|
Indusium
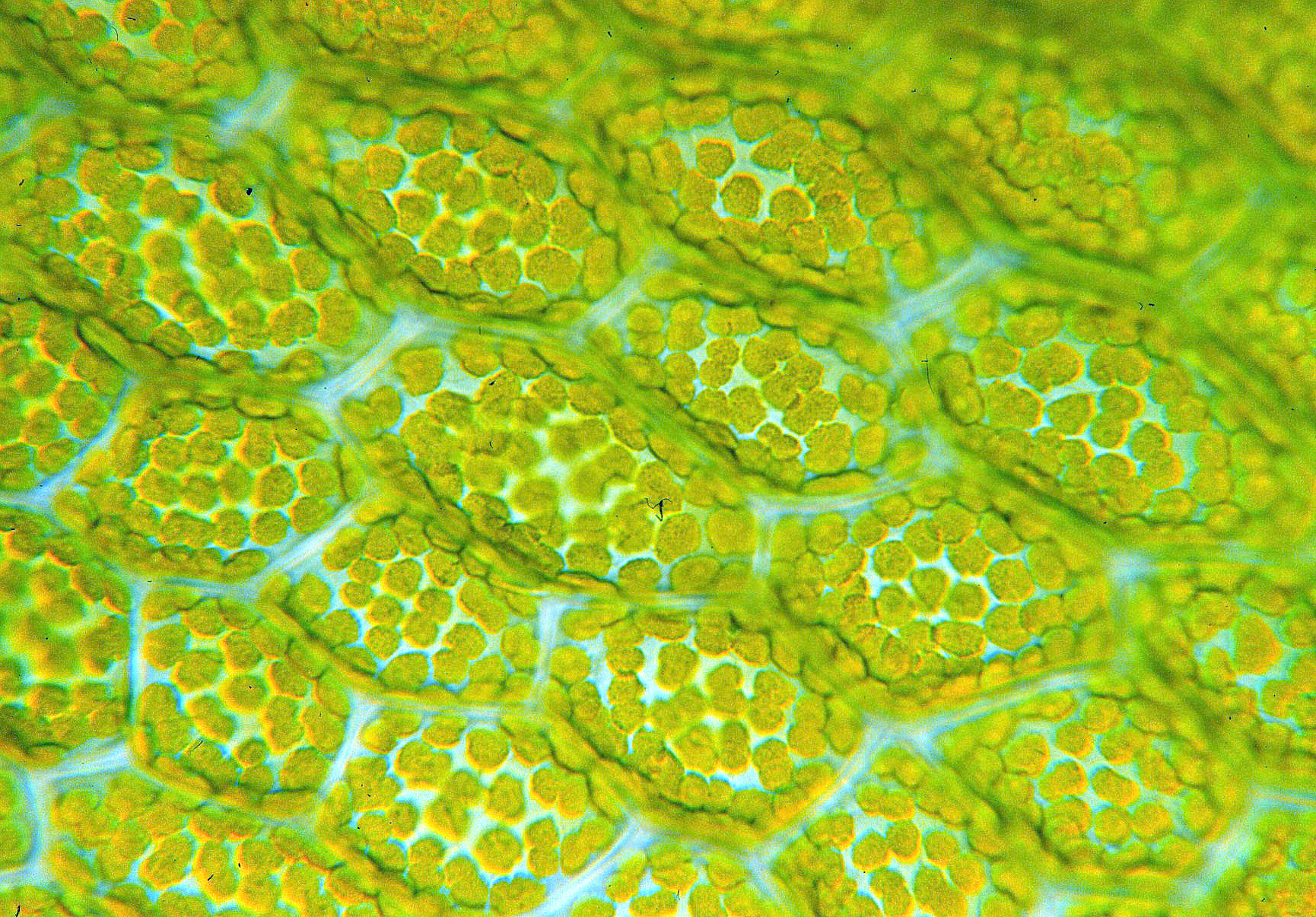
A sorus (pl. sori) is a cluster of sporangia (structures producing and containing spores) in ferns and fungi. A coenosorus (plural coenosori) is a compound sorus composed of multiple, fused sori. Etymology This New Latin word is from Ancient Greek σωρός (''sōrós'' 'stack, pile, heap'). Structure In lichens and other fungi, the sorus is surrounded by an external layer. In some red algae, it may take the form of depression into the thallus. In ferns, the sori form a yellowish or brownish mass on the edge or underside of a fertile frond. In some species, they are protected during development by a scale or film of tissue called the indusium, which forms an umbrella-like cover. Lifecycle significance Sori occur on the sporophyte generation, the sporangia within producing haploid meiospores. As the sporangia mature, the indusium shrivels so that spore release is unimpeded. The sporangia then burst and release the spores. As an aid to identification The shape, arrangemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Anatomy
Plant anatomy or phytotomy is the general term for the study of the internal structure of plants. Originally it included plant morphology, the description of the physical form and external structure of plants, but since the mid-20th century plant anatomy has been considered a separate field referring only to internal plant structure. Plant anatomy is now frequently investigated at the cellular level, and often involves the sectioning of tissues and microscopy. Structural divisions Some studies of plant anatomy use a systems approach, organized on the basis of the plant's activities, such as nutrient transport, flowering, pollination, embryogenesis or seed development. Others are more classically divided into the following structural categories: : Flower anatomy, including study of the Calyx, Corolla, Androecium, and Gynoecium : Leaf anatomy, including study of the Epidermis, stomata and Palisade cells : Stem anatomy, including Stem structure and vascular tissues, buds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorocarp
A sorocarp (from the Greek word ''soros'' "a heap" + ''karpos'' "fruit") is the fruiting body characteristic of certain cellular slime moulds (e.g., Dictyosteliida). Each sorocarp consists of both a sorophore (stalk) and a sorus.Lawrence, E. 2005. Henderson's Dictionary of Biology, 13th Ed. Prentice Hall, London Sorocarps release spore In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, f ...s. References Mycetozoa {{microbiology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sword Fern (other)
Sword fern is a common name for several ferns and may refer to: *''Nephrolepis'', a tropical genus of ferns, especially: **''Nephrolepis exaltata'', commonly cultivated as a houseplant, including the Boston fern *''Polystichum'', a cosmopolitan genus of ferns, especially: **''Polystichum munitum ''Polystichum munitum'', the western swordfern, is an evergreen perennial fern native to western North America, where it is one of the most abundant ferns in forested areas. It occurs along the Pacific coast from southeastern Alaska to southern ...'', native to western North America * Giant swordfern {{Plant common name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meadowsweet Rust Gall
''Triphragmium ulmariae'' is a species of rust fungus in the family Sphaerophragmiaceae. It causes meadowsweet rust gall, which develops as a chemically induced swelling, arising from the lower surface of the meadowsweet (''Filipendula ulmaria'') leaves. Life cycle The fungus grows in the petioles and/or midribs of the perennial plant meadowsweet (''Filipendula ulmaria''), a member of the rose family Rosaceae (), the rose family, is a medium-sized family of flowering plants that includes 4,828 known species in 91 genera. The name is derived from the type genus ''Rosa''. Among the most species-rich genera are '' Alchemilla'' (270), ''Sorbus ..., causing swelling and distortion. Sori develop with bright orange spores. The rust's spores reach the new meadowsweet plants via air movements. The rust has a severe effect on the survival of meadowsweet seedlings. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q6803444 Pucciniales Galls Fungi described in 1808 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlebodium Aureum
''Phlebodium aureum'' (golden polypody, golden serpent fern, cabbage palm fern, gold-foot fern, blue-star fern, hare-foot fern; syn. ''Polypodium aureum'', ''Polypodium leucotomos'') is an epiphytic fern native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas. Description It is a rhizomatous fern, with the creeping rhizome 8–15 mm (rarely 30 mm) in diameter, densely covered in the golden-brown scales that give the species its name. The fronds are large and pinnatifid (deeply lobed), from 30–130 cm long and 10–50 cm broad, with up to 35 pinnae; they vary in color from bright green to glaucous green and have undulate margins. Several round sori run along each side of the pinna midrib, and the minute spores are wind-dispersed. The fronds are evergreen in areas with year-round rainfall, semi-evergreen or briefly deciduous in areas with a marked dry season. Distribution It is confined to the eastern side of the continents, extending north into the United States to Florida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporophyte
A sporophyte () is the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or alga which produces asexual spores. This stage alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. Life cycle The sporophyte develops from the zygote produced when a haploid egg cell is fertilized by a haploid sperm and each sporophyte cell therefore has a double set of chromosomes, one set from each parent. All land plants, and most multicellular algae, have life cycles in which a multicellular diploid sporophyte phase alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. In the seed plants, the largest groups of which are the gymnosperms and flowering plants (angiosperms), the sporophyte phase is more prominent than the gametophyte, and is the familiar green plant with its roots, stem, leaves and cones or flowers. In flowering plants the gametophytes are very reduced in size, and are represented by the germinated pollen and the embryo sac. The sporophyte produces spores (hence t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores. Fungi In some phyla of fungi, the sporangium plays a role in asexual reproduction, and may play an indirect role in sexual reproduction. The sporangium forms on the sporangiophore and contains haploid nuclei and cytoplasm. Spores are formed in the sporangiophore by encasing each haploid nucleus and cytoplasm in a tough outer membrane. During asexual reproduction, these spores are dispersed via wind and germinate into haploid hyphae. Although sexual reproduction in fungi varies between phyla, for some fungi the sporangium plays an indirect role in sexual reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
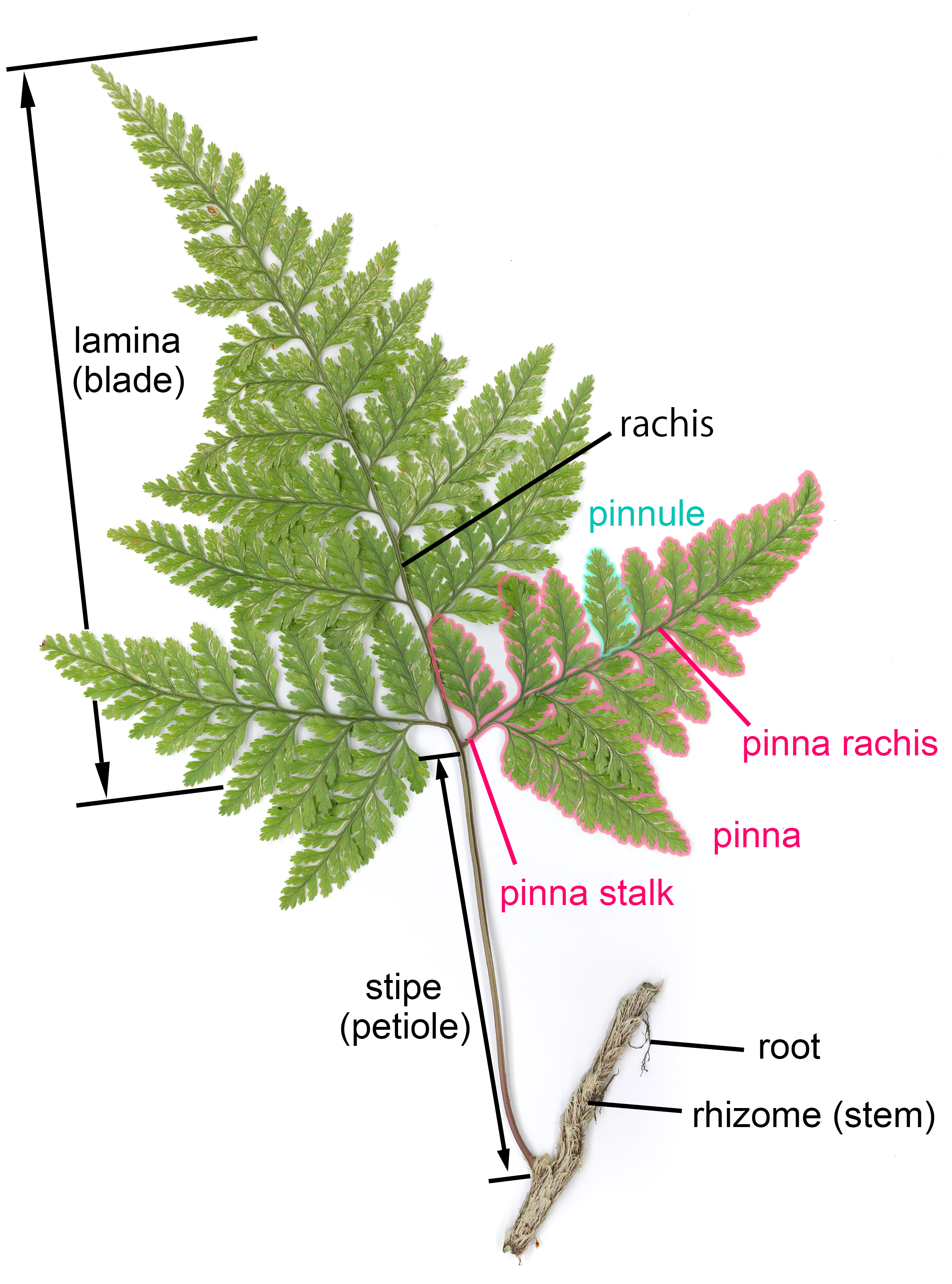
Frond
A frond is a large, divided leaf. In both common usage and botanical nomenclature, the leaves of ferns are referred to as fronds and some botanists restrict the term to this group. Other botanists allow the term frond to also apply to the large leaves of cycads, as well as palms (Arecaceae) and various other flowering plants, such as mimosa or sumac. "Frond" is commonly used to identify a large, compound leaf, but if the term is used botanically to refer to the leaves of ferns and algae it may be applied to smaller and undivided leaves. Fronds have particular terms describing their components. Like all leaves, fronds usually have a stalk connecting them to the main stem. In botany, this leaf stalk is generally called a petiole, but in regard to fronds specifically it is called a stipe, and it supports a flattened blade (which may be called a lamina), and the continuation of the stipe into this portion is called the rachis. The blades may be simple (undivided), pinnatifid ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |