|
Implanon
Etonogestrel is a medication which is used as a means of hormonal contraceptive, birth control for women. It is available as an implant placed under the skin of the upper arm under the brand names Nexplanon and Implanon, and in combination with ethinylestradiol, an estrogen (medication), estrogen, as a contraceptive vaginal ring, vaginal ring under the brand names ''NuvaRing'' and ''Circlet''. Etonogestrel is effective as a means of birth control and lasts at least three or four years with some data showing effectiveness for five years. Following removal, fertility quickly returns. Side effects of etonogestrel include menstrual irregularities, breast tenderness, mood (psychology), mood changes, acne, headaches, vaginitis, and others. Etonogestrel is a progestin, or a synthetic compound, synthetic progestogen (medication), progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. It works by stopping ovulation, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormonal Contraceptive
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The original hormonal method—the combined oral contraceptive pill—was first marketed as a contraceptive in 1960. In the ensuing decades many other delivery methods have been developed, although the oral and injectable methods are by far the most popular. Hormonal contraception is highly effective: when taken on the prescribed schedule, users of steroid hormone methods experience pregnancy rates of less than 1% per year. Perfect-use pregnancy rates for most hormonal contraceptives are usually around the 0.3% rate or less. Currently available methods can only be used by women; the development of a male hormonal contraceptive is an active research area. There are two main types of hormonal contraceptive formulations: ''combined methods'' which con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestogen (medication)
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic compound, synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal contraception, hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogen (medication), estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of drug formulation, formulations and for use by many different route of administration, routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone (medication), progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic compound, synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal contraception, hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogen (medication), estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of drug formulation, formulations and for use by many different route of administration, routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone (medication), progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic compound, synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal contraception, hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogen (medication), estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of drug formulation, formulations and for use by many different route of administration, routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone (medication), progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestogen (medication)
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic compound, synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal contraception, hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogen (medication), estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of drug formulation, formulations and for use by many different route of administration, routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone (medication), progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Implant
In medicine, a subcutaneous implant, or subcutaneous pellet, is an implant that is delivered under the skin into the subcutaneous tissue by surgery or injection and is used to deliver a drug for a long period of time. Examples of drugs that can be administered in this way include leuprorelin and the sex steroids estradiol and testosterone Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar .... References Skin care {{treatment-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginitis
Vaginitis, also known as vulvovaginitis, is inflammation of the vagina and vulva. Symptoms may include itching, burning, pain, discharge, and a bad smell. Certain types of vaginitis may result in complications during pregnancy. The three main causes are infections, specifically bacterial vaginosis, vaginal yeast infection, and trichomoniasis. Other causes include allergies to substances such as spermicides or soaps or as a result of low estrogen levels during breast-feeding or after menopause. More than one cause may exist at a time. The common causes vary by age. Prepubescent girls are often at risk for development of vulvovaginitis because of low amounts of estrogen and an underdeveloped labia minora. Diagnosis generally include examination, measuring the pH, and culturing the discharge. Other causes of symptoms such as inflammation of the cervix, pelvic inflammatory disease, cancer, foreign bodies, and skin conditions should be ruled out. Treatment depends on the und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as |
Biological Target
A biological target is anything within a living organism to which some other entity (like an endogenous ligand or a drug) is directed and/or binds, resulting in a change in its behavior or function. Examples of common classes of biological targets are proteins and nucleic acids. The definition is context-dependent, and can refer to the biological target of a pharmacologically active drug compound, the receptor target of a hormone (like insulin), or some other target of an external stimulus. Biological targets are most commonly proteins such as enzymes, ion channels, and receptors. Mechanism The external stimulus (''i.e.'', the drug or ligand) physically binds to ("hits") the biological target. The interaction between the substance and the target may be: * noncovalent – A relatively weak interaction between the stimulus and the target where no chemical bond is formed between the two interacting partners and hence the interaction is completely reversible. * reversible covalent � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone Receptor
The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone. In humans, PR is encoded by a single ''PGR'' gene residing on chromosome 11q22, it has two isoforms, PR-A and PR-B, that differ in their molecular weight. The PR-B is the positive regulator of the effects of progesterone, while PR-A serve to antagonize the effects of PR-B. Mechanism Progesterone is necessary to induce the progesterone receptors. When no binding hormone is present the carboxyl terminal inhibits transcription. Binding to a hormone induces a structural change that removes the inhibitory action. Progesterone antagonists prevent the structural reconfiguration. After progesterone binds to the receptor, restructuring with dimerization follows and the complex enters the nucleus and binds to DNA. There transcription takes place, resulting in formation of messenger RNA that is tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
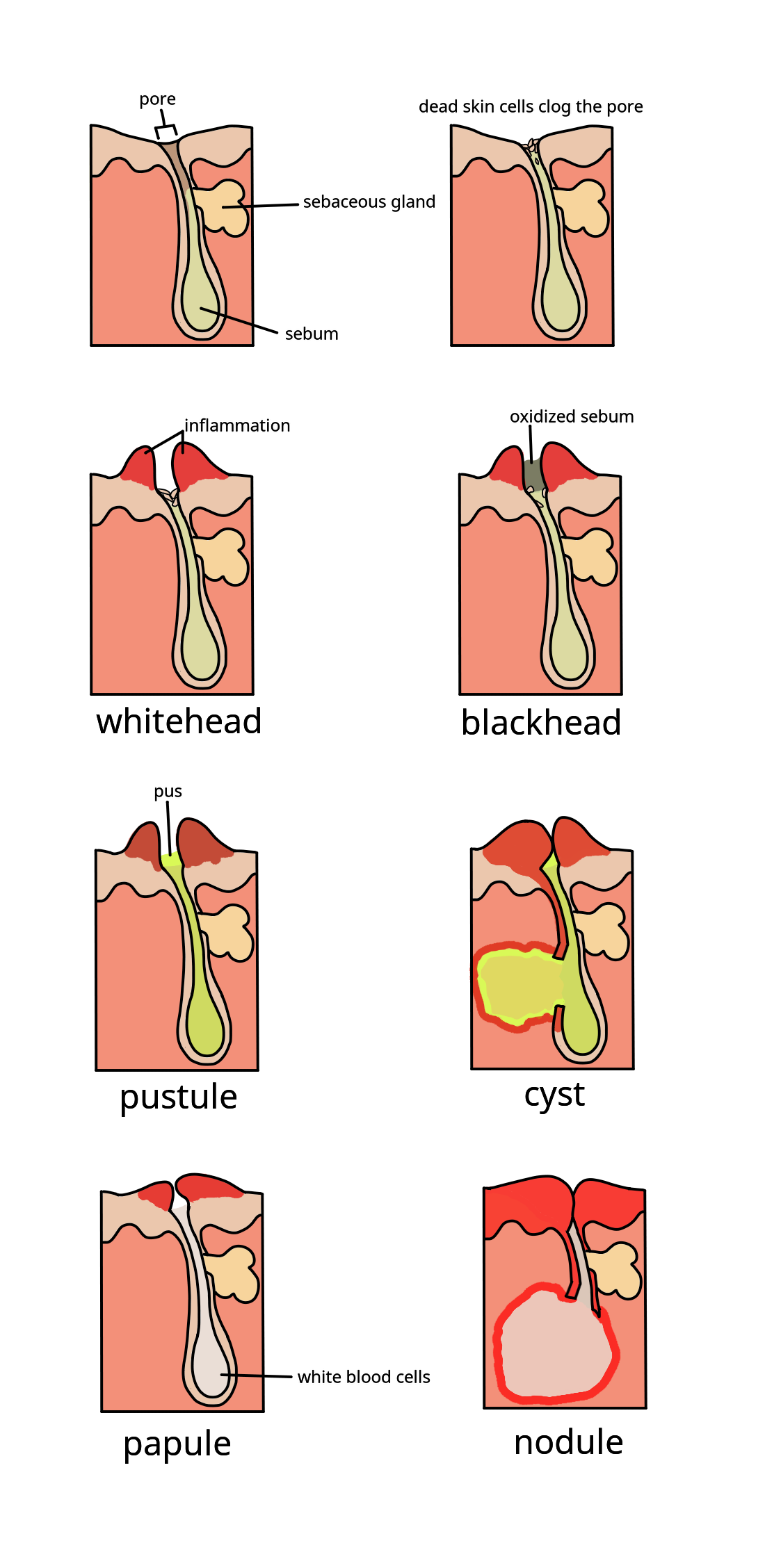
Acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of sebaceous gland, oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety (mood), anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, clinical depression, depression or suicidal ideations, thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither hygiene, cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |