|
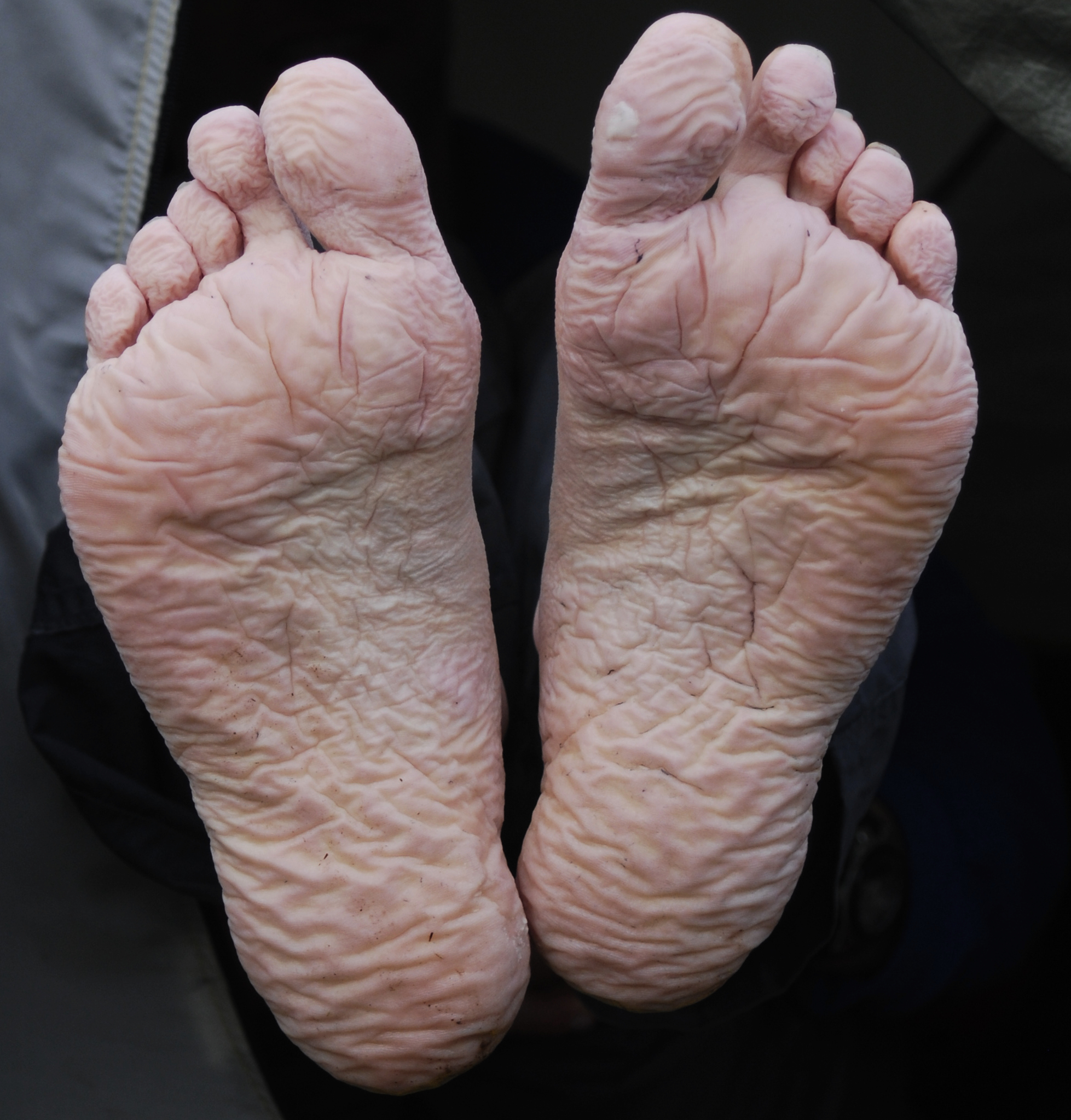
Immersion Foot
Immersion foot syndromes are a class of foot injury caused by water absorption in the outer layer of skin. There are different subclass names for this condition based on the temperature of the water to which the foot is exposed. These include trench foot, tropical immersion foot, and warm water immersion foot. In one 3-day military study, it was found that submersion in water allowing for a higher skin temperature resulted in worse skin maceration and pain. Causes Trench foot ''Trench foot '' is a medical condition caused by prolonged exposure of the feet to damp, unsanitary, and cold conditions. The use of the word ''trench'' in the name of this condition is a reference to trench warfare, mainly associated with World War I. Affected feet may become numb, affected by erythrosis (turning red) or cyanosis (turning blue) as a result of poor vascular supply, and feet may begin to have a decaying odour due to the possibility of the early stages of necrosis setting in. As the condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench Foot
Trench foot is a type of foot damage due to moisture. Initial symptoms often include tingling or itching which can progress to numbness. The feet may become red or bluish in color. As the condition worsens the feet can start to swell and smell of decay. Complications may include skin breakdown or infection. Trench foot occurs due to prolonged exposure of the feet to cold, damp, and often unsanitary conditions. Unlike frostbite, trench foot usually occurs at temperatures above freezing, and can be classed as a form of non-freezing cold injury. Onset can be as rapid as 10 hours. Risk factors include overly tight boots and not moving. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve constriction of blood vessels resulting in insufficient blood flow to the feet. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and examination. Prevention involves keeping the feet warm, dry, and clean. After the condition has occurred, pain medications may be required during the gradual rewarming process. Pain m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Condition
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, conditions of the mucous membrane), morphology ( chronic blistering conditions), cause (skin conditions result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Conditions Resulting From Physical Factors
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, dolphins, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immersion Foot Syndromes
Immersion foot syndromes are a class of foot injury caused by water absorption in the outer layer of skin. There are different subclass names for this condition based on the temperature of the water to which the foot is exposed. These include trench foot, tropical immersion foot, and warm water immersion foot. In one 3-day military study, it was found that submersion in water allowing for a higher skin temperature resulted in worse skin maceration and pain. Causes Trench foot ''Trench foot '' is a medical condition caused by prolonged exposure of the feet to damp, unsanitary, and cold conditions. The use of the word ''trench'' in the name of this condition is a reference to trench warfare, mainly associated with World War I. Affected feet may become numb, affected by erythrosis (turning red) or cyanosis (turning blue) as a result of poor vascular supply, and feet may begin to have a decaying odour due to the possibility of the early stages of necrosis setting in. As the condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whale Oil
Whale oil is oil obtained from the blubber of whales. Whale oil from the bowhead whale was sometimes known as train oil, which comes from the Dutch word ''traan'' ("tears, tear" or "drop"). Sperm oil, a special kind of oil obtained from the head cavities of sperm whales, differs chemically from ordinary whale oil: it is composed mostly of liquid wax. Its properties and applications differ from those of regular whale oil, and it was sold for a higher price. Source and use Emerging industrial societies used whale oil in oil lamps and to Soap#History, make soap. In the 20th century it was made into margarine. With the commercial development of the petroleum industry and vegetable oils, the use of whale oils declined considerably from its peak in the 19th century into the 20th century. This is said to have saved whales from extinction. In the 21st century, with most countries having banned whaling, the sale and use of whale oil has practically ceased. Whale oil was obtained by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulcer (dermatology)
An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation. They can also be caused due to a lack of mobility, which causes prolonged pressure on the tissues. This stress in the blood circulation is transformed to a skin ulcer, commonly known as bedsores or decubitus ulcers. Ulcers often become infected, and pus forms. Signs and symptoms Skin ulcers appear as open craters, often round, with layers of skin that have eroded. The skin around the ulcer may be red, swollen, and tender. Patients may feel pain on the skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanch (medical)
When skin is blanched, it takes on a whitish appearance as blood flow to the region is prevented. This occurs during and is the basis of the physiologic test known as diascopy. Blanching of the fingers is also one of the most clinically evident signs of Raynaud's phenomenon. Blanching is prevented in gangrene as the red blood corpuscles are extravasated and impart red color to the gangrenous part. See also *Diascopy *Pallor Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eyes o ... References Dermatologic terminology {{dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. Etymology The word "foot", in the sense of meaning the "terminal part of the leg of a vertebrate animal" comes from "Old English fot "foot," from Proto-Germanic *fot (source also of Old Frisian fot, Old Saxon fot, Old Norse fotr, Danish fod, Swedish fot, Dutch voet, Old High German fuoz, German Fuß, Gothic fotus "foot"), from PIE root *ped- "foot". The "plural form feet is an instance of i-mutation." Structure The human foot is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing 26 bones, 33 joints (20 of which are actively articulated), and more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments.Podiatry Channel, ''Anatomy of the foot and ankle'' The joints of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paddy Field
A paddy field is a flooded field (agriculture), field of arable land used for growing Aquatic plant, semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro. It originates from the Neolithic rice-farming cultures of the Yangtze River basin in southern China, associated with Austronesian peoples#Neolithic China, pre-Austronesian and Hmong–Mien languages, Hmong-Mien cultures. It was spread in prehistoric times by the Austronesian peoples#Austronesian expansion, expansion of Austronesian peoples to Island Southeast Asia, Southeast Asia including Northeastern India, Madagascar, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. The technology was also acquired by other cultures in mainland Asia for rice farming, spreading to East Asia, Mainland Southeast Asia, and South Asia. Fields can be built into steep hillsides as Terrace (agriculture), terraces or adjacent to depressed or steeply sloped features such as rivers or marshes. They require a great deal of labor and materials to create and need l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)