|
Indium Gallium Arsenide Phosphide
Indium gallium arsenide phosphide () is a quaternary compound semiconductor material, an alloy of gallium arsenide, gallium phosphide, indium arsenide, or indium phosphide. This compound has applications in photonic devices, due to the ability to tailor its band gap via changes in the alloy mole ratios, ''x'' and ''y''. Indium phosphide-based photonic integrated circuits, or PICs, commonly use alloys of to construct quantum wells, waveguides and other photonic structures, lattice matched to an InP substrate, enabling single-crystal epitaxial growth onto InP. Many devices operating in the near-infrared 1.55 μm wavelength window utilize this alloy, and are employed as optical components (such as laser transmitters, photodetectors Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Compound
In chemistry, a quaternary compound is a compound consisting of exactly four chemical elements. In another use of the term in organic chemistry, a quaternary compound is or has a cation consisting of a central positively charged atom with four substituents, especially organic (alkyl and aryl) groups, discounting hydrogen atoms. The best-known quaternary compounds are quaternary ammonium salts, having a nitrogen atom at the centre. For example, in the following reaction, the nitrogen atom is said to be quaternized as it has gone from 3 to 4 substituents: :R3N + RCl -> R4N+Cl- Other examples include substituted phosphonium salts (), substituted arsonium salts () like arsenobetaine, as well as some arsenic-containing superconductors. Substituted stibonium () and bismuthonium salts () have also been described. See also *Binary compound *Ternary compound *Onium ion *Quaternary phase In materials chemistry, a quaternary phase is a chemical compound containing four element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
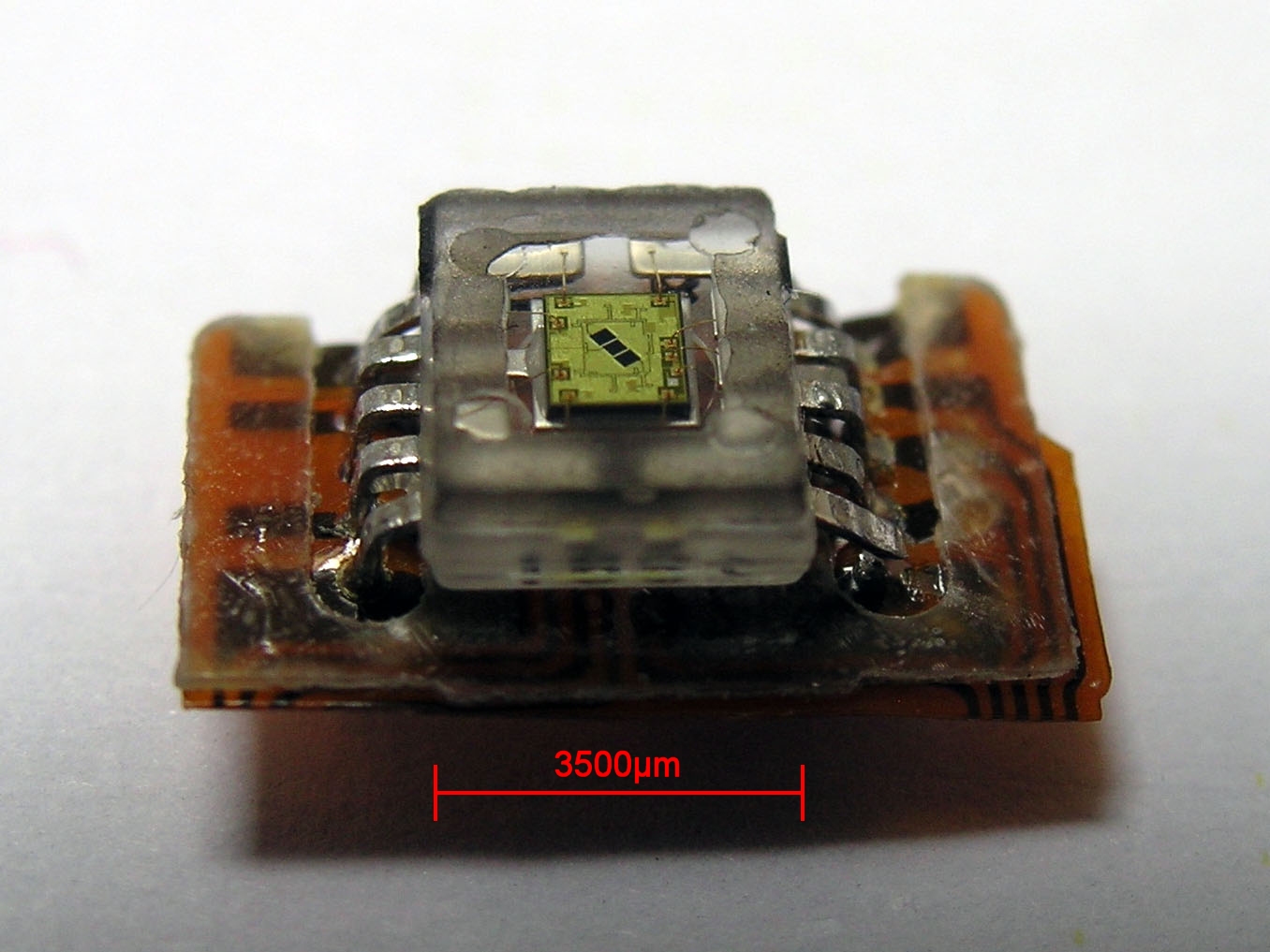
Photodetectors
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, or by various performance metrics, such as spectral response. Semiconductor-based photodetectors typically photo detector have a p–n junction that converts light photons into current. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy. Types Photodetectors may be classified by their mechanism for detection: * Photoemission or photoelectric effect: Photons cause electrons to transition from the conduction band of a material to free electrons in a vacuum or gas. * Thermal: Photons cause electrons to transition to mid-gap states then decay back to lower bands, inducing ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Compounds
Gallium compounds compounds containing the element gallium. These compounds are found primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The +1 oxidation state is also found in some compounds, although it is less common than it is for gallium's heavier congeners indium and thallium. For example, the very stable GaCl2 contains both gallium(I) and gallium(III) and can be formulated as GaIGaIIICl4; in contrast, the monochloride is unstable above 0 °C, disproportionating into elemental gallium and gallium(III) chloride. Compounds containing Ga–Ga bonds are true gallium(II) compounds, such as GaS (which can be formulated as Ga24+(S2−)2) and the dioxan complex Ga2Cl4(C4H8O2)2.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 240 Aqueous chemistry Strong acids dissolve gallium, forming gallium(III) salts such as (gallium nitrate). Aqueous solutions of gallium(III) salts contain the hydrated gallium ion, . Gallium(III) hydroxide, , may be precipitated from gallium(III) solutions by adding ammonia. Dehydrating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Compounds
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts per million of the Earth's crust. Indium has a melting point higher than sodium and gallium, but lower than lithium and tin. Chemically, indium is similar to gallium and thallium, and it is largely intermediate between the two in terms of its properties. Indium was discovered in 1863 by Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymous Theodor Richter by spectroscopic methods. They named it for the indigo blue line in its spectrum. Indium was isolated the next year. Indium is a minor component in zinc sulfide ores and is produced as a byproduct of zinc refinement. It is most notably used in the semiconductor industry, in low-melting-point metal alloys such as solders, in soft-metal high-vacuum seals, and in the production of transparent conductive coatings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
III-V Semiconductors
Semiconductor materials are nominally small band gap insulators. The defining property of a semiconductor material is that it can be compromised by doping it with impurities that alter its electronic properties in a controllable way. Because of their application in the computer and photovoltaic industry—in devices such as transistors, lasers, and solar cells—the search for new semiconductor materials and the improvement of existing materials is an important field of study in materials science. Most commonly used semiconductor materials are crystalline inorganic solids. These materials are classified according to the periodic table groups of their constituent atoms. Different semiconductor materials differ in their properties. Thus, in comparison with silicon, compound semiconductors have both advantages and disadvantages. For example, gallium arsenide (GaAs) has six times higher electron mobility than silicon, which allows faster operation; wider band gap, which allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Cell Efficiency
Solar-cell efficiency refers to the portion of energy in the form of sunlight that can be converted via photovoltaics into electricity by the solar cell. The efficiency of the solar cells used in a photovoltaic system, in combination with latitude and climate, determines the annual energy output of the system. For example, a solar panel with 20% efficiency and an area of 1 m2 will produce 200 kWh/yr at Standard Test Conditions if exposed to the Standard Test Condition solar irradiance value of 1000 W/m2 for 2.74 hours a day. Usually solar panels are exposed to sunlight for longer than this in a given day, but the solar irradiance is less than 1000 W/m2 for most of the day. A solar panel can produce more when the sun is high in the sky and will produce less in cloudy conditions or when the sun is low in the sky, usually the sun is lower in the sky in the winter. Two location dependant factors that affect solar PV efficiency are the dispersion and intensity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Indium Arsenide Antimonide Phosphide
Gallium indium arsenide antimonide phosphide ( or GaInPAsSb) is a semiconductor material. Research has shown that GaInAsSbP can be used in the manufacture of mid-infrared light-emitting diodesRoom temperature midinfrared electroluminescence from GaInAsSbP light emitting diodes, A. Krier, V. M. Smirnov, P. J. Batty, V. I. Vasil’ev, G. S. Gagis, and V. I. Kuchinskii, Appl. Phys. Lett. vol. 90 pp. 211115 (2007) Lattice-matched GaInPAsSb/InAs structures for devices of infrared optoelectronics, M. Aidaraliev, N. V. Zotova, S. A. Karandashev, B. A. Matveev, M. A. Remennyi, N. M. Stus’, G. N. Talalakin, V. V. Shustov, V. V. Kuznetsov and E. A. Kognovitskaya, Semiconductors vol. 36 num. 8 pp. 944-949 (2002) and thermophotovoltaic cells.Low Bandgap GaInAsSbP Pentanary Thermophotovoltaic Diodes, K. J. Cheetham, P. J. Carrington, N. B. Cook and A. Krier, Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, vol. 95 pp. 534-537 (2011) GaInAsSbP layers can be grown by heteroepitaxy on indium arsenide, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Gallium Phosphide
Indium gallium phosphide (InGaP), also called gallium indium phosphide (GaInP), is a semiconductor composed of indium, gallium and phosphorus. It is used in high-power and high-frequency electronics because of its superior electron velocity with respect to the more common semiconductors silicon and gallium arsenide. It is used mainly in HEMT and HBT structures, but also for the fabrication of high efficiency solar cells used for space applications and, in combination with aluminium (AlGaInP alloy) to make high brightness LEDs with orange-red, orange, yellow, and green colors. Some semiconductor devices such as EFluor Nanocrystal use InGaP as their core particle. Indium gallium phosphide is a solid solution of indium phosphide and gallium phosphide. Ga0.5In0.5P is a solid solution of special importance, which is almost lattice matched to GaAs. This allows, in combination with (AlxGa1−x)0.5In0.5, the growth of lattice matched quantum wells for red emitting semiconductor laser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple-junction Solar Cell
Multi-junction (MJ) solar cells are solar cells with multiple p–n junctions made of different semiconductor materials. Each material's p-n junction will produce electric current in response to different wavelengths of light. The use of multiple semiconducting materials allows the absorbance of a broader range of wavelengths, improving the cell's sunlight to electrical energy conversion efficiency. Traditional single-junction cells have a maximum theoretical efficiency of 33.16%. Theoretically, an infinite number of junctions would have a limiting efficiency of 86.8% under highly concentrated sunlight. As of 2008 the best lab examples of traditional crystalline silicon (c-Si) solar cells had efficiencies between 20% and 25%, while lab examples of multi-junction cells have demonstrated performance over 46% under concentrated sunlight. Commercial examples of tandem cells are widely available at 30% under one-sun illumination, and improve to around 40% under concentrated sunlight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraunhofer Institute For Solar Energy Systems
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE (or Fraunhofer ISE) is an institute of the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft. Located in Freiburg, Germany, The Institute performs applied scientific and engineering research and development for all areas of solar energy. Fraunhofer ISE has three external branches in Germany which carry out work on solar cell and semiconductor material development: the Laboratory and Service Center (LSC) in Gelsenkirchen, the Technology Center of Semiconductor Materials (THM) in Freiberg, and the Fraunhofer Center for Silicon Photovoltaics (CSP) in Halle. Since 2006, Prof. Dr. Eicke R. Weber is the director of Fraunhofer ISE. With over 1,100 employees, Fraunhofer ISE is the largest institute for applied solar energy research in Europe. The 2012 Operational Budget including investments is 74.3 million euro. History Fraunhofer ISE was founded in 1981 by Adolf Goetzberger in Freiburg, Germany. It was the first non-university establishment for applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C Band (IEEE)
The C band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in the microwave range of frequencies ranging from 4.0 to 8.0 gigahertz (GHz). However, the U.S. Federal Communications Commission C band proceeding and auction, designated 3.7–4.2 GHz as C band. The C band is used for many satellite communications transmissions, some Wi-Fi devices, some cordless telephones, as well as some Radar and weather radar systems. Use in satellite communication The communications C band was the first frequency band that was allocated for commercial telecommunications via satellites. The same frequencies were already in use for terrestrial microwave radio relay chains. Nearly all C-band communication satellites use the band of frequencies from 3.7 to 4.2 GHz for their downlinks, and the band of frequencies from 5.925 to 6.425 GHz for their uplinks. Note that by using the band from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses of ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |