|
Incremental Funding Methodology
The Incremental Funding Methodology (IFM) is an ROI-informed approach to software development in which software is developed and delivered in carefully prioritized chunks of customer valued functionality. These chunks are known as Minimum Marketable Features (MMFs). IFM integrates traditional software engineering activities with financially informed project management strategies. IFM heuristics provide clarity into important metrics such as project level NPV, ROI, initial start-up investment costs, and time needed for a project to reach self-funding status. It enables developers, customers, and business stakeholders to answer critical questions related to the development and delivery of a product and to optimize strategies accordingly. In short, IFM equips developers and project managers with techniques and principles for increasing the financial returns of a software project and for identifying development schedules that make a project financially feasible. See also * Minimum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Of Return
In finance, return is a profit on an investment. It comprises any change in value of the investment, and/or cash flows (or securities, or other investments) which the investor receives from that investment over a specified time period, such as interest payments, coupons, cash dividends and stock dividends. It may be measured either in absolute terms (e.g., dollars) or as a percentage of the amount invested. The latter is also called the holding period return. A loss instead of a profit is described as a '' negative return'', assuming the amount invested is greater than zero. To compare returns over time periods of different lengths on an equal basis, it is useful to convert each return into a return over a period of time of a standard length. The result of the conversion is called the rate of return. Typically, the period of time is a year, in which case the rate of return is also called the annualized return, and the conversion process, described below, is called ''annualiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, writing source code, code, in that it includes conceiving the goal, evaluating feasibility, analyzing software requirements, requirements, software design, design, software testing, testing and software release life cycle, release. The process is part of software engineering which also includes management, organizational management, Software project management, project management, configuration management and other aspects. Software development involves many skills and job specializations including software programmer, programming, software test, testing, Technical writing, documentation, graphic design, user support, marketing, and fundraising. Software development involves many software tools, tools including: compiler, integrated develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principles and computer programming expertise to develop software systems that meet user needs. The terms ''programmer'' and ''coder'' overlap ''software engineer'', but they imply only the construction aspect of a typical software engineer workload. A software engineer applies a software development process, which involves defining, Implementation, implementing, Software testing, testing, Project management, managing, and Software maintenance, maintaining software systems, as well as developing the software development process itself. History Beginning in the 1960s, software engineering was recognized as a separate field of engineering. The development of software engineering was seen as a struggle. Problems included software that was over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Project Management
Software project management is the process of planning and leading software projects. It is a sub-discipline of project management in which software projects are planned, implemented, monitored and controlled. History In the 1970s and 1980s, the software industry grew very quickly, as computer companies quickly recognized the relatively low cost of software production compared to hardware production and circuitry. To manage new development efforts, companies applied the established project management methods, but project schedules slipped during test runs, especially when confusion occurred in the gray zone between the user specifications and the delivered software. To be able to avoid these problems, ''software'' project management methods focused on matching user requirements to delivered products, in a method known now as the waterfall model. As the industry has matured, analysis of software project management failures has shown that the following are the most common caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Present Value
The net present value (NPV) or net present worth (NPW) is a way of measuring the value of an asset that has cashflow by adding up the present value of all the future cash flows that asset will generate. The present value of a cash flow depends on the interval of time between now and the cash flow because of the Time value of money (which includes the annual effective discount rate). It provides a method for evaluating and comparing capital projects or financial products with cash flows spread over time, as in loans, investments, payouts from insurance contracts plus many other applications. Time value of money dictates that time affects the value of cash flows. For example, a lender may offer 99 cents for the promise of receiving $1.00 a month from now, but the promise to receive that same dollar 20 years in the future would be worth much less today to that same person (lender), even if the payback in both cases was equally certain. This decrease in the current value of future c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
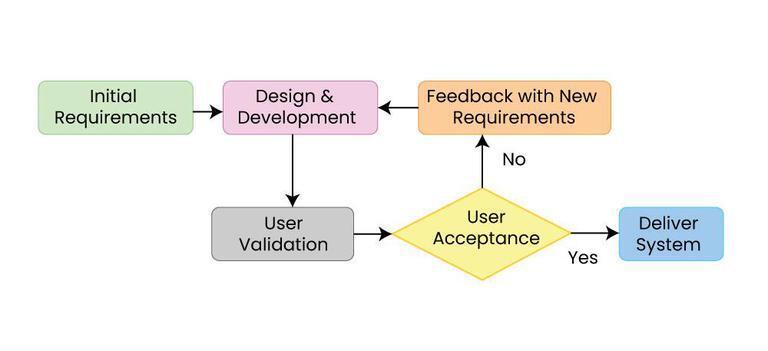
Minimum Viable Product
A minimum viable product (MVP) is a version of a product with just enough features to be usable by early customers who can then provide feedback for future product development. A focus on releasing an MVP means that developers potentially avoid lengthy and (possibly) unnecessary work. Instead, they iterate on working versions and respond to feedback, challenging and validating assumptions about a product's requirements. The term was coined and defined in 2001 by Frank Robinson and then popularized by Steve Blank and Eric Ries.W. S. Junk,The Dynamic Balance Between Cost, Schedule, Features, and Quality in Software Development Projects, Computer Science Dept., University of Idaho, SEPM-001, April 2000. It may also involve carrying out market analysis beforehand. The MVP is analogous to experimentation in the scientific method applied in the context of validating business hypotheses. It is utilized so that prospective entrepreneurs would know whether a given business idea would ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |