|
Image Histogram
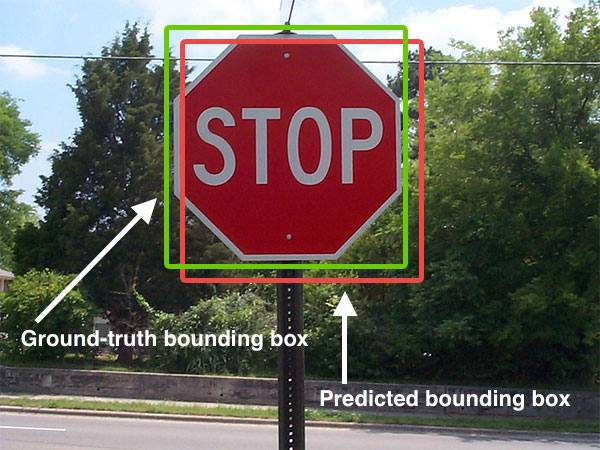
An image histogram is a type of histogram that acts as a graphical representation of the Lightness (color), tonal distribution in a digital image. It plots the number of pixels for each tonal value. By looking at the histogram for a specific image a viewer will be able to judge the entire tonal distribution at a glance. Image histograms are present on many modern services. Photographers can use them as an aid to show the distribution of tones captured, and whether image detail has been lost to blown-out highlights or blacked-out shadows. This is less useful when using a raw image format, as the Tonal range, dynamic range of the displayed image may only be an approximation to that in the raw file. The horizontal axis of the graphics, graph represents the tonal variations, while the vertical axis represents the total number of pixels in that particular tone. The left side of the horizontal axis represents the dark areas, the middle represents mid-tone values and the right hand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histogram
A histogram is a visual representation of the frequency distribution, distribution of quantitative data. To construct a histogram, the first step is to Data binning, "bin" (or "bucket") the range of values— divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals—and then count how many values fall into each interval. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping interval (mathematics), intervals of a variable. The bins (intervals) are adjacent and are typically (but not required to be) of equal size. Histograms give a rough sense of the density of the underlying distribution of the data, and often for density estimation: estimating the probability density function of the underlying variable. The total area of a histogram used for probability density is always normalized to 1. If the length of the intervals on the ''x''-axis are all 1, then a histogram is identical to a relative frequency plot. Histograms are sometimes confused with bar charts. In a his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the form of decisions. "Understanding" in this context signifies the transformation of visual images (the input to the retina) into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory. The scientific discipline of computer vision is concerned with the theory behind artificial systems that extract information from images. Image data can take many forms, such as video sequences, views from multiple cameras, multi-dimensional data from a 3D scanning, 3D scanner, 3D point clouds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Editing
Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are Digital photography, digital photographs, traditional Photographic processing, photo-chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known as photo manipulation, photo retouching, using tools such as an airbrush to modify photographs or edit illustrations with any traditional art medium. Graphic software programs, which can be broadly grouped into vector graphics editors, raster graphics editors, and 3D modelers, are the primary tools with which a user may manipulate, enhance, and transform images. Many image editing programs are also used to artistic rendering, render or create computer art from scratch. The term "image editing" usually refers only to the editing of 2D images, not 3D ones. Basics of image editing Raster graphics, Raster images are stored on a computer in the form of a grid of picture elements, or pixels. These pixels contain the image's color and brightn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histogram Matching
In image processing, histogram matching or histogram specification is the transformation of an image so that its image histogram, histogram matches a specified histogram. The well-known histogram equalization method is a special case in which the specified histogram is uniform distribution (discrete), uniformly distributed. It is possible to use histogram matching to balance detector responses as a relative detector calibration technique. It can be used to normalize two images, when the images were acquired at the same local illumination (such as shadows) over the same location, but by different sensors, atmospheric conditions or global illumination. Implementation Consider a grayscale input image X. It has a probability density function pr(r), where r is a grayscale value, and pr(r) is the probability of that value. This probability can easily be computed from the histogram of the image by p_r (r_j )= Where nj is the frequency of the grayscale value rj, and n is the total nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
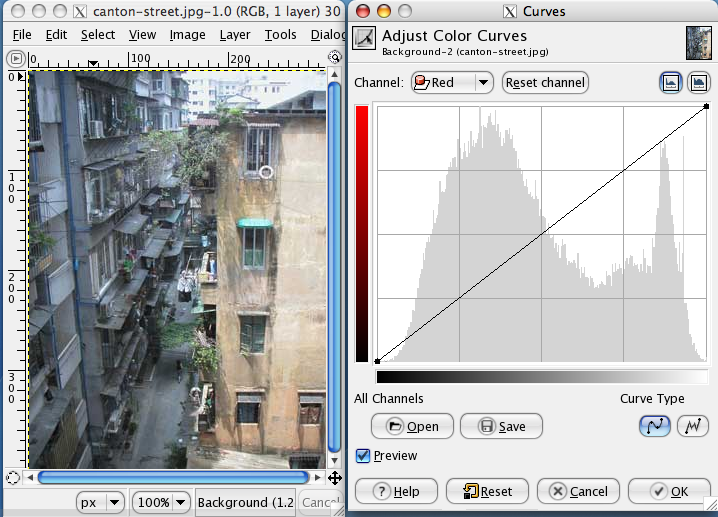
Curve (tonality)
In image editing, a curve is a remapping of image tonality, specified as a function from input level to output level, used as a way to emphasize colours or other elements in a picture. Curves can usually be applied to all channels together in an image, or to each channel individually. Applying a curve to all channels typically changes the brightness in part of the spectrum. Light parts of a picture can be easily made lighter and dark parts darker to increase contrast. Applying a curve to individual channels can be used to stress a colour. This is particularly efficient in the Lab color space, Lab colour space due to the separation of luminance and chromaticity, but it can also be used in RGB color model, RGB, CMYK color model, CMYK or whatever other color model, colour models the software supports. See also * Blend modes * Image histogram * Hurter–Driffield curve * Tone reproduction curve References {{reflist External links Defanging the Curves Vampire Dan Margulis, De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Histogram
In image processing and photography, a color histogram is a representation of the distribution of colors in an image. For digital images, a color histogram represents the number of pixels that have colors in each of a fixed list of color ranges that span the image's color space (the set of all possible colors). A color histogram can be built for any kind of color space, although the term is more often used for three-dimensional spaces such as RGB color space, RGB or HSV color space, HSV. For monochromatic images, the term intensity histogram may be used instead. For multi-spectral images, where each pixel is represented by an arbitrary number of measurements (for example, beyond the three measurements in RGB), a color histogram is ''N''-dimensional, with N being the number of measurements taken. Each measurement has its own wavelength range of the light spectrum, some of which may be outside the visible spectrum. If the set of possible color values is sufficiently small, each o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Co-occurrence Matrix
A co-occurrence matrix or co-occurrence distribution (also referred to as : ''gray-level co-occurrence matrices'' GLCMs) is a matrix (mathematics), matrix that is defined over an Digital image, image to be the distribution of co-occurring pixel values (grayscale values, or colors) at a given offset. It is used as an approach to texture analysis with various applications especially in medical image analysis. Method Given a grey-level image I, co-occurrence matrix computes how often pairs of pixels with a specific value and offset occur in the image. * The offset, (\Delta x, \Delta y), is a position operator that can be applied to any pixel in the image (ignoring edge effects): for instance, (1, 2) could indicate "one down, two right". * An image with p different pixel values will produce a p \times p co-occurrence matrix, for the given offset. * The (i, j)^\text value of the co-occurrence matrix gives the number of times in the image that the i^\text and j^\text pixel values occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Segmentation
In digital image processing and computer vision, image segmentation is the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple image segments, also known as image regions or image objects (Set (mathematics), sets of pixels). The goal of segmentation is to simplify and/or change the representation of an image into something that is more meaningful and easier to analyze.Linda Shapiro, Linda G. Shapiro and George C. Stockman (2001): "Computer Vision", pp 279–325, New Jersey, Prentice-Hall, Image segmentation is typically used to locate objects and Boundary tracing, boundaries (lines, curves, etc.) in images. More precisely, image segmentation is the process of assigning a label to every pixel in an image such that pixels with the same label share certain characteristics. The result of image segmentation is a set of segments that collectively cover the entire image, or a set of Contour line, contours extracted from the image (see edge detection). Each of the pixels in a region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge Detection
Edge or EDGE may refer to: Technology Computing * Edge computing, a network load-balancing system * Edge device, an entry point to a computer network * Adobe Edge, a graphical development application * Microsoft Edge, a web browser developed by Microsoft * Microsoft Edge Legacy, a discontinued web browser developed by Microsoft * EdgeHTML, the layout engine used in Microsoft Edge Legacy * ThinkPad Edge, a Lenovo laptop computer series marketed from 2010 * Silhouette edge, in computer graphics, a feature of a 3D body projected onto a 2D plane * Explicit data graph execution, a computer instruction set architecture Telecommunication(s) * EDGE (telecommunication), a 2G digital cellular communications technology * Edge Wireless, an American mobile phone provider * Motorola Edge series, a series of smartphones made by Motorola * Samsung Galaxy Note Edge, a phablet made by Samsung * Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge or Samsung Galaxy S6 Edge, smartphones made by Samsung * Ubuntu Edg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thresholding (image Processing)
In digital image processing, thresholding is the simplest method of segmenting images. From a grayscale image, thresholding can be used to create binary images. Definition The simplest thresholding methods replace each pixel in an image with a black pixel if the image intensity I_ is less than a fixed value called the threshold T, or a white pixel if the pixel intensity is greater than that threshold. In the example image on the right, this results in the dark tree becoming completely black, and the bright snow becoming completely white. Automatic thresholding While in some cases, the threshold T can be selected manually by the user, there are many cases where the user wants the threshold to be automatically set by an algorithm. In those cases, the threshold should be the "best" threshold in the sense that the partition of the pixels above and below the threshold should match as closely as possible the actual partition between the two classes of objects represented by those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histogram Equalization
Histogram equalization is a method in image processing of contrast adjustment using the image's histogram. Histogram equalization is a specific case of the more general class of histogram remapping methods. These methods seek to adjust the image to make it easier to analyze or improve visual quality (e.g., retinex). Overview This method usually increases the global contrast of many images, especially when the image is represented by a narrow range of intensity values. Through this adjustment, the intensities can be better distributed on the histogram utilizing the full range of intensities evenly. This allows for areas of lower local contrast to gain a higher contrast. Histogram equalization accomplishes this by effectively spreading out the highly populated intensity values, which tend to degrade image contrast. The method is useful in images with backgrounds and foregrounds that are both bright or both dark. In particular, the method can lead to better views of bone s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Representation
Graphic communication as the name suggests is communication using graphic elements. These elements include symbols such as glyphs and icons, images such as drawings and photographs, and can include the passive contributions of substrate, colour and surroundings. It is the process of creating, producing, and distributing material incorporating words and images to convey data, concepts, and emotions.Definition of Graphic Communications Graphic Comm Central, 2008. Accessed 25 Feb 2009. The field of graphics communications encompasses all phases of the graphic communications processes from origination of the idea (design, layout, and typography) through reproduction, finishing and distribution of two- or three-dimensional products or electronic transmission. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |