|
Ilya Chashnik
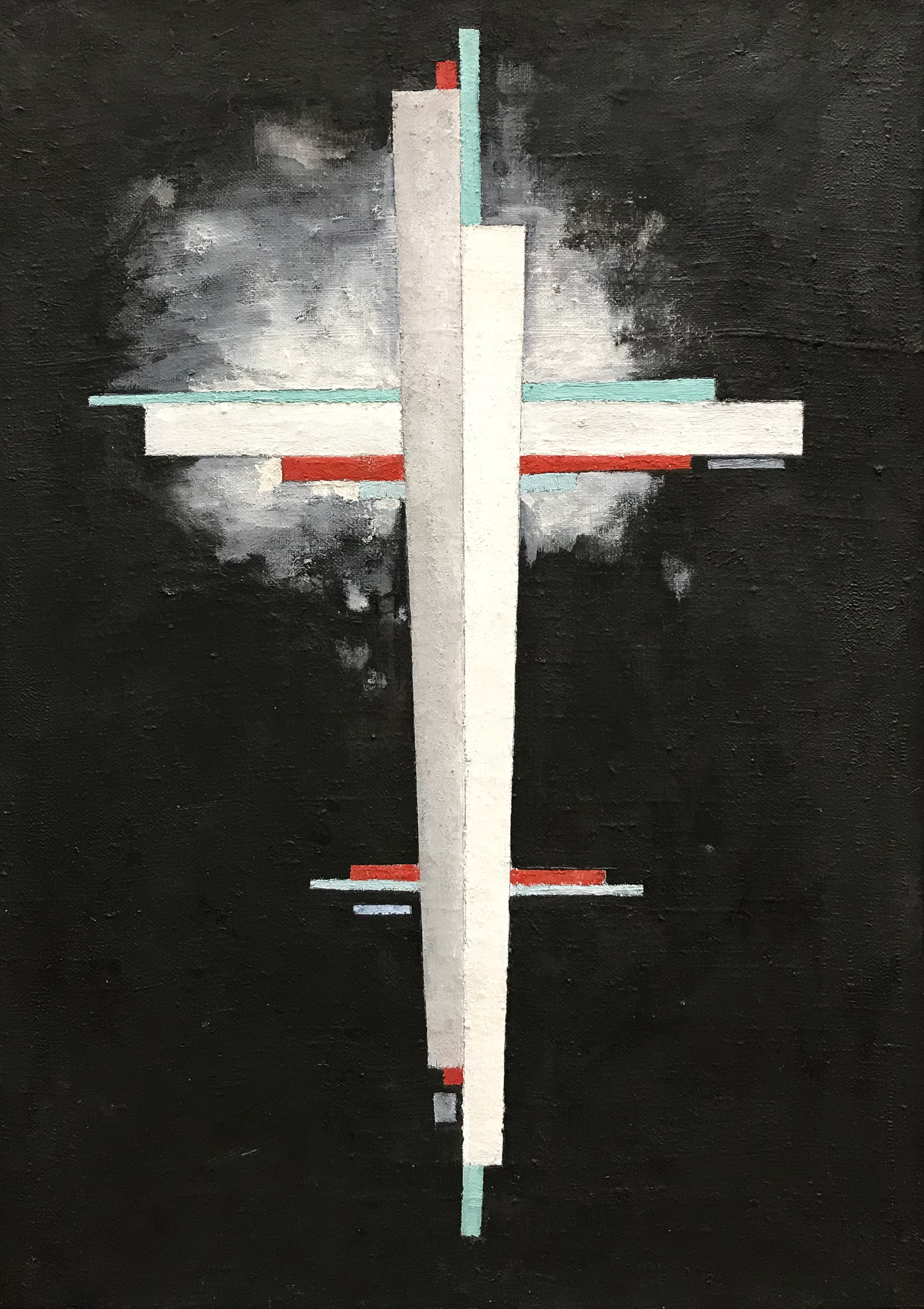
Ilya Grigorevich Chashnik (1902, Lucyn, Russian Empire, currently Ludza, Latvia - 1929, Leningrad) was a suprematist artist, a pupil of Kazimir Malevich and a founding member of the UNOVIS school. Biography Chashnik was born to a Jewish family in 1902, Lucyn, Russian Empire, currently Ludza, Latvia. He started studying in Yehuda Pen's art school at Vitebsk when he was just eleven years old. He became a student of Marc Chagall. By 1918, he moved to Moscow to work in an art workshop directed by Kazimir Malevich. He returned after Malevich accepted a senior teaching position at ''Vitebsk School of Drawing and Painting.'' Chashnik was notably able in a variety of media. Aleksandra Semenovna Shatskikh describes him as "famous for his inexhaustible inventiveness and ability to apply Suprematist principles to virtually all forms of art, including easel painting." He painted, was proficient in metalwork, and designed ceramics produced at the Imperial Porcelain Factory (then known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNOVIS
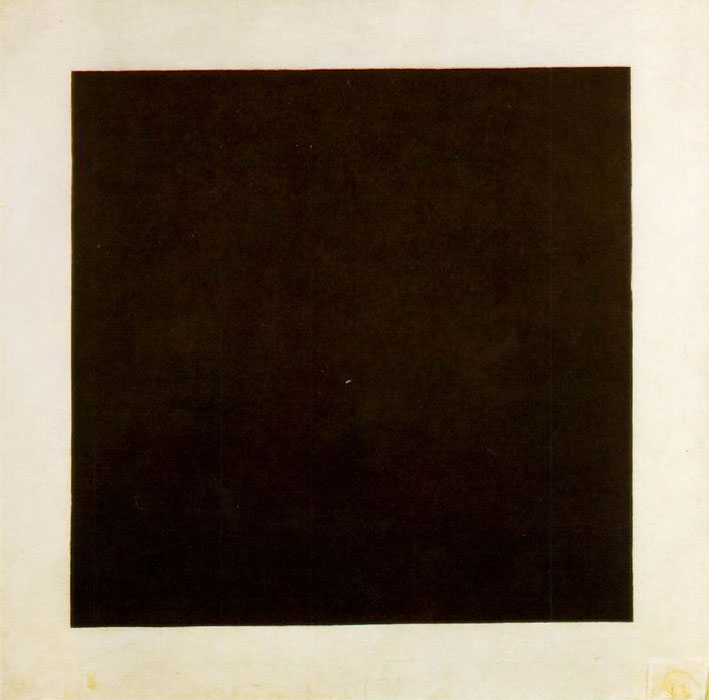
UNOVIS (also known as MOLPOSNOVIS and POSNOVIS) was a short-lived but influential group of artists, founded and led by Kazimir Malevich at the Vitebsk Art School in 1919. Initially formed by students and known as MOLPOSNOVIS, the group formed to explore and develop new theories and concepts in art. Under the leadership of Malevich they renamed to UNOVIS, chiefly focusing on his ideas on Suprematism and producing a number of projects and publications whose influence on the avant-garde in Russia and abroad was immediate and far-reaching.Essay: ''Black Square: In the Circle of Malevich and UNOVIS Group'' The group disbanded in 1922. The name UNOVIS is an |
Lucyn
Ludza (; pl, Lucyn, german: Ludsen, russian: Лудза, ''Ludza'') is a town in the Latgale region of eastern Latvia. Ludza is the oldest town in Latvia and this is commemorated by a key in its coat of arms. Ludza is the administrative centre of Ludza Municipality that is located nearby the Russian border. The population as of 2020 was 7,667. History After Nikolay Karamzin, Ludza was first mentioned as ''Лючин'' in Hypatian Codex dating back to 1173 or 1177. In 1399 the Livonian Order built a stone fortress atop an older Latgalian fortress and used Ludza as an eastern outpost in Livonia. Ludza Castle ruins can be visited nowadays. Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth After the dissolution of the Livonian Order in 1561, Ludza was incorporated to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and became part of Wenden Voivodeship. In January 1626, during the Polish-Swedish War, Ludza was captured without a battle by Sweden due to defeat of the forces of Polish-Lithuanian marshal Jan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale University Press
Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day, and became an official department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and operationally autonomous. , Yale University Press publishes approximately 300 new hardcover and 150 new paperback books annually and has a backlist of about 5,000 books in print. Its books have won five National Book Awards, two National Book Critics Circle Awards and eight Pulitzer Prizes. The press maintains offices in New Haven, Connecticut and London, England. Yale is the only American university press with a full-scale publishing operation in Europe. It was a co-founder of the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Harvard University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Series and publishing programs Yale Series of Younger Poets Since its inception in 1919, the Yale Series of Younger Poets Competition has published the first collection of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1929 Deaths
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album '' Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1902 Births
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album '' Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipkn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Monthly
''Texas Monthly'' (stylized as ''TexasMonthly'') is a monthly American magazine headquartered in Downtown Austin, Texas. ''Texas Monthly'' was founded in 1973 by Michael R. Levy and has been published by Emmis Publishing, L.P. since 1998 and is now owned by Enterprise Products Co. ''Texas Monthly'' chronicles life in contemporary Texas, writing on politics, the environment, industry, and education. The magazine also covers leisure topics such as music, art, dining, and travel. It is a member of the City and Regional Magazine Association (CRMA). In 2019, ''Texas Monthly'' was purchased by billionaire Randa Williams. In 2021, ''Texas Monthly'' acquired ''Texas Country Reporter''. Circulation ''Texas Monthly'' has a paid circulation of 300,000 and it has a monthly readership of 2.5 million people—one out of seven Texan adults. Its audience comprises a roughly equal number of men and women, most of whom are between the ages of 30 and 55. Subject matter ''Texas Monthly'' takes as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Texas At Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 graduate students and 3,133 teaching faculty as of Fall 2021, it is also the largest institution in the system. It is ranked among the top universities in the world by major college and university rankings, and admission to its programs is considered highly selective. UT Austin is considered one of the United States's Public Ivies. The university is a major center for academic research, with research expenditures totaling $679.8 million for fiscal year 2018. It joined the Association of American Universities in 1929. The university houses seven museums and seventeen libraries, including the LBJ Presidential Library and the Blanton Museum of Art, and operates various auxiliary research facilities, such as the J. J. Pickle Research Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Suetin
Nikolai Suetin (; 1897–1954) was a Russian Suprematist artist. He worked as a graphic artist, a designer, and a ceramics painter. Suetin studied at the Vitebsk Higher Institute of Art, (1918–1922) under Kazimir Malevich, founder of Suprematism, an early abstract art movement which developed a style based on 'non objective' geometric shapes in alignment. From 1920 the artist participated in exhibitions including those of the UNOVIS group (Vitebsk, 1920 and 1921; Moscow 1929, 1921 and 1922), Petrograd exhibitions, an International Exhibition of Decorative Art (held in Paris, 1925), the Exhibition of Soviet Porcelain (1926 and 1927), and the First Exhibition of Leningrad artists in the Russian Museum among others. He lived in Petrograd from 1923, and worked at the State Lomonosov Ceramics Factory. He also worked at the State Petrograd Lomonossov Porcelain Plant (from 1922 until 1924), and at the Porcelain Plant in Government of Novgorod (from 1924 until 1925). Suetin was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Porcelain Factory, Saint Petersburg
The Imperial Porcelain Factory (russian: Императорский Фарфоровый Завод, Imperatorskii Farforovyi Zavod), also known as the Imperial Porcelain Manufactory (abbreviated as IPM), is a producer of hand-painted ceramics in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It was established by Dmitry Ivanovich Vinogradov in 1744 and was supported by the Russian tsars since Empress Elizabeth. Many still refer to the factory by its well-known former name, the Lomonosov Porcelain Factory. History 18th century Attempts to reveal the secret of hard paste true porcelain-making had expanded to Russia since the visit of Peter the Great to Saxony in 1718; there, he saw Meissen porcelain at the Dresden court. Dmitry Ivanovich Vinogradov, a talented mining engineer who studied metallurgy at Freiberg, Saxony, invented the formula for the first porcelain manufactory in Russia, established in 1744 by order of Empress Elizabeth, daughter of Peter the Great, to "serve native trade and nativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chashnik Suprematism
Ilya Grigorevich Chashnik (1902, Lucyn, Russian Empire, currently Ludza, Latvia - 1929, Leningrad) was a suprematist artist, a pupil of Kazimir Malevich and a founding member of the UNOVIS school. Biography Chashnik was born to a Jewish family in 1902, Lucyn, Russian Empire, currently Ludza, Latvia. He started studying in Yehuda Pen's art school at Vitebsk when he was just eleven years old. He became a student of Marc Chagall. By 1918, he moved to Moscow to work in an art workshop directed by Kazimir Malevich. He returned after Malevich accepted a senior teaching position at ''Vitebsk School of Drawing and Painting.'' Chashnik was notably able in a variety of media. Aleksandra Semenovna Shatskikh describes him as "famous for his inexhaustible inventiveness and ability to apply Suprematist principles to virtually all forms of art, including easel painting." He painted, was proficient in metalwork, and designed ceramics produced at the Imperial Porcelain Factory (then known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest city. It is served by Vitebsk Vostochny Airport and Vitebsk Air Base. History Before 1945 Vitebsk developed from a river harbor where the Vićba River (Віцьба, from which it derives its name) flows into the larger Daugava River, Western Dvina, which is spanned in the city by the Kirov Bridge. Archaeological research indicates that Baltic tribes had settlements at the mouth of Vitba. In the 9th century, Slavic settlements of the tribal union of the Krivichs replaced them. According to the ''Chronicle of Michael Brigandine'' (1760), Princess Olga of Kiev founded Vitebsk (also recorded as Dbesk, Vidbesk, Videbsk, Vitepesk, or Vicibesk) in 974. Other versions give 947 or 914. Academician Boris Rybakov and historian Leonid Alekseyev ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)