|
Implantation SNIF-NMR Dans Le Monde
{{disambiguation ...
Implantation may refer to: * Implantation (embryology), in which an embryo adheres to the wall of the uterus * Implant (medicine), insertion of implants * Endometrial transplantation, as part of the theory of retrograde menstruation in endometriosis * Ion implantation, insertion of ions, in semiconductor device fabrication * Implantation bleeding * Implantation of tooth * Implantation rate * Implantation spotting See also *Implant (other) Implant can refer to: Medicine *Implant (medicine), or specifically: **Brain implant **Breast implant ** Buttock implant **Cochlear implant **Contraceptive implant **Dental implant ** Fetal tissue implant ** Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implantation (embryology)
Implantation (nidation) is the stage in the embryonic development of mammals in which the blastocyst hatches as the embryo, adheres, and invades into the wall of the female's uterus. Implantation is the first stage of gestation, and when successful the female is considered to be pregnant. In a woman, an implanted embryo is detected by the presence of increased levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a pregnancy test. The implanted embryo will receive oxygen and nutrients in order to grow. There is an extensive variation in the type of trophoblast cells, and structures of the placenta across the different species of mammals. Of the five recognised stages of implantation including two pre-implantation stages that precede placentation, the first four are similar across the species. The five stages are migration and hatching, pre-contact, attachment, adhesion, and invasion. The two pre-implantation stages are associated with the pre-implantation embryo. In humans following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implant (medicine)
An implant is a medical device manufactured to replace a missing biological structure, support a damaged biological structure, or enhance an existing biological structure. Medical implants are man-made devices, in contrast to a Organ transplant, transplant, which is a transplanted biomedical tissue. The surface of implants that contact the body might be made of a Biomaterial, biomedical material such as titanium, silicone, or apatite depending on what is the most functional. In some cases implants contain electronics, e.g. artificial pacemaker and cochlear implants. Some implants are Biological activity, bioactive, such as Subcutaneous tissue, subcutaneous drug delivery devices in the form of implantable pills or drug-eluting stents. Applications Implants can roughly be categorized into groups by application: Sensory and neurological Perception, Sensory and Neurotechnology#Implant technologies, neurological implants are used for disorders affecting the major senses and the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
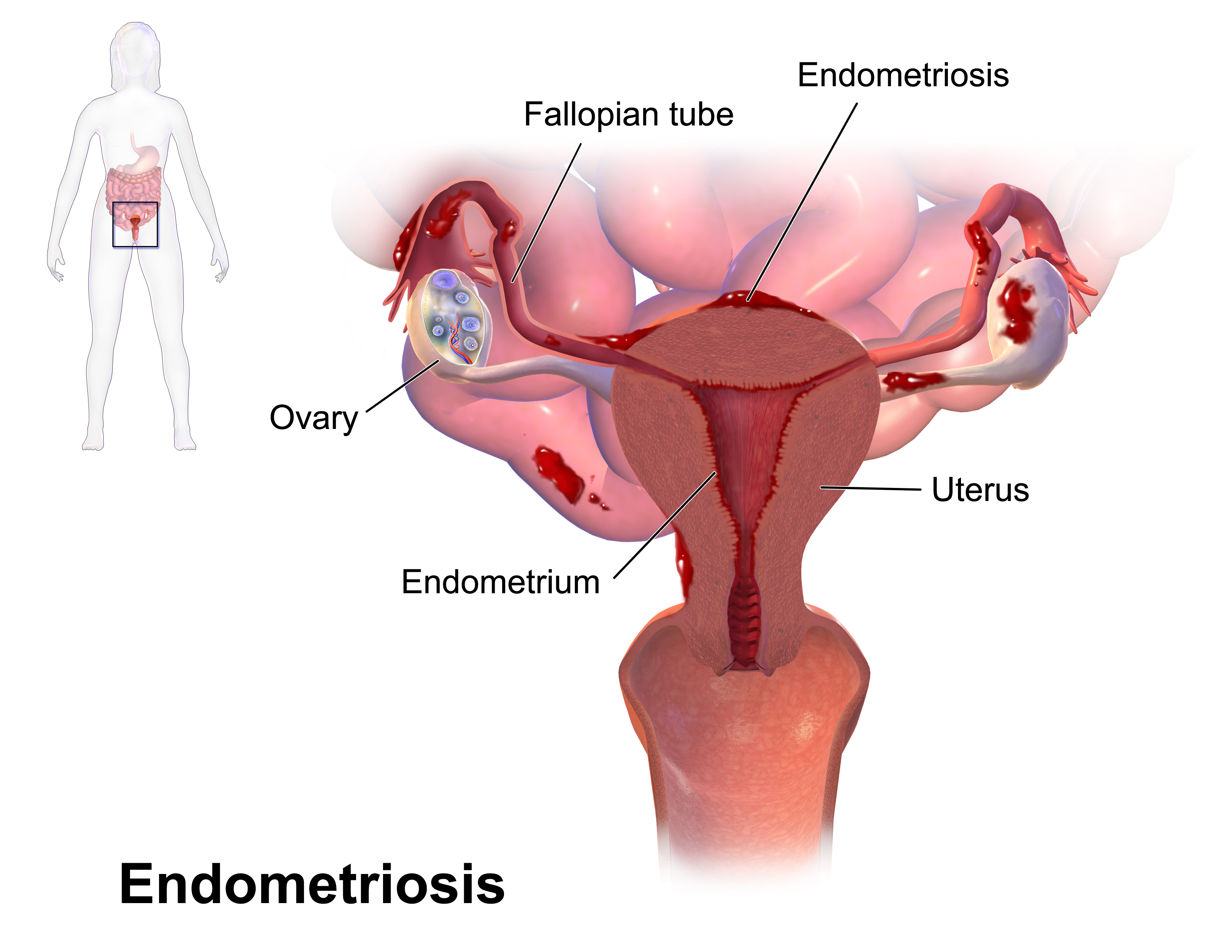
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease of the female reproductive system in which cells similar to those in the endometrium, the layer of tissue that normally covers the inside of the uterus, grow outside the uterus. Most often this is on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and tissue around the uterus and ovaries; in rare cases it may also occur in other parts of the body. Some symptoms include pelvic pain, heavy periods, pain with bowel movements, and infertility. Nearly half of those affected have chronic pelvic pain, while in 70% pain occurs during menstruation. Pain during sexual intercourse is also common. Infertility occurs in up to half of affected individuals. About 25% of individuals have no symptoms and 85% of those seen with infertility in a tertiary center have no pain. Endometriosis can have both social and psychological effects. The cause is not entirely clear. Risk factors include having a family history of the condition. The areas of endometriosis bleed each month (menstrua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Implantation
Ion implantation is a low-temperature process by which ions of one element are accelerated into a solid target, thereby changing the physical, chemical, or electrical properties of the target. Ion implantation is used in semiconductor device fabrication and in metal finishing, as well as in materials science research. The ions can alter the elemental composition of the target (if the ions differ in composition from the target) if they stop and remain in the target. Ion implantation also causes chemical and physical changes when the ions impinge on the target at high energy. The crystal structure of the target can be damaged or even destroyed by the energetic collision cascades, and ions of sufficiently high energy (10s of MeV) can cause nuclear transmutation. General principle Ion implantation equipment typically consists of an ion source, where ions of the desired element are produced, an accelerator, where the ions are electrostatically accelerated to a high energy, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implantation Bleeding
Implantation (nidation) is the stage in the embryonic development of mammals in which the blastocyst hatches as the embryo, adheres, and invades into the wall of the female's uterus. Implantation is the first stage of gestation, and when successful the female is considered to be pregnant. In a woman, an implanted embryo is detected by the presence of increased levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a pregnancy test. The implanted embryo will receive oxygen and nutrients in order to grow. There is an extensive variation in the type of trophoblast cells, and structures of the placenta across the different species of mammals. Of the five recognised stages of implantation including two pre-implantation stages that precede placentation, the first four are similar across the species. The five stages are migration and hatching, pre-contact, attachment, adhesion, and invasion. The two pre-implantation stages are associated with the pre-implantation embryo. In humans following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implantation Of Tooth
A dental implant (also known as an endosseous implant or fixture) is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biologic process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or zirconia form an intimate bond to bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic (a tooth, bridge or denture) is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic/crown. Success or failure of implants depends on the health of the person receiving the treatment, drugs which affect the chances of osseointegration, and the health of the tissues in the mouth. The amount of stress that will be put on the impl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implantation Rate
Pregnancy rate is the success rate for getting pregnant. It is the percentage of all attempts that leads to pregnancy, with attempts generally referring to menstrual cycles where insemination or any artificial equivalent is used, which may be simple artificial insemination (AI) or AI with additional in vitro fertilization (IVF). Definitions There is no universally accepted definition of the term. Thus in IVF pregnancy rates may be based on initiated treatment cycles, cycles that underwent oocyte retrieval, or cycles where an embryo transfer was performed. In terms of outcome, "pregnancy" may refer to a positive pregnancy test, evidence of a pregnancy with a "viable" fetus or implantation. Furthermore, pregnancy rates can be influenced in IVF by transferring multiple embryos that may result in multiple births. A strict definition in the IVF setting would refer to the singleton pregnancy rate that determines how many live singletons are born in relation to initiated IVF cycles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implantation Spotting
Implantation (nidation) is the stage in the embryonic development of mammals in which the blastocyst hatches as the embryo, adheres, and invades into the wall of the female's uterus. Implantation is the first stage of gestation, and when successful the female is considered to be pregnant. In a woman, an implanted embryo is detected by the presence of increased levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a pregnancy test. The implanted embryo will receive oxygen and nutrients in order to grow. There is an extensive variation in the type of trophoblast cells, and structures of the placenta across the different species of mammals. Of the five recognised stages of implantation including two pre-implantation stages that precede placentation, the first four are similar across the species. The five stages are migration and hatching, pre-contact, attachment, adhesion, and invasion. The two pre-implantation stages are associated with the pre-implantation embryo. In humans foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |