|
Ikarbus
Ikarbus a.d. (''Ikarbus - Fabrika autobusa i specijalnih vozila a.d.'') is a Serbian bus manufacturer based in Zemun. It was originally established as an aircraft manufacturer in 1923, under the name Ikarus. In 1954, it commenced bus production and since 1960 it completely shifted towards it. In 1992, it changed its name to Ikarbus. History On 13 October 1923, the company was established under name "Ikarus – the first Serbian airplane, car and engine industry Kovačević and Co", with headquarters in Novi Sad. The founders were Dimitrije Konjović, brothers Dušan and Milivoj Kovačević, Đoka Radulović and Josif Mikl. On 20 November 1923, "Ikarus" started business officially after the registration before the Novi Sad District Court. In the beginning, the company manufactured a number of foreign designs under licence, such as the French Potez 25, Czechoslovakian Avia BH-33 and English Hawker Fury; Bristol Blenheim as well as the locally designed Ikarus ŠM, Ikarus IO, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOKO
Soko ( sh-Cyrl, Соко) was a Yugoslav aircraft manufacturer based in Mostar, SR Bosnia and Herzegovina. The company was responsible for the production of many military aircraft for the Yugoslav Air Force. SOKO was created in 1950 by the relocation of the aircraft factory section of Ikarus company from Zemun, SR Serbia. Officially founded as "Preduzeće Soko" (Soko Corporation, ''soko'' meaning "falcon" in Serbian), soon after it was renamed "Soko Vazduhoplovna Industrija, RO Vazduhoplovstvo" (Soko Aeronautical Industry, RO Aeronautics). Its first director was Yugoslav People's Army colonel Ivan Sert. The following directors of the company were engineers Miljenko Pješčić and Tomislav Mirić. The serial manufacture of numerous types of aircraft was projected by the Aeronautical Technical Institute in Belgrade. Besides aircraft, SOKO also produced helicopters under licence. Located in the vicinity of Mostar, it mostly used the Mostar Airport for test flights. By the 1980s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikarus ŠM
The Ikarus ŠM (Serbian Cyrillic:Икарус ШМ), ŠM (for ''Školski Mornarički'' en:School Navy) was the first design of Eng. Josip Mikl for the Yugoslav company Ikarus, it was a side-by-side two-seat biplane flying boat powered by a 100 hp (75 kW) Mercedes engine. The aircraft used for training by the Yugoslav Royal Navy. Development During 1921 and 1922, the engineer Joseph Mikl and his colleagues from the Air Force arsenal made design and manufacturing drawings of the new training biplane seaplane. Mikl engineer's drawings seaplane offered the Ministry of the Army and Navy of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, who bought them for his Naval Aviation. The contract was signed in early 1924. Kingdom SHS free ceded drawings seaplane factory " Ikarus", which started working on the first batch of six aircraft. The prototype was completed by the end of October and the first flight took place on November 10, 1924th, the winter quarters of the Danube in No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikarus S-451MM
Icarus is a character in Greek mythology. Icarus or Ikarus may also refer to: People * Roger Squires (born 1932), crossword compiler who has used the pseudonym Icarus * Icarus (wrestler) (born 1982), wrestler with the Chikara organization Places * Icarus (island), in the Aegean Sea * Ikaros (Failaka Island), in the Persian Gulf Aviation Aircraft * Icarus I, Icarus II and Icarus V, series of rigid-wing hang gliders designed by Taras Kiceniuk, Jr. * Ikarus C42, a microlight aircraft * Ikarus IK-2, the most notable indigenous Yugoslav aircraft of the 1930s and World War II era * Icarus, a prototype space rescue vehicle tested by Aleksandr Serebrov Aviation businesses and organizations * Ikarus Drachen Tomas Pellicci, a German hang glider manufacturer * Icaro Air, an Ecuadorian airline * Icarus School, a military aviation academy * Icarus, a Greek airline that preceded Olympic Airlines * Ikarus, a Yugoslav aircraft manufacturer later renamed Ikarbus Other uses in aviation * Coupe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikarus Orkan
The Ikarus Orkan (Serbian Cyrillic: Икарус Оркан) was a three-seat twin-engined monoplane designed as a light bomber/reconnaissance aircraft in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia before World War II. It was designed and built at the Ikarus factory in Zemun-Belgrade. Development The Orkan was created as a private project by two young designers S. Momcilovic and D. Radojkovic. They tried to create a light two-engine bomber. By the end of 1937 most of the prototype documentation was complete. A wooden model was tested in early 1938 in the wind tunnel in Paris. The aircraft was high-winged with very clean aerodynamic fuselage and of full metal construction. The wing had a NACA 23012 airfoil with root thickness of 12% and the top sash thickness of 6%. The Yugoslav Air Force command was interested in the aircraft for the competition for the new Yugoslav twin engine medium bomber. The prototype had to be shipped by June 14, 1939. Ikarus is committed to provide engines for aircraft and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikarus S-49
The Ikarus S-49 was a Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav single-seat, single-engine fighter aircraft built for the Yugoslav Air Force ( sh, Ratno vazduhoplovstvo i protivvazdušna obrana – RV i PVO) shortly after World War II. Following the Tito–Stalin Split in 1948, the Yugoslav Air Force was left with an aircraft inventory consisting of mostly Soviet Union, Soviet aircraft. Unable to acquire new aircraft or spare parts for its existing fleet, they turned to its domestic aviation industry in order to create an indigenous design to fulfill the need for additional aircraft. The result was the S-49A, designed by Kosta Sivčev, Svetozar Popović and Slobodan Zrnić, on the basis of the pre-war Rogožarski IK-3. The S-49A was surpassed by the improved S-49C, featuring an all-metal construction and a more powerful engine. A total of 45 S-49A and 113 S-49C were produced by the Ikarbus, Ikarus Aircraft Factory in Zemun. The last aircraft were retired from service in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
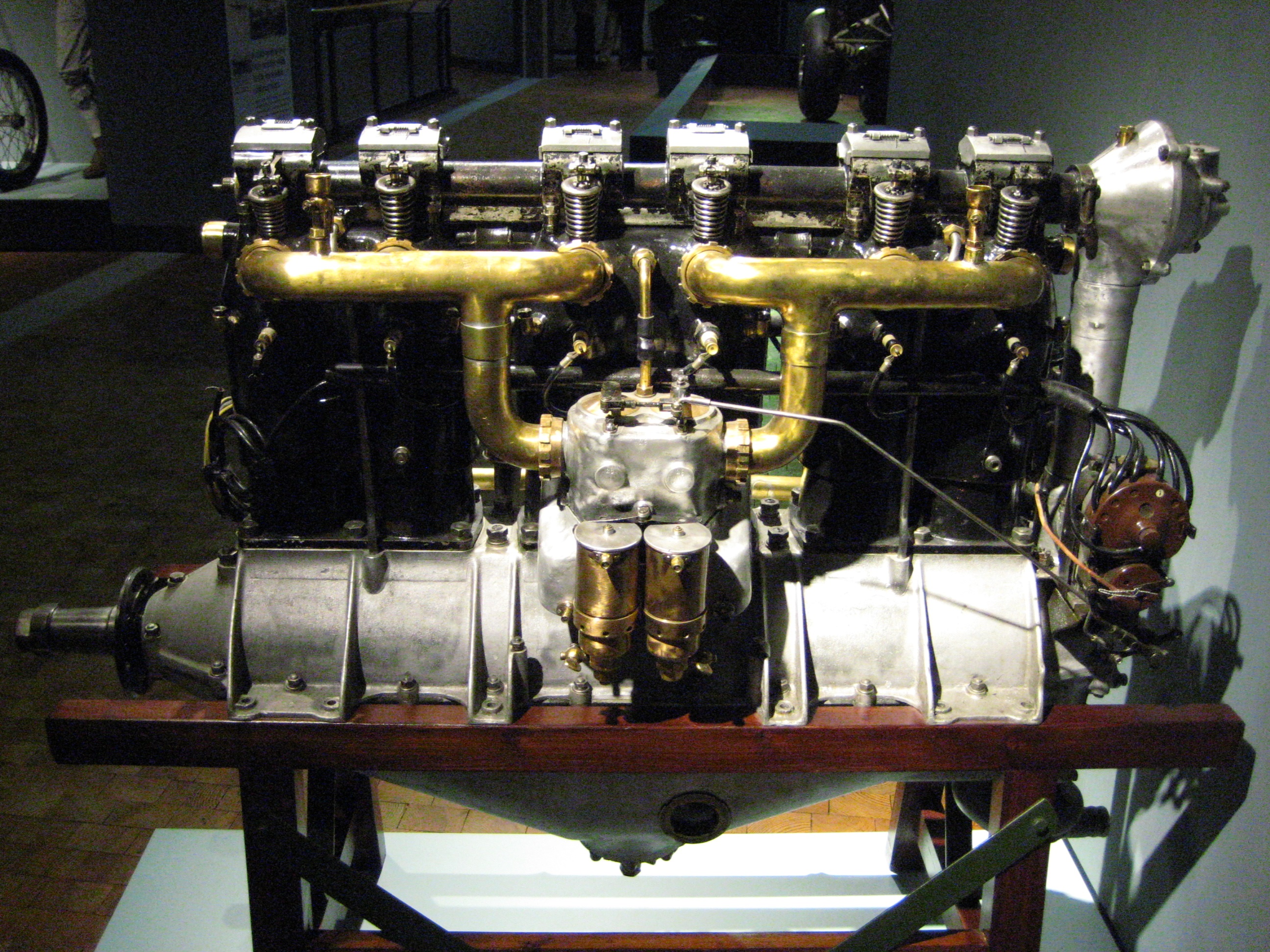
Ikarus IK-2
The Ikarus IK-2 was a 1930s high-wing, single-seat, monoplane fighter aircraft of Yugoslav design built for the Royal Yugoslav Army Air Force. The IK-2 was designed by French-trained engineers Kosta Sivčev and Ljubomir Ilić, who saw the desirability of developing a home-grown aircraft industry. A gull-wing design, it was armed with a hub-firing autocannon and fuselage-mounted synchronised machine guns. Just 12 production models were built, as the aircraft was obsolescent at the time it was brought into service in 1935, and only eight were serviceable at the time of the German-led Axis invasion of Yugoslavia in April 1941. After the defeat of Yugoslavia, the remaining four aircraft were taken onto the strength of the air force of the Axis puppet state, the Independent State of Croatia, but none survived the war. Background In the late 1920s, a scheme promoted by the Royal Yugoslav Army Air Force ( sh, Vazduhoplovstvo vojske Kraljevine Jugoslavije, VVKJ) and the Royal Aero Club ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikarus S-451M
Icarus is a character in Greek mythology. Icarus or Ikarus may also refer to: People * Roger Squires (born 1932), crossword compiler who has used the pseudonym Icarus * Icarus (wrestler) (born 1982), wrestler with the Chikara organization Places * Icarus (island), in the Aegean Sea * Ikaros (Failaka Island), in the Persian Gulf Aviation Aircraft * Icarus I, Icarus II and Icarus V, series of rigid-wing hang gliders designed by Taras Kiceniuk, Jr. * Ikarus C42, a microlight aircraft * Ikarus IK-2, the most notable indigenous Yugoslav aircraft of the 1930s and World War II era * Icarus, a prototype space rescue vehicle tested by Aleksandr Serebrov Aviation businesses and organizations * Ikarus Drachen Tomas Pellicci, a German hang glider manufacturer * Icaro Air, an Ecuadorian airline * Icarus School, a military aviation academy * Icarus, a Greek airline that preceded Olympic Airlines * Ikarus, a Yugoslav aircraft manufacturer later renamed Ikarbus Other uses in aviation * Coupe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikarus IO
The Ikarus IO (Serbian Cyrillic:Икарус ИО – Извиђач Обални) was a biplane flying boat produced in Yugoslavia in the late 1920s. It was a conventional flying boat design for its day, featuring a large single-bay wing cellule, the staggered wings of slightly uneven span braced with N-struts. The pilot and observer sat side by side in an open cockpit, and a gunner sat in an open position ahead of them, in the bow. The pusher engine and frontal radiator were carried on struts in the inter-plane gap. Development After the crash of the Ikarus IM prototype reconnaissance seaplane (Serbian Cyrillic:Икарус ИМ – Извиђач Морнарички) with BMW IV engine, on 31 May 1926, Ikarus immediately started development of a second reconnaissance seaplane prototype powered by a Liberty L-12 engine, also designed by Josef Mikl, the Ikarus Technical Manager. The new prototype was named Ikarus IO (Coastal Reconnaissance) and the first test flight took pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potez 25
Potez 25 (also written as Potez XXV) was a French twin-seat, single-engine biplane designed during the 1920s. A multi-purpose fighter-bomber, it was designed as a line aircraft and used in a variety of roles, including fighter and escort missions, tactical bombing and reconnaissance missions. In the late 1920s and early 1930s, Potez 25 was the standard multi-purpose aircraft of over 20 air forces, including French and Polish. It was also popular among private operators, notably mail transport companies. The aircraft was further developed into the 25M, a standard parasol-wing monoplane, which never entered production. Design and development In 1923, the Avions Henry Potez aircraft works started production of a successful Potez 15 reconnaissance biplane. Basing on experience gathered during the construction of that aircraft, Henry Potez started working on a new design of a heavier and faster multi-purpose aircraft. Designated Potez XXV or Potez 25, the prototype was built alrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Fury
The Hawker Fury is a British biplane fighter aircraft used by the Royal Air Force in the 1930s. It was a fast, agile aircraft, and the first interceptor in RAF service capable of speed higher than 200 mph (321 kmh). It was the fighter counterpart to the Hawker Hart light bomber. Design and development The Hawker Fury was a development of the earlier Hawker F.20/27 prototype fighter, replacing the radial engine of the F.20/27 with the new Rolls-Royce F.XI V-12 engine (later known as the Rolls-Royce Kestrel), which was also used by Hawker's new light bomber, the Hawker Hart. The new fighter prototype, known as the Hawker Hornet, first flew at Brooklands, Surrey, in March 1929.Mason 1992, p.213. The Hornet was a single-engined biplane, with single bay wings, initially powered by a 420 hp (313 kW) Rolls-Royce F.XIC engine enclosed by a smooth, streamlined cowling but was quickly re-engined with a 480 hp (358 kW) Kestrel IS.Goulding 1986, p.37. The prototyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The development of New Belgrade in the late 20th century expanded the continuous urban area of Belgrade and merged it with Zemun. The town was conquered by the Kingdom of Hungary in the 12th century and in the 15th century it was given as a personal possession to the Serbian despot Đurađ Branković. After the Serbian Despotate fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1459, Zemun became an important military outpost. Its strategic location near the confluence of the Sava and the Danube placed it in the center of the continued border wars between the Habsburg and the Ottoman empires. The Treaty of Belgrade of 1739 finally placed the town into Habsburg possession, the Military Frontier was organized in the region in 1746, and the town of Zemun was granted the rig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAN SE
MAN SE (abbreviation of ''Maschinenfabrik Augsburg-Nürnberg'', ) was a manufacturing and engineering company based in Munich, Germany. Its primary output was commercial vehicles and diesel engines through its MAN Truck & Bus and MAN Latin America divisions, and participation in the manufacturer Sinotruk. MAN SE was majority-owned by Traton, the heavy commercial vehicle subsidiary of automaker Volkswagen AG, until August 2021 when Traton completed a squeeze out of all remaining shareholders and formally merged MAN SE into Traton SE, meaning the former subsidiaries of MAN SE were now directly owned by Traton, and MAN SE ceased to exist. History Foundation MAN traces its origins back to 1758, when the "St. Antony" ironworks commenced operation in Oberhausen, as the first heavy-industry enterprise in the Ruhr region. In 1808, the three ironworks "St. Antony", "Gute Hoffnung" (English: "Good Hope"), and "Neue Essen" (English: "New Forges") merged, to form the Hüttengewerks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)