infections, and may also cause colon cancer. Also known as ''C. difficile'', or ''C. diff'' (), is Gram-positive species of spore-forming bacteria. ''Clostridioides'' spp. are anaerobic, motile bacteria, ubiquitous in nature and especially prevalent in soil. Its vegetative cells are rod-shaped, pleomorphic, and occur in pairs or short chains. Under the microscope, they appear as long, irregular (often drumstick- or spindle-shaped) cells with a bulge at their terminal ends (forms subterminal spores). Under Gram staining, ''C. difficile'' cells are Gram-positive and show optimum growth on blood agar at human body temperatures in the absence of oxygen. ''C. difficile'' is catalase- and superoxide dismutase-negative, and produces up to three types of toxins: enterotoxin A, cytotoxin B and Clostridioides difficile transferase (CDT). Under stress condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019. MRSA is any strain of ''S. aureus'' that has developed (through natural selection) or acquired (through horizontal gene transfer) a multiple drug resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics are a broad-spectrum group that include some penams (penicillin derivatives such as methicillin and oxacillin) and cephems such as the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-susceptible ''S. aureus'', or MSSA. MRSA is common in hospitals, prisons, and nursing homes, where people with open wounds, invasive devices such as catheters, and weakened immune systems are at greater risk of healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
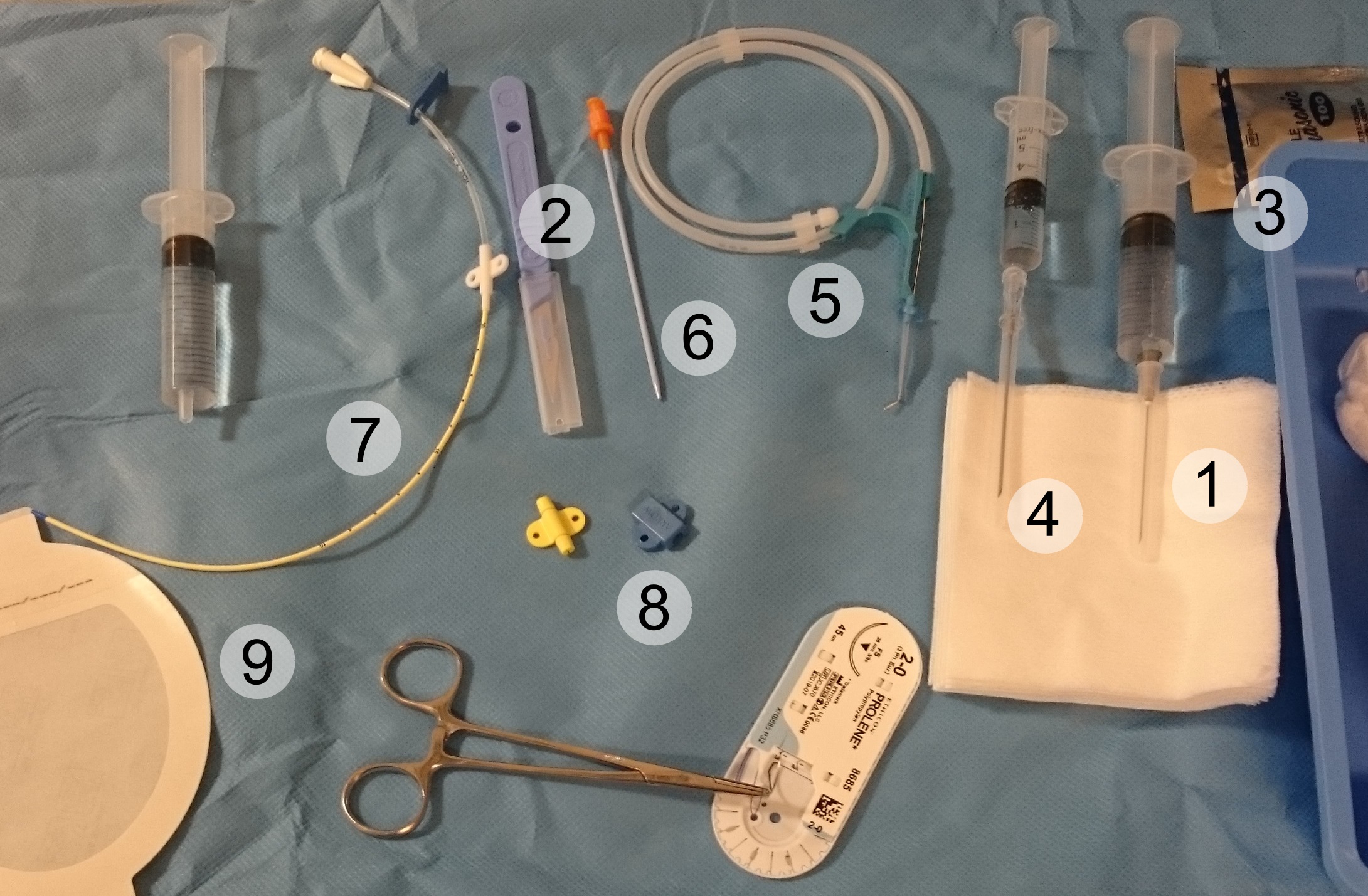
Surgical Site Infection
Perioperative mortality has been defined as any death, regardless of cause, occurring within 30 days after surgery in or out of the hospital. Globally, 4.2 million people are estimated to die within 30 days of surgery each year. An important consideration in the decision to perform any surgical procedure is to weigh the benefits against the risks. Anesthesiologists and surgeons employ various methods in assessing whether a patient is in optimal condition from a medical standpoint prior to undertaking surgery, and various statistical tools are available. ASA score is the most well known of these. Intraoperative causes Immediate complications during the surgical procedure, e.g. bleeding or perforation of organs may have lethal sequelae. Complications following surgery Infection Countries with a low human development index (HDI) carry a disproportionately greater burden of surgical site infections (SSI) than countries with a middle or high HDI and might have higher rates of antibio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection
Catheter-associated urinary tract Infection, or CAUTI, is a urinary tract infection associated with urinary catheter use. __TOC__ Core prevention A number of combined practices such as improved hand hygiene, enhanced barrier protection and reduced catheter use when managing incontinence appear to reduce CAUTI. Urinary catheters should be inserted using aseptic technique and sterile equipment (including sterile gloves, drape, sponges, antiseptic and sterile solution), particularly in an acute care setting. Although catheter use should be minimized in all patients, particularly those at higher risk of CAUTI and mortality (e.g. the elderly or those with impaired immunity), a meta analysis suggests there is insufficient evidence to determine the value of different policies for replacing long term urinary catheters on patient outcomes. Incidence Bacteria and yeast, including those naturally occurring as part of the human microbiome, can grow within biofilm that forms along the surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Line-associated Bloodstream Infection
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line(c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. These catheters are commonly placed in veins in the neck (internal jugular vein), chest (subclavian vein or axillary vein), groin (femoral vein), or through veins in the arms (also known as a PICC line, or peripherally inserted central catheters). Central lines are used to administer medication or fluids that are unable to be taken by mouth or would harm a smaller peripheral vein, obtain blood tests (specifically the "central venous oxygen saturation"), administer fluid or blood products for large volume resuscitation, and measure central venous pressure. The catheters used are commonly 15� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection Control
Infection prevention and control is the discipline concerned with preventing healthcare-associated infections; a practical rather than academic sub-discipline of epidemiology. In Northern Europe, infection prevention and control is expanded from healthcare into a component in public health, known as "infection protection" (''smittevern, smittskydd, Infektionsschutz'' in the local languages). It is an essential part of the infrastructure of health care. Infection control and hospital epidemiology are akin to public health practice, practiced within the confines of a particular health-care delivery system rather than directed at society as a whole. Infection control addresses factors related to the spread of infections within the healthcare setting, whether among patients, from patients to staff, from staff to patients, or among staff. This includes preventive measures such as hand washing, cleaning, disinfecting, sterilizing, and vaccinating. Other aspects include surveillance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environment), often focusing on negative, undesirable consequences. Many different definitions have been proposed. The international standard definition of risk for common understanding in different applications is “effect of uncertainty on objectives”. The understanding of risk, the methods of assessment and management, the descriptions of risk and even the definitions of risk differ in different practice areas (business, economics, environment, finance, information technology, health, insurance, safety, security etc). This article provides links to more detailed articles on these areas. The international standard for risk management, ISO 31000, provides principles and generic guidelines on managing risks faced by organizations. Definitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hospital-acquired Infection
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital settings, it is sometimes instead called a healthcare–associated infection. Such an infection can be acquired in hospital, nursing home, rehabilitation facility, outpatient clinic, diagnostic laboratory or other clinical settings. Infection is spread to the susceptible patient in the clinical setting by various means. Health care staff also spread infection, in addition to contaminated equipment, bed linens, or air droplets. The infection can originate from the outside environment, another infected patient, staff that may be infected, or in some cases, the source of the infection cannot be determined. In some cases the microorganism originates from the patient's own skin microbiota, becoming opportunistic after surgery or other procedures that compromise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |