|
Infant Feeding
Infant nutrition is the description of the dietary needs of infants. A diet lacking essential calories, minerals, vitamins, or fluids is considered inadequate. Breast milk provides the best nutrition for these vital first months of growth when compared to infant formula. For example, breastfeeding aids in preventing anemia, obesity, and sudden infant death syndrome; and it promotes digestive health, immunity, intelligence, and dental development. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends exclusively feeding an infant breast milk, or iron-fortified formula, for the first six months of life and continuing for one year or longer as desired by infant and mother. Infants are usually not introduced to solid foods until four to six months of age. Historically, breastfeeding infants was the only option for nutrition otherwise the infant would perish. Breastfeeding is rarely contraindicated, but is not recommended for mothers being treated for cancer, those with active tuberculosis, HIV, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, an infant who is only hours, days, or up to one month old. In medical contexts, a newborn or neonate (from Latin, ''neonatus'', newborn) is an infant in the first 28 days after birth; the term applies to premature, full term, and postmature infants. Before birth, the offspring is called a fetus. The term ''infant'' is typically applied to very young children under one year of age; however, definitions may vary and may include children up to two years of age. When a human child learns to walk, they are called a toddler instead. Other uses In British English, an ''infant school'' is for children aged between four and seven. As a legal term, ''infancy'' is more lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactoferrin
Lactoferrin (LF), also known as lactotransferrin (LTF), is a multifunctional protein of the transferrin family. Lactoferrin is a globular glycoprotein with a molecular mass of about 80 kDa that is widely represented in various secretory fluids, such as milk, saliva, tears, and nasal secretions. Lactoferrin is also present in secondary granules of PMNs and is secreted by some acinar cells. Lactoferrin can be purified from milk or produced recombinantly. Human colostrum (''"first milk"'') has the highest concentration, followed by human milk, then cow milk (150 mg/L). Lactoferrin is one of the components of the immune system of the body; it has antimicrobial activity (bacteriocide, fungicide) and is part of the innate defense, mainly at mucoses. In particular, lactoferrin provides antibacterial activity to human infants. Lactoferrin interacts with DNA and RNA, polysaccharides and heparin, and shows some of its biological functions in complexes with these ligands. Lactoferri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colostrum
Colostrum, also known as beestings or first milk, is the first form of milk produced by the mammary glands of mammals (including humans) immediately following delivery of the newborn. Colostrum powder is rich in high protein and low in sugar and fat. It strengthens your baby's immune system and is filled with white blood cells to protect it from infection. Most species will begin to generate colostrum just prior to giving birth. Colostrum has an especially high amount of bioactive compounds compared to mature milk to give the newborn the best possible start to life. Specifically, colostrum contains antibodies to protect the newborn against disease and infection, and immune and growth factors and other bioactives that help to activate a newborn's immune system, jumpstart gut function, and seed a healthy gut microbiome in the first few days of life. The bioactives found in colostrum are essential for a newborn's health, growth and vitality. At birth, the surroundings of the newborn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation. The cause of cavities is acid from bacteria dissolving the hard tissues of the teeth ( enamel, dentin and cementum). The acid is produced by the bacteria when they break down food debris or sugar on the tooth surface. Simple sugars in food are these bacteria's primary energy source and thus a diet high in simple sugar is a risk factor. If mineral breakdown is greater than build up from sources such as saliva, caries results. Risk factors include conditions that result in less saliva such as: diabetes mellitus, Sjögren syndrome and some medications. Medications that decrease saliva production include antihistamines and antide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Immunity
Passive immunity is the transfer of active humoral immunity of ready-made antibodies. Passive immunity can occur naturally, when maternal antibodies are transferred to the fetus through the placenta, and it can also be induced artificially, when high levels of antibodies specific to a pathogen or toxin (obtained from humans, horses, or other animals) are transferred to non-immune persons through blood products that contain antibodies, such as in immunoglobulin therapy or antiserum therapy. Passive immunization is used when there is a high risk of infection and insufficient time for the body to develop its own immune response, or to reduce the symptoms of ongoing or immunosuppressive diseases.Microbiology and Immunology On-Line Textbook : USC School of Medicine Passive immunization can be provided when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriostatic Agent
A bacteriostatic agent or bacteriostat, abbreviated Bstatic, is a biological or chemical agent that stops bacteria from reproducing, while not necessarily killing them otherwise. Depending on their application, bacteriostatic antibiotics, disinfectants, antiseptics and preservatives can be distinguished. When bacteriostatic antimicrobials are used, the duration of therapy must be sufficient to allow host defense mechanisms to eradicate the bacteria. Upon removal of the bacteriostat, the bacteria usually start to grow rapidly. This is in contrast to bactericides, which kill bacteria. Bacteriostats are often used in plastics to prevent growth of bacteria on surfaces. Bacteriostats commonly used in laboratory work include sodium azide (which is acutely toxic) and thiomersal. __TOC__ Bacteriostatic antibiotics Bacteriostatic antibiotics limit the growth of bacteria by interfering with bacterial protein production, DNA replication, or other aspects of bacterial cellular metabolism. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colostrum
Colostrum, also known as beestings or first milk, is the first form of milk produced by the mammary glands of mammals (including humans) immediately following delivery of the newborn. Colostrum powder is rich in high protein and low in sugar and fat. It strengthens your baby's immune system and is filled with white blood cells to protect it from infection. Most species will begin to generate colostrum just prior to giving birth. Colostrum has an especially high amount of bioactive compounds compared to mature milk to give the newborn the best possible start to life. Specifically, colostrum contains antibodies to protect the newborn against disease and infection, and immune and growth factors and other bioactives that help to activate a newborn's immune system, jumpstart gut function, and seed a healthy gut microbiome in the first few days of life. The bioactives found in colostrum are essential for a newborn's health, growth and vitality. At birth, the surroundings of the newborn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
From Colostrum To Breastmilk - 4241
From may refer to: * From, a preposition * From (SQL), computing language keyword * From: (email message header), field showing the sender of an email * FromSoftware, a Japanese video game company * Full range of motion, the travel in a range of motion * Isak From (born 1967), Swedish politician * Martin Severin From (1825–1895), Danish chess master * Sigfred From Sigfred From (12 December 1925 – April 1998), was a Danish chess player. Biography From the begin of 1960s to the begin of 1970s Sigfred From was one of Danish leading chess players. He regularly played in Danish Chess Championships. Her best ... (1925–1998), Danish chess master * ''From'' (TV series), a sci-fi-horror series that debuted on Epix in 2022 {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
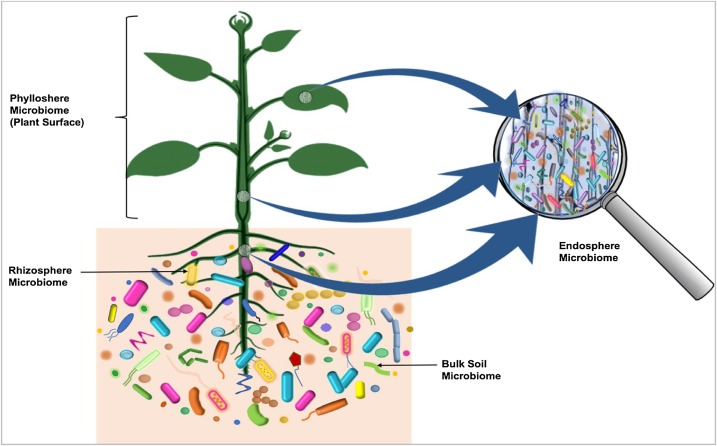
Microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term ''microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or within the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product (short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simple life fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |