|
Incremental Backup
An incremental backup is one in which successive copies of the data contain only the portion that has changed since the preceding backup copy was made. When a full recovery is needed, the restoration process would need the last full backup plus all the incremental backups until the point of restoration. Incremental backups are often desirable as they reduce storage space usage, and are quicker to perform than differential backups. Variants Incremental The most basic form of incremental backup consists of identifying, recording and thus, preserving only those files that have changed since the last backup. Since changes are typically low, incremental backups are much smaller and quicker than full backups. For instance, following a full backup on Friday, a Monday backup will contain only those files that changed since Friday. A Tuesday backup contains only those files that changed since Monday, and so on. A full restoration of data will naturally be slower, since all increments mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Backup
A differential backup is a type of data backup that preserves data, saving only the difference in the data since the last full backup. The rationale in this is that, since changes to data are generally few compared to the entire amount of data in the data repository, the amount of time required to complete the backup will be smaller than if a full backup was performed every time that the organization or data owner wishes to back up changes since the last full backup. Another advantage, at least as compared to the incremental backup method of data backup, is that at data restoration time, at most two backup media are ever needed to restore all the data. This simplifies data restores as well as increases the likelihood of shortening data restoration time. Meaning A differential backup is a cumulative backup of ''all'' changes made since the last ''full'' backup, i.e., the ''differences'' since the last full backup. The advantage to this is the quicker recovery time, requiring only a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rsync
rsync (remote sync) is a utility for transferring and synchronizing files between a computer and a storage drive and across networked computers by comparing the modification times and sizes of files. It is commonly found on Unix-like operating systems and is under the GPL-3.0-or-later license. rsync is written in C as a single- threaded application. The rsync algorithm is a type of delta encoding, and is used for minimizing network usage. Zstandard, LZ4, or Zlib may be used for additional data compression, and SSH or stunnel can be used for security. rsync is typically used for synchronizing files and directories between two different systems. For example, if the command rsync local-file user@remote-host:remote-file is run, rsync will use SSH to connect as user to remote-host. Once connected, it will invoke the remote host's rsync and then the two programs will determine what parts of the local file need to be transferred so that the remote file matches the local one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Mirror
Mirror sites or mirrors are replicas of other websites. The concept of mirroring applies to network services accessible through any protocol, such as HTTP or FTP. Such sites have different URLs than the original site, but host identical or near-identical content. Mirror sites are often located in a different geographic region than the original, or upstream site. The purpose of mirrors is to reduce network traffic, improve access speed, ensure availability of the original site for technical or political reasons, or provide a real-time backup of the original site. Mirror sites are particularly important in developing countries, where internet access may be slower or less reliable. Mirror sites were heavily used on the early internet, when most users accessed through dialup and the Internet backbone had much lower bandwidth than today, making a geographically-localized mirror network a worthwhile benefit. Download archives such as Info-Mac, Tucows and CPAN maintained worldwide netwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intronis
Barracuda Networks, Inc. provides security, networking and storage products based on network appliances and cloud services. History Barracuda Networks was founded in 2003 by CEO Dean Drako, Michael Perone, and Zach Levow, and the company introduced the Barracuda Spam and Virus Firewall in the same year. In 2007, the company moved its headquarters to Campbell, California, and opened an office in Ann Arbor, Michigan. In January 2006, it closed its first outside investment of $40 million from Sequoia Capital and Francisco Partners. On January 29, 2008, Barracuda Networks was sued by Trend Micro over their use of the open source anti-virus software Clam AntiVirus, which Trend Micro claimed to be in violation of their patent on 'anti-virus detection on an SMTP or FTP gateway'. In addition to providing samples of prior art in an effort to render Trend Micro's patent invalid, in July 2008 Barracuda launched a countersuit against Trend Micro claiming Trend Micro violated several ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zetta
A metric prefix is a unit prefix that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a multiple or submultiple of the unit. All metric prefixes used today are decadic. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to any unit symbol. The prefix ''kilo'', for example, may be added to ''gram'' to indicate ''multiplication'' by one thousand: one kilogram is equal to one thousand grams. The prefix '' milli'', likewise, may be added to ''metre'' to indicate ''division'' by one thousand; one millimetre is equal to one thousandth of a metre. Decimal multiplicative prefixes have been a feature of all forms of the metric system, with six of these dating back to the system's introduction in the 1790s. Metric prefixes have also been used with some non-metric units. The SI prefixes are metric prefixes that were standardised for use in the International System of Units (SI) by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) in resolutions dating from 1960 to 2022. Since 2009, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is a model of computer data storage in which data, said to be on "the cloud", is stored remotely in logical pools and is accessible to users over a network, typically the Internet. The physical storage spans multiple servers (sometimes in multiple locations), and the physical environment is typically owned and managed by a cloud computing provider. These cloud storage providers are responsible for keeping the data available and accessible, and the physical environment secured, protected, and running. People and organizations buy or lease storage capacity from the providers to store user, organization, or application data. Cloud storage services may be accessed through a colocated cloud computing service, a web service application programming interface (API) or by applications that use the API, such as cloud desktop storage, a cloud storage gateway or Web-based content management systems. History Cloud computing is believed to have been invented by J. C. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backup Rotation Scheme
A backup rotation scheme is a system of backing up data to computer media (such as tapes) that minimizes, by re-use, the number of media used. The scheme determines how and when each piece of removable storage is used for a backup job and how long it is retained once it has backup data stored on it. Different techniques have evolved over time to balance data retention and restoration needs with the cost of extra data storage media. Such a scheme can be quite complicated if it takes incremental backups, multiple retention periods, and off-site storage into consideration. Schemes First in, first out A first in, first out (FIFO) backup scheme saves new or modified files onto the "oldest" media in the set, i.e. the media that contain the oldest and thus least useful previously backed up data. Performing a daily backup onto a set of 14 media, the backup depth would be 14 days. Each day, the oldest media would be inserted when performing the backup. This is the simplest rotation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Encoding
Delta encoding is a way of storing or transmitting data in the form of '' differences'' (deltas) between sequential data rather than complete files; more generally this is known as data differencing. Delta encoding is sometimes called delta compression, particularly where archival histories of changes are required (e.g., in revision control software). The differences are recorded in discrete files called "deltas" or "diffs". In situations where differences are small – for example, the change of a few words in a large document or the change of a few records in a large table – delta encoding greatly reduces data redundancy. Collections of unique deltas are substantially more space-efficient than their non-encoded equivalents. From a logical point of view, the difference between two data values is the information required to obtain one value from the other – see relative entropy. The difference between identical values (under some equivalence) is often called ''0'' or the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dump (Unix)
The dump command is a program on Unix and Unix-like operating systems used to back up file systems. It operates on blocks, below filesystem abstractions such as files and directories. Dump can back up a file system to a tape or another disk. It is often used across a network by piping its output through bzip2 then SSH. A dump utility first appeared in Version 6 AT&T UNIX. A dump command is also part of ASCII's ''MSX-DOS2 Tools'' for MSX-DOS version 2. Usage dump 0123456789acLnSu B records b blocksize C cachesize D dumpdates d density -P pipecommand h level s feet T datefilesystem $ dump -W , -w See also *tar (file format) *cpio *rsync rsync (remote sync) is a utility for transferring and synchronizing files between a computer and a storage drive and across networked computers by comparing the modification times and sizes of files. It is commonly found on Unix-like opera ... References External linksHome page of the Linux Ext2 filesystem dump/restore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incremental Computing
Incremental computing, also known as incremental computation, is a software feature which, whenever a piece of data changes, attempts to save time by only recomputing those outputs which depend on the changed data. When incremental computing is successful, it can be significantly faster than computing new outputs naively. For example, a spreadsheet software package might use incremental computation in its recalculation features, to update only those cells containing formulas which depend (directly or indirectly) on the changed cells. When incremental computing is implemented by a tool that can implement it for a variety of different pieces of code automatically, that tool is an example of a program analysis tool for optimization. Static versus dynamic Incremental computing techniques can be broadly separated into two types of approaches: '' Static approaches'' attempt to derive an incremental program from a conventional program P using, e.g., either manual design and refactori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
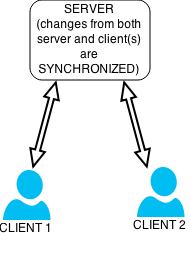
Data Synchronization
Data synchronization is the process of establishing consistency between source and target data stores, and the continuous harmonization of the data over time. It is fundamental to a wide variety of applications, including file synchronization and mobile device synchronization. Data synchronization can also be useful in encryption for synchronizing public key servers. Data synchronization is needed to update and keep multiple copies of a set of data coherent with one another or to maintain data integrity, Figure 3. For example, database replication is used to keep multiple copies of data synchronized with database servers that store data in different locations. Examples Examples include: * File synchronization, such as syncing a hand-held MP3 player to a desktop computer; * Cluster file systems, which are file systems that maintain data or indexes in a coherent fashion across a whole computing cluster; * Cache coherency, maintaining multiple copies of data in sync across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |