|
Impulse 21
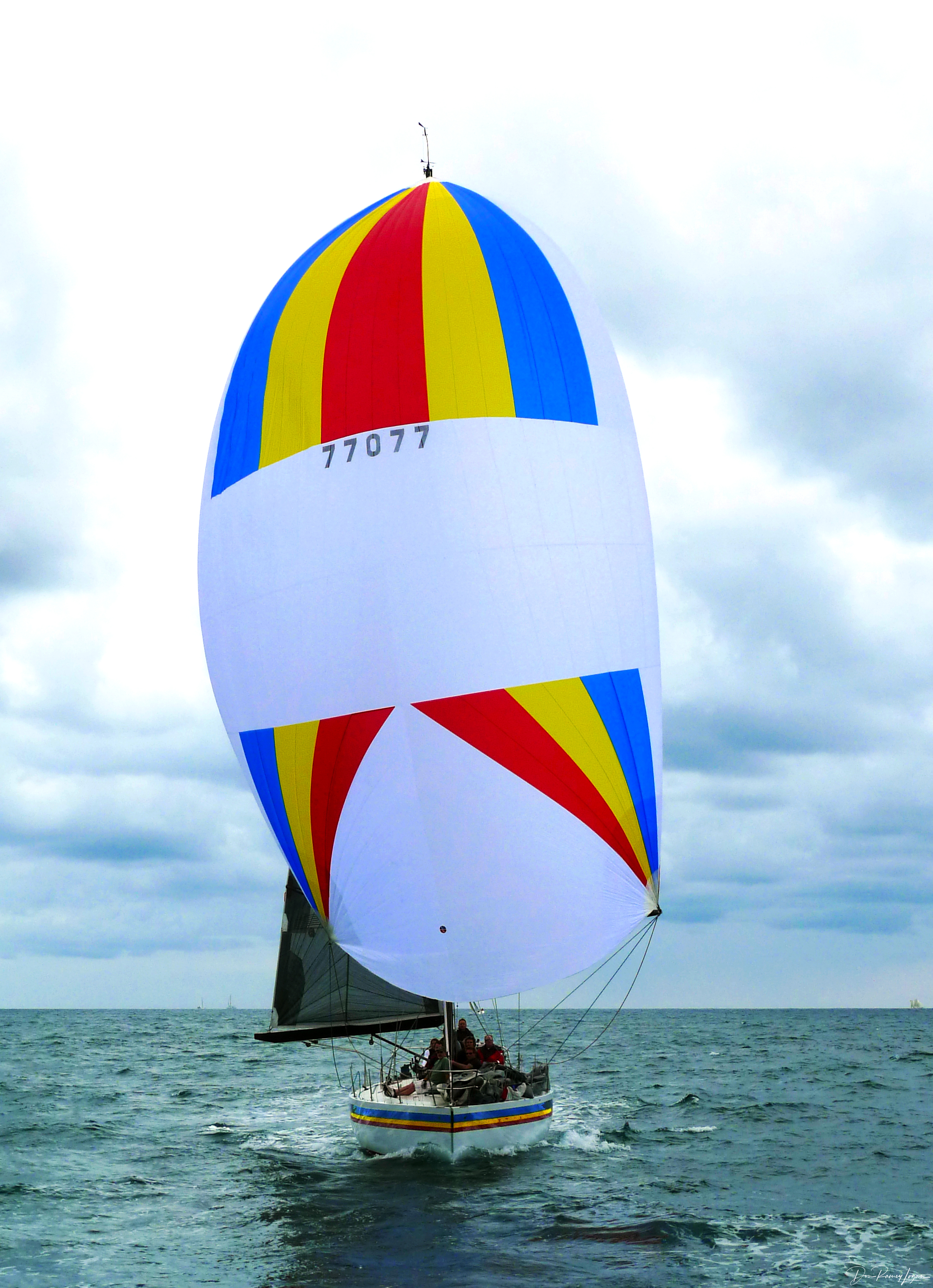
The Impulse 21, also called the Impulse Eagle, is an American trailerable sailboat that was designed by William E. Cook as a one-design racer and day sailer, It was first built in 1986.Sherwood, Richard M.: ''A Field Guide to Sailboats of North America, Second Edition'', pages 110-111. Houghton Mifflin Company, 1994. Production The design was initially built by Impulse Marine in the United States. After the first 10-12 boats were completed, it was then built under contract by Johnson Boatworks on behalf of Impulse Marine. A total of 150 boats were completed, but it is now out of production. Design The Impulse 21 is a recreational keelboat, built predominantly of fiberglass, with a Klegecell core. It has a fractional sloop rig, a raked stem, a cut-out, walk-through, sharply reverse transom that allows ease of boarding, an internally mounted spade-type rudder controlled by a tiller and a fixed fin keel. It displaces and carries of ballast. The boat has a draft of wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William E
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name should b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houghton Mifflin Company
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt (; HMH) is an American publisher of textbooks, instructional technology materials, assessments, reference works, and fiction and non-fiction for both young readers and adults. The company is based in the Boston Financial District. It was formerly known as Houghton Mifflin Company, but it changed its name following the 2007 acquisition of Harcourt Publishing. Prior to March 2010, it was a subsidiary of Education Media and Publishing Group Limited, an Irish-owned holding company registered in the Cayman Islands and formerly known as Riverdeep. History Ticknor and Allen, 1832 In 1832, William Ticknor and John Allen purchased a bookselling business in Boston and began to involve themselves in publishing; James T. Fields joined as a partner in 1843. Fields and Ticknor gradually gathered an impressive list of writers, including Ralph Waldo Emerson, Nathaniel Hawthorne, and Henry David Thoreau. The duo formed a close relationship with Riverside Press, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sailing Boat Types
The following is a partial list of sailboat types and sailing classes, including keelboats, dinghies and multihull ( catamarans and trimarans). Olympic classes World Sailing Classes Historically known as the IYRU (International Yacht Racing Union), the organization evolved into the ISAF (International Sailing Federation) in 1996, and as of December 2015 is now World Sailing. Dinghies Keelboats & yachts Multihulls Boards Radio-controlled Former World Sailing-classes Dinghies Keelboats & yachts Multihulls Boards Other classes and sailboat types Dinghies Keelboats & yachts Multihulls See also * Classic dinghy classes * List of boat types * List of historical ship types * List of keelboat classes designed before 1970 * Olympic sailing classes * Small-craft sailing * Clansman 30 Notes References {{DEFAULTSORT:Sailing boat types Types * Boat types A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth Yardstick
The Portsmouth Yardstick (PY) or Portsmouth handicap scheme is a term used for a number of related systems of empirical handicapping used primarily in small sailboat racing. The handicap is applied to the time taken to sail any course, and the handicaps can be used with widely differing types of sailboats. Portsmouth Numbers are updated with data from race results, normally annually. The various schemes are not directly linked, and ratings for the same class can and often do vary in the different schemes. The most prominent Portsmouth Yardstick systems are probably those administered in the United States by the Portsmouth Numbers Committee, in the United Kingdom by the Royal Yachting Association ( RYA) and in Australia by Victoria Yachting. History The original UK Portsmouth Yardstick was developed by Stanley Milledge, who was in charge of handicapping racing at the '' Langstone Sailing Club'' in 1947 using the ''Island One'' design as the scratch boat (having a value 100). In 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinnaker
A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind on courses between a reach (wind at 90° to the course) to downwind (course in the same direction as the wind). Spinnakers are constructed of lightweight fabric, usually nylon, and are often brightly colored. They may be designed to perform best as either a reaching or a running spinnaker, by the shaping of the panels and seams. They are attached at only three points and said to be ''flown''. Nomenclature Informal names for a spinnaker are ''kite'' or ''chute'' (owing to their resemblance to a parachute in both construction and appearance). Boats may have more than one spinnaker, differentiated by a letter to indicate symmetric (S) or asymmetric (A) and a number to indicate size (with higher numbers indicating smaller size), e.g. ''A1'' would be a large asymmetric sail and ''S3'' would be a smaller symmetric sail. Operation A spinnaker is used for sailing with the direction of the wind. Symmetrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooler
A cooler, portable ice chest, ice box, cool box, chilly bin (in New Zealand), or esky (Australia) is an insulated box used to keep food or drink cool. Ice cubes are most commonly placed in it to help the contents inside stay cool. Ice packs are sometimes used, as they either contain the melting water inside, or have a gel sealed inside that stays cold longer than plain ice (absorbing heat as it changes phase). Coolers are often taken on picnics, and on vacation or holiday. Where summers are hot, they may also be used just for getting cold groceries home from the store, such as keeping ice cream from melting in a hot automobile. Even without adding ice, this can be helpful, particularly if the trip home will be lengthy. Some coolers have built-in cupholders in the lid. They are usually made with interior and exterior shells of plastic, with a hard foam in between. They come in sizes from small personal ones to large family ones with wheels. Disposable ones are made solely f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuddy Cabin
A cuddy is a small room or cupboard, particularly on a boat. Sometimes a cuddy refers to a small but cosy hut. The origin of the term is not clear. Cuddy was in use in colonial America as early as 1655. The term may derive from the Dutch ''kajuit'', meaning a small cabin, or from the French ''cahute'', meaning a hut. Nautical uses The term cuddy is used particularly in nautical contexts. In the 19th century it referred to a saloon cabin at the stern of immigrant ships, where wealthy immigrants could travel in greater comfort than the steerage passengers below.John Wilson (2012The voyage out - Cabin and steerage Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 13 July 2012. A cuddy boat is a boat with a small shelter cabin with maybe a small head A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in British and American shipbuilding traditions the construction is dated from this event. Etymology The word "keel" comes from Old English , Old Norse , = "ship" or "keel". It has the distinction of being regarded by some scholars as the first word in the English language recorded in writing, having been recorded by Gildas in his 6th century Latin work ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', under the spelling ''cyulae'' (he was referring to the three ships that the Saxons first arrived in). is the Latin word for "keel" and is the origin of the term careen (to clean a keel and the hull in general, often by rolling the ship on its side). An example of this use is Careening Cove, a suburb of Sydney, Australia, where careening was carried out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiller
A tiller or till is a lever used to steer a vehicle. The mechanism is primarily used in watercraft, where it is attached to an outboard motor, rudder post or stock to provide leverage in the form of torque for the helmsman to turn the rudder. A tiller may also be used in vehicles outside of water, and was seen in early automobiles. On vessels, a tiller can be used by the helmsman directly pulling or pushing it, but it may also be moved remotely using tiller lines or a ship's wheel. Rapid or excessive movement of the tiller results in an increase in drag and will result in braking or slowing the boat. Description A tiller is a lever used to steer a vehicle. It provides leverage in the form of torque to turn the device that changes the direction of the vehicle, such as a rudder on a watercraft or the surface wheels on a wheeled vehicle. A tiller can be used by directly pulling or pushing it, but it may also be moved remotely using tiller lines or a ship's wheel; some kayaks wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transom
A transom is the vertical reinforcement which strengthens the stern of a boat. This flat termination of the stern is typically above the waterline. The term was used as far back as Middle English in the 1300s, having come from Latin ''transversus'' (transverse) via Old French ''traversain'' (set crosswise). The stern of a boat is typically vertical. It can be raked such that there is an overhang above the water, as at the bow. A reverse transom is angled from the waterline forwards. Transoms can be used to support a rudder, outboard motor, or as a swimming and access platform. Gallery File:The Bermuda cedar (Juniperus bermudiana) transom of Spirit of Bermuda, 2016.jpg, The Bermuda cedar transom of the Spirit of Bermuda File:Sea Scooter transom.jpg, Flat transom on a dinghy with mount points for a rudder. File:Coble on shore at Boulmer (2) - geograph.org.uk - 1381157.jpg, Raked transom with rudder mount points. File:CS 30 Sailboat Kelsea 0297.jpg, Reverse transom with rudder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raked Stem
The stem is the most forward part of a boat or ship's bow and is an extension of the keel itself. It is often found on wooden boats or ships, but not exclusively. Description The stem is the curved edge stretching from the keel below, up to the gunwale of the boat. It is part of the physical structure of a wooden boat or ship that gives it strength at the critical section of the structure, bringing together the port and starboard side planks of the hull. Plumb and raked stem There are two styles of stems: ''plumb'' and ''raked''. When the stem comes up from the water, if it is perpendicular to the waterline it is "plumb". If it is inclined at an angle to the waterline it is "raked". (For example, "The hull is single decked and characterized by a plumb stem, full bows, straight keel, moderate deadrise, and an easy turn of bilge.") Stemhead Because the stem is very sturdy, the top end of it may have something attached, either ornamental or functional in nature. On small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Rig
A fractional rig on a sailing vessel consists of a foresail, such as a jib or genoa sail, that does not reach all the way to the top of the mast. The forestay is a wire that secures the mast to the front of the boat. With a fractional rig, the forestay is attached between about 1/8 and 1/4 of the length of the mast lower down, rather than being attached to the top of the mast as in a masthead rig. The foresail (jib or genoa) is then rigged to this stay. The mast is farther forward on the boat than on a masthead rig and so it has a larger mainsail. Masthead rigs are most common on larger keelboats or cruisers. A fractional rig is typically used on sailing dinghies and racing oriented keelboats, such as the J/24. Fractional rigs were introduced on race boats in order to allow more controllability of the surface of the mainsail and also less drag when sailing upwind. According to one manufacturer, "a key to making fast boats easier to sail than slow boats is the 'fractional rig' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |