|
Improved Layer 2 Protocol
IL2P (Improved Layer 2 Protocol) is a data link layer protocol originally derived from layer 2 of the X.25 protocol suite and designed for use by amateur radio operators. It is used exclusively on amateur packet radio networks. IL2P occupies the data link layer, the second layer of the OSI model. It is responsible for establishing link-layer connections, transferring data encapsulated in frames between nodes, and detecting errors introduced by the communications channel. The Improved Layer 2 Protocol (IL2P) was created by Nino Carrillo, KK4HEJ, based on AX.25 version 2.0 and implements Reed Solomon Forward Error Correction for greater accuracy and throughput than either AX.25 or FX.25. Specifically, in order to achieve greater stability on link speeds greater than 1200 baud. IL2P can be used with a variety of modulation methods including AFSK and GFSK. Thdirewolf software TNCcontains the first open source implementation of the protocol. IL2P Specification The IL2P draft sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Link Layer
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and may also provide the means to detect and possibly correct errors that can occur in the physical layer. The data link layer is concerned with local delivery of frames between nodes on the same level of the network. Data-link frames, as these protocol data units are called, do not cross the boundaries of a local area network. Inter-network routing and global addressing are higher-layer functions, allowing data-link protocols to focus on local delivery, addressing, and media arbitration. In this way, the data link layer is analogous to a neighborhood traffic cop; it endeavors to arbitrate between parties contending for access to a medium, without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Frequency-shift Keying
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier signal. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. The simplest FSK is binary FSK (BFSK). BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary (0s and 1s) information. With this scheme, the 1 is called the mark frequency and the 0 is called the space frequency. Modulating and demodulating Reference implementations of FSK modems exist and are documented in detail. The demodulation of a binary FSK signal can be done using the Goertzel algorithm very efficiently, even on low-power microcontrollers. Variations Multiple frequency-shift keying Continuous-phase frequency-shift keying In principle FSK can be implemented by using completely independent free-running os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear-feedback Shift Register
In computing, a linear-feedback shift register (LFSR) is a shift register whose input bit is a linear function of its previous state. The most commonly used linear function of single bits is exclusive-or (XOR). Thus, an LFSR is most often a shift register whose input bit is driven by the XOR of some bits of the overall shift register value. The initial value of the LFSR is called the seed, and because the operation of the register is deterministic, the stream of values produced by the register is completely determined by its current (or previous) state. Likewise, because the register has a finite number of possible states, it must eventually enter a repeating cycle. However, an LFSR with a well-chosen feedback function can produce a sequence of bits that appears random and has a very long cycle. Applications of LFSRs include generating pseudo-random numbers, pseudo-noise sequences, fast digital counters, and whitening sequences. Both hardware and software implementation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Encoding
In digital communications, differential coding is a technique used to provide ''unambiguous'' signal reception when using some types of modulation. It makes data to be transmitted to depend not only on the current signal state (or symbol), but also on the previous one. The common types of modulation that require differential coding include phase-shift keying and quadrature amplitude modulation. Purposes of differential coding When data is transmitted over twisted-pair wires, it is easy to accidentally insert an extra half-twist in the cable between the transmitter and the receiver. When this happens, the received signal is inverted. Similarly for BPSK. To demodulate BPSK, one needs to make a local oscillator ''synchronous'' with the remote one. This is accomplished by a carrier recovery circuit. However, the integer part of the recovered carrier is ambiguous. There are ''n'' valid but not equivalent phase shifts between the two oscillators. For BPSK, ''n'' = 2; the symbols appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer; The layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. This layer may be implemented by a PHY chip. The physical layer provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface to the transmission medium. The shapes and properties of the electrical connectors, the frequencies to broadcast on, the line code to use and similar low-level parameters, are specified by the physical layer. Role The physical layer defines the means of transmitting a stream of raw bits over a physical data link connecting network nodes. The bitstream may be grouped into code words or symbols and converted to a physical signal that is transmitted over a transmission medium. The physical layer consists of the electronic circuit transmission technologies of a network. It is a fundamental layer underlying the higher level functions in a network, and can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squelch
In telecommunications, squelch is a circuit function that acts to suppress the audio (or video) output of a receiver in the absence of a strong input signal. Essentially, squelch is a specialized type of noise gate designed to suppress weak signals. Squelch is used in two-way radios and VHF/UHF radio scanners to eliminate the sound of noise when the radio is not receiving a desired transmission. Carrier squelch A carrier squelch or noise squelch is the most simple variant of all. It operates strictly on the signal strength, such as when a television mutes the audio or blanks the video on "empty" channels, or when a walkie-talkie mutes the audio when no signal is present. In some designs, the squelch threshold is preset. For example, television squelch settings are usually preset. Receivers in base stations, or repeaters at remote mountain top sites, are usually not adjustable remotely from the control point. In two-way radios (also known as radiotelephones), the rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit-stuffing
In data transmission and telecommunication, bit stuffing (also known—uncommonly—as positive justification) is the insertion of non-information bits into data. Stuffed bits should not be confused with overhead bits. Bit stuffing is used for various purposes, such as for bringing bit streams that do not necessarily have the same or rationally related bit rates up to a common rate, or to fill buffers or frames. The location of the stuffing bits is communicated to the receiving end of the data link, where these extra bits are removed to return the bit streams to their original bit rates or form. Bit stuffing may be used to synchronize several channels before multiplexing or to rate-match two single channels to each other. Another use of bit stuffing is for run length limited coding: to limit the number of consecutive bits of the same value in the data to be transmitted. A bit of the opposite value is inserted after the maximum allowed number of consecutive bits. Since this is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
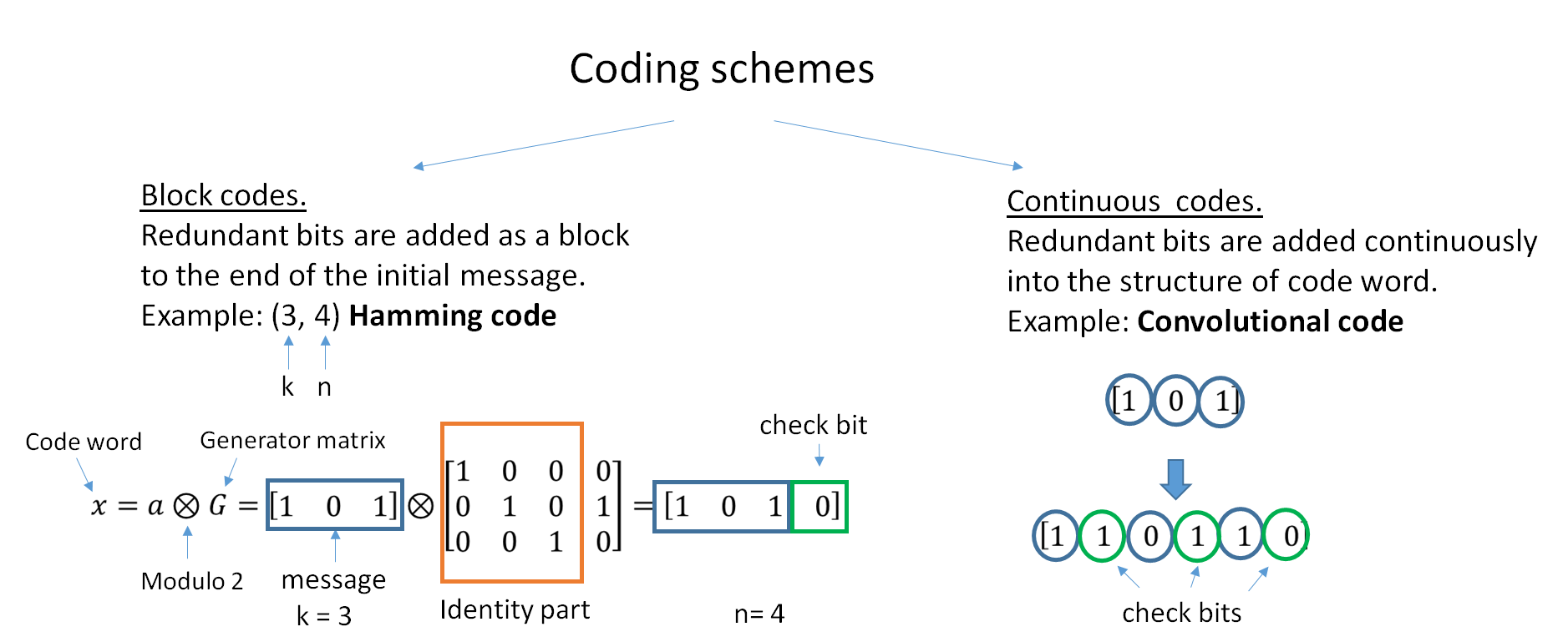
Error Correction Code
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is the sender encodes the message with redundant information in the form of an ECC. The redundancy allows the receiver to detect a limited number of errors that may occur anywhere in the message, and often to correct these errors without retransmission. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. ECC contrasts with error detection in that errors that are encountered can be corrected, not simply detected. The advantage is that a system using ECC does not require a reverse channel to request retransmission of data when an error occurs. The downside is that there is a fixed overhead that is added to the message, thereby requiring a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Strength In Telecommunications
In telecommunications, particularly in radio frequency engineering, signal strength refers to the transmitter power output as received by a reference antenna at a distance from the transmitting antenna. High-powered transmissions, such as those used in broadcasting, are expressed in dB- millivolts per metre (dBmV/m). For very low-power systems, such as mobile phones, signal strength is usually expressed in dB- microvolts per metre (dBμV/m) or in decibels above a reference level of one milliwatt ( dBm). In broadcasting terminology, 1 mV/m is 1000 μV/m or 60 dBμ (often written dBu). ;Examples: *100 dBμ or 100 mV/m: blanketing interference may occur on some receivers *60 dBμ or 1.0 mV/m: frequently considered the edge of a radio station's protected area in North America *40 dBμ or 0.1 mV/m: the minimum strength at which a station can be received with acceptable quality on most receivers Relationship to average radiated power The electric field strength at a specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem. Definition Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input): : \mathrm = \frac, where is average power. Both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth. Depending on whether the signal is a constant () or a random variable (), the signal-to-noise ratio for random noise becomes: : \mathrm = \frac where E refers to the expected value, i.e. in thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Frequency Shift Keying
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier signal. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. The simplest FSK is binary FSK (BFSK). BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary (0s and 1s) information. With this scheme, the 1 is called the mark frequency and the 0 is called the space frequency. Modulating and demodulating Reference implementations of FSK modems exist and are documented in detail. The demodulation of a binary FSK signal can be done using the Goertzel algorithm very efficiently, even on low-power microcontrollers. Variations Multiple frequency-shift keying Continuous-phase frequency-shift keying In principle FSK can be implemented by using completely independent free-running os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocol (computing)
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses pre-determined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there is a close analogy between protocols and programming languages: ''protocols are to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |