|
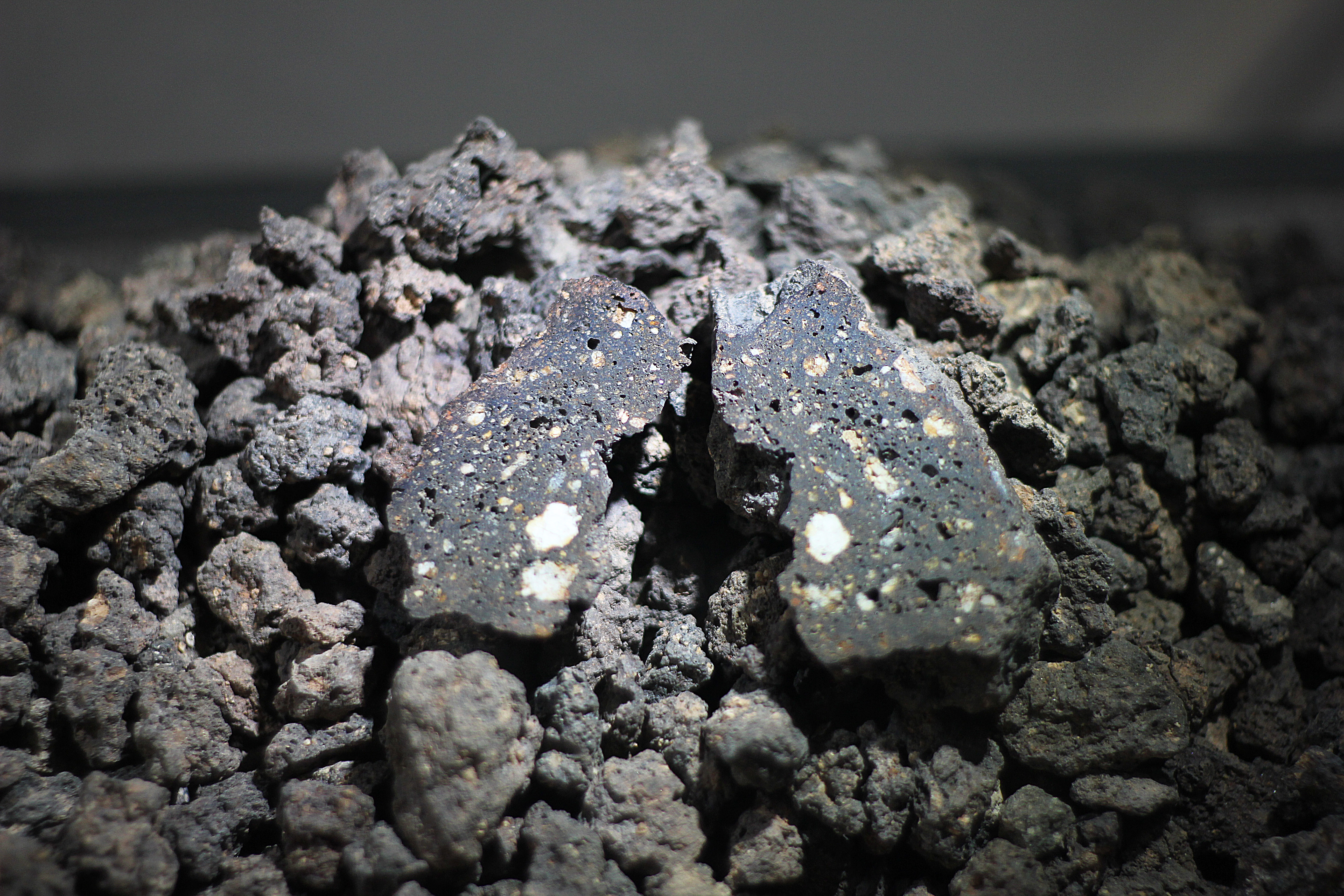
Impactite
Impactite is rock created or modified by one or more impacts of a meteorite. Impactites are considered metamorphic rock, because their source materials were modified by the heat and pressure of the impact. On Earth, impactites consist primarily of modified terrestrial material, sometimes with pieces of the original meteorite. Creation When a large meteorite hits a planet, it can radically deform the rocks and regolith that it hits. The heat, pressure, and shock of the impact changes these materials into impactite. Only very massive impacts generate the heat and pressure needed to transform a rock, so impactites are created rarely. Characteristics Impactite includes shock-metamorphosed target rocks, melts ( suevites) and mixtures of the two, as well as sedimentary rocks with significant impact-derived components (shocked mineral grains, tektites, anomalous geochemical signatures, etc.). In June 2015, NASA reported that impact glass has been detected on the planet Mars. Such ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life On Mars
The possibility of life on Mars is a subject of interest in astrobiology due to the planet's proximity and similarities to Earth. To date, no proof of past or present life has been found on Mars. Cumulative evidence suggests that during the ancient Noachian time period, the surface environment of Mars had liquid water and may have been habitable for microorganisms, but habitable conditions do not necessarily indicate life. Scientific searches for evidence of life began in the 19th century and continue today via telescopic investigations and deployed probes. While early work focused on phenomenology and bordered on fantasy, the modern scientific inquiry has emphasized the search for water, chemical biosignatures in the soil and rocks at the planet's surface, and biomarker gases in the atmosphere. Mars is of particular interest for the study of the origins of life because of its similarity to the early Earth. This is especially true since Mars has a cold climate and lacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos and Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a large impact feature. Days and seasons on Mars are comparable to those of Earth, as the planets have a similar rotation period a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Metamorphism
Shock metamorphism or impact metamorphism describes the effects of shock-wave related deformation and heating during impact events. The formation of similar features during explosive volcanism is generally discounted due to the lack of metamorphic effects unequivocally associated with explosions and the difficulty in reaching sufficient pressures during such an event. Effects Mineral microstructures Planar fractures Planar fractures are parallel sets of multiple planar cracks or cleavages in quartz grains; they develop at the lowest pressures characteristic of shock waves (~5–8 GPa) and a common feature of quartz grains found associated with impact structures. Although the occurrence of planar fractures is relatively common in other deformed rocks, the development of intense, widespread, and closely spaced planar fractures is considered diagnostic of shock metamorphism. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tektites
Tektites (from grc, τηκτός , meaning 'molten') are gravel-sized bodies composed of black, green, brown or grey natural glass formed from terrestrial debris ejected during meteorite impacts. The term was coined by Austrian geologist Franz Eduard Suess (1867–1941), son of Eduard Suess. They generally range in size from millimetres to centimetres. Millimetre-scale tektites are known as microtektites.French, B. M. (1998) ''Traces of Catastrophe: A Handbook of Shock-Metamorphic Effects in Terrestrial Meteorite Impact Structures.'' LPI Contribution No. 954. Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, Texas. 120 pp.McCall, G. J. H. (2001) ''Tektites in the Geological Record: Showers of Glass from the Sky.'' The Geological Society Publishing House, Bath, United Kingdom. 256 pp. Montanari, A., and C. Koeberl (2000) ''Impact Stratigraphy. The Italian Record.'' Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences Series no. 93. Springer-Verlag, New York, New York. 364 pp. Tektites are characterized by: # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwin Crater
Darwin Crater is a suspected meteorite impact crater in Western Tasmania about south of Queenstown, just within the Franklin-Gordon Wild Rivers National Park. The crater is expressed as a rimless circular flat-floored depression, in diameter, within mountainous and heavily forested terrain. It is east of the West Coast Range and the former North Mount Lyell Railway formation. Discovery and description The crater was discovered by the geologist R. J. Ford in 1972, after a search for the source of Darwin glass, an impact glass found over more than of southwestern Tasmania. Geophysical investigations and drilling have shown that the crater is filled with up to of breccia capped by Pleistocene lake sediments. Although definitive proof of an impact origin of the crater is lacking, the impact hypothesis is strongly supported by the relationship of the glass to the crater, as well as the stratigraphy and deformation of the crater-filling material. If the crater is indeed the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamo Bolide Impact
The Alamo bolide impact occurred 377–378 million years ago, when one or more hypervelocity objects from space slammed into shallow marine waters at a site that is now the Devonian Guilmette Formation of the Worthington Mountains and Schell Creek Range of southeastern Nevada; the event is named for breccias of metamorphosed crushed rock deposits, found near the town of Alamo, Nevada (the "Alamo Breccia"). This catastrophic impact event resulted in what is one of the best-exposed and has become the most accurately dated impact events; it occurred within the Frasnian age of the Devonian at about 377-378 Ma, a moment in time that was about 5.9 Ma prior to the Frasnian/Famennian extinction events, which it is unlikely to have affected. The actual impact site has not yet been significantly documented—even its precise diameter and its internal structural features are not yet clear enough to make speculations on the mass and trajectory genuinely useful. The "tectonic overprint" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-G
A&G, AG, Ag or ag may refer to Businesses and organizations * A&G Railroad (former reporting mark AG) * Action Group (Nigeria), a political party during the Nigerian First Republic * Aktiengesellschaft, a German type of corporation * Assemblies of God, the world's largest Pentecostal organization * Associated Group, a Pakistani company * Astronomische Gesellschaft, a German astronomical society * IATA code for Aruba Airlines Entertainment * '' American Gladiators'' (1989–1996 TV series) * ''American Gladiators'' (2008 TV series) Government and military * Adjutant general, the Army branch responsible for personnel * Administrator-General of South West Africa, the head of government in Namibia prior to independence in 1990 * Aerographer's mate, a rating or specialty in the US Navy that deals with weather and oceanography * American Holland-class submarine (''Amerikansky Golland''), a class of Imperial Russian submarines * Army green, the color of the US Army service unifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barringer Crater
Meteor Crater, or Barringer Crater, is a meteorite impact crater about east of Flagstaff and west of Winslow in the desert of northern Arizona, United States. The site had several earlier names, and fragments of the meteorite are officially called the Canyon Diablo Meteorite, after the adjacent Cañon Diablo. Because the United States Board on Geographic Names recognizes names of natural features derived from the nearest post office, the feature acquired the name of "Meteor Crater" from the nearby post office named Meteor. Meteor Crater lies at an elevation of above sea level. It is about in diameter, some deep, and is surrounded by a rim that rises above the surrounding plains. The center of the crater is filled with of rubble lying above crater bedrock. One of the interesting features of the crater is its squared-off outline, believed to be caused by existing regional jointing (cracks) in the strata at the impact site. Despite historic attempts to make the crat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlevoix Impact Structure
The Charlevoix impact structure is a large eroded meteorite impact structure in the Charlevoix region of Quebec, Canada. Only part of the impact structure is exposed at the surface, the rest lying beneath the Saint Lawrence River. Description The original impact structure is estimated to have been in diameter and the age of the impact is estimated to be 450 ± 20 million years (Ordovician to Silurian age).Schmieder, M., Shaulis, B.J., Lapen, T.J., Buchner, E. and Kring, D.A., 2019. ''In situ U–Pb analysis of shocked zircon from the Charlevoix impact structure, Québec, Canada.'' ''Meteoritics & Planetary Science.'' 54(8) pp. 1808-1827. The projectile was probably a stony asteroid, at least in diameter, and weighing an estimated . The Mont des Éboulements, situated in the exact centre of the impact structure, is interpreted as the central uplift, a consequence of elastic rebound.Interpretation Centre, Parc national des Grands-Jardins, Charlevoix The impact structure is clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breccia
Breccia () is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or rocks cemented together by a fine-grained matrix. The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of different origins, as indicated by the named types including sedimentary breccia, tectonic breccia, igneous breccia, impact breccia, and hydrothermal breccia. A megabreccia is a breccia composed of very large rock fragments, sometimes kilometers across, which can be formed by landslides, impact events, or caldera collapse. Types Breccia is composed of coarse rock fragments held together by cement or a fine-grained matrix. Like conglomerate, breccia contains at least 30 percent of gravel-sized particles (particles over 2mm in size), but it is distinguished from conglomerate because the rock fragments have sharp edges that have not been worn down. These indicate that the gravel was deposited very close to its source area, since other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |