|
Indo-Corinthian Capital
Indo-Corinthian capitals are capitals crowning columns or pilasters, which can be found in the northwestern Indian subcontinent, and usually combine Hellenistic and Indian elements. These capitals are typically dated to the first centuries of the Common Era, and constitute an important aspect of Greco-Buddhist art. Corinthian design Indo-Corinthian capitals display a design and foliage structure which is derived from the academic Corinthian capital developed in Greece. Its importation to India followed the road of Hellenistic expansion in the East in the centuries after the conquests of Alexander the Great. In particular the Greco-Bactrian kingdom, centered on Bactria (today's northern Afghanistan), upheld the type at the doorstep of India, in such places as Ai-Khanoum until the end of the 2nd century BCE. In India, the design was often adapted, usually taking a more elongated form and sometimes being combined with scrolls, generally within the context of Buddhist stupas and templ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects other than the capitals of the columns. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon: the Tuscan order and the Composite order. The Corinthian, with its offshoot the Composite, is the most ornate of the orders. This architectural style is characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls. There are many variations. The name ''Corinthian'' is derived from the ancient Greek city of Corinth, although the style had its own model in Roman practice, following precedents set by the Tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation. In Buddhism, circumambulation or ''pradakhshina'' has been an important ritual and devotional practice since the earliest times, and stupas always have a ''pradakhshina'' path around them. The original South Asian form is a large solid dome above a tholobate or drum with vertical sides, which usually sits on a square base. There is no access to the inside of the structure. In large stupas there may be walkways for circumambulation on top of the base as well as on the ground below it. Large stupas have or had ''vedikā'' railings outside the path around the base, often highly decorated with sculpture, especially at the torana gateways, of which there are usually four. At the top of the dome is a thin vertical element, with one of more horizontal discs spreadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turin City Museum Of Ancient Art
The Museo Civico d'Arte Antica is an art museum located in the Palazzo Madama in Turin, Italy. It has a renowned collection of paintings from the medieval, Renaissance and Baroque periods. It reopened in 2006 after several years of restorations. History The museum was founded in 1934, as the heir of the Pinacoteca Regia and the Galleria Reale, which had been established in Palazzo Madama by King Charles Albert of Savoy in 1832. A Civic Museum had been founded in 1860 in the wake of the unification of Italy although, three years later, the collections were moved to another location in Turin, in Via Gaudenzio Ferrari. These were increased gradually with acquisitions from private collectors, from closed residences of the House of Savoy, or from donations by the same family. In 1898 the collections of "ancient art" were separated from those of "modern art". The former were moved to the current location in 1934 by the director Vittorio Viale. The collection of Asian art, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azes II
Azes II (Greek: , epigraphically ; Kharosthi: , ), may have been the last Indo-Scythian king, speculated to have reigned circa 35–12 BCE, in the northern Indian subcontinent (modern day Pakistan). His existence has been questioned; if he did not exist, artefacts attributed to his reign, such as coins, are likely to be those of Azes I. After the death of Azes II, the rule of the Indo-Scythians in northwestern India and Pakistan finally crumbled with the conquest of the Kushans, one of the five tribes of the Yuezhi who had lived in Bactria for more than a century, and who were then expanding into India to create a Kushan Empire. Soon after, the Parthians invaded from the west. Their leader Gondophares temporarily displaced the Kushans and founded the Indo-Parthian Kingdom that was to last until the middle of the 1st century CE. The Kushans ultimately regained northwestern India circa 75 CE, where they were to prosper for several centuries. Name Azes's name is attested on his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butkara Stupa
The Butkara Stupa (Pashto: بت کړه سټوپا) is an important Buddhist stupa near Mingora, in the area of Swat, Pakistan. It may have been built by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka, but it is generally dated slightly later to the 2nd century BCE. The stupa was enlarged on five occasions during the following centuries, every time by building over, and encapsulating, the previous structure. Excavation The stupa was excavated by an Italian mission (IsIOAO: Istituto Italiano per l'Africa e l'Oriente), led by archaeologist Domenico Faccenna from 1956, to clarify the various steps of the construction and enlargements. The mission established that the stupa was "monumentalized" by the addition of Hellenistic architectural decorations during the 2nd century BCE, suggesting a direct involvement of the Indo-Greeks, rulers of northwestern India during that period, in the development of Greco-Buddhist architecture. An Indo-Corinthian capital representing a Buddhist devotee within foliage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamal Garhi
Jamal Garhi is a small town located 13 kilometers from Mardan at Katlang-Mardan road in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province in northern Pakistan. Jamal Garhi was a Buddhist monastery from the first until the fifth century AD at a time when Buddhism flourished in this part of the Indian subcontinent. There is a beautiful monastery and main stupa, surrounded by chapels closely packed together. The site is called "The Jamal Garhi Kandarat or Kafiro Kote" by the locals. Discovery The ruins of Jamal Garhi were first discovered by the British explorer and archaeologist Sir Alexander Cunningham in 1848. The stupa at the site was opened by Colonel Lumsden in 1852 but little of value was found at the time. In 1871, the site was excavated by Lieutenant Cromten, who unearthed a large number of Buddhist sculptures which are now part of the collections of the British Museum and the Indian Museum in Calcutta. At the monastery a Kharoshti inscription was also discovered which is now kept in Peshawa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor pilasters are expressed, on an astylar wall it lies upon the architrave ("main beam") and is capped by the moldings of the cornice. A frieze can be found on many Greek and Roman buildings, the Parthenon Frieze being the most famous, and perhaps the most elaborate. This style is typical for the Persians. In interiors, the frieze of a room is the section of wall above the picture rail and under the crown moldings or cornice. By extension, a frieze is a long stretch of painted, sculpted or even calligraphic decoration in such a position, normally above eye-level. Frieze decorations may depict scenes in a sequence of discrete panels. The material of which the frieze is made of may be plasterwork, carved wood or other decorative medium. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxila (modern)
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. In 326 BCE, Alexander the Great gained control of the city without a battle, as it was immediately surrendered to him by Omphis. Old Taxila was an important city of ancient India, situated on the eastern shore of the Indus River—the pivotal junction of the Indian subcontinent and Central Asia;Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin''The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan''.Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 it was founded around 1000 BCE. Some ruins at Taxila date to the time of the Achaemenid Persian Empire, followed successively by the Maurya Empire, the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the Indo-Scythians, and the Kushan Empire. Owing to its strategic location, Taxila has changed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
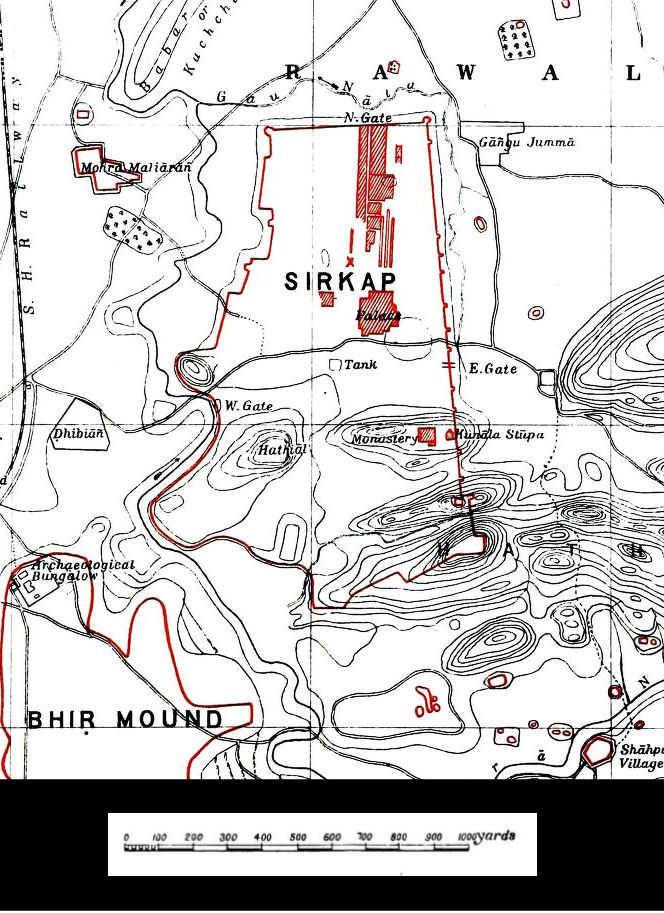
Sirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and pnb, ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan. The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. Demetrius founded an Indo-Greek kingdom that was to last until around 10 BC. Sirkap is also said to have been rebuilt by king Menander I. Archaeological excavations The excavation of the old city was carried out under the supervision of Sir John Marshall by Hergrew from 1912–1930. In 1944 and 1945 further parts were excavated by Mortimer Wheeler and his colleagues. Most of the discoveries at Sirkap related to the Indo-Scythian and Indo-Parthian periods (1st-2nd century CE). Overall excavations to the Greek levels have been very limited, and probably much remains hidden underground: in Sirkap, only about one eight of the excavations were made down to the Indo-Greek and early Indo-Scythian levels, and this only in an area far removed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthus (ornament)
The acanthus ( grc, ἄκανθος) is one of the most common plant forms to make foliage ornament and decoration, and even as the leaf distinguishing the heraldic coronet of a manorial lord from other coronets of royalty or nobility, which use strawberry leaves. Architecture In architecture, an ornament may be carved into stone or wood to resemble leaves from the Mediterranean species of the '' Acanthus'' genus of plants, which have deeply cut leaves with some similarity to those of the thistle and poppy. Both ''Acanthus mollis'' and the still more deeply cut ''Acanthus spinosus'' have been claimed as the main model, and particular examples of the motif may be closer in form to one or the other species; the leaves of both are, in any case, rather variable in form. The motif is found in decoration in nearly every medium. The relationship between acanthus ornament and the acanthus plant has been the subject of a long-standing controversy. Alois Riegl argued in his ''Stilfragen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterranean Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics of the Soviet Union, republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which are colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan", meaning "land of". The current geographical location of Central Asia was formerly part of the historic region of Turkestan, Turkistan, also known as Turan. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. After expansion by Turkic peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)





.png)